|
Multiplier (economics)
In macroeconomics, a multiplier is a factor of proportionality that measures how much an endogenous variable changes in response to a change in some exogenous variable. For example, suppose variable ''x'' changes by ''k'' units, which causes another variable ''y'' to change by ''M'' × ''k'' units. Then the multiplier is ''M''. Common uses Two multipliers are commonly discussed in introductory macroeconomics. Commercial banks create money, especially under the fractional-reserve banking system used throughout the world. In this system, money is created whenever a bank gives out a new loan. This is because the loan, when drawn on and spent, mostly finishes up as a deposit back in the banking system and is counted as part of money supply. After putting aside a part of these deposits as mandated bank reserves, the balance is available for the making of further loans by the bank. This process continues multiple times, and is called the multiplier effect. The multiplier ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrange Multiplier
In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers is a strategy for finding the local maxima and minima of a function subject to equality constraints (i.e., subject to the condition that one or more equations have to be satisfied exactly by the chosen values of the variables). It is named after the mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange. The basic idea is to convert a constrained problem into a form such that the derivative test of an unconstrained problem can still be applied. The relationship between the gradient of the function and gradients of the constraints rather naturally leads to a reformulation of the original problem, known as the Lagrangian function. The method can be summarized as follows: in order to find the maximum or minimum of a function f(x) subjected to the equality constraint g(x) = 0, form the Lagrangian function :\mathcal(x, \lambda) = f(x) + \lambda g(x) and find the stationary points of \mathcal considered as a function of x and the Lagrange m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
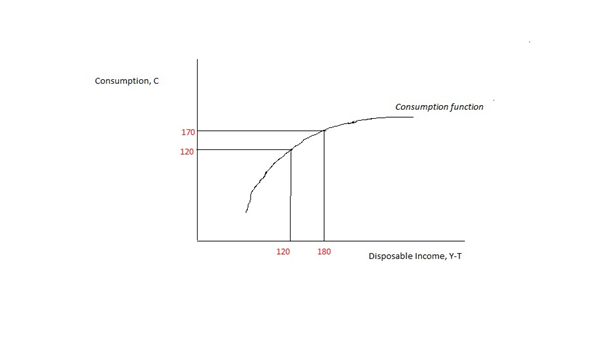
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending ( consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. The MPC is higher in the case of poorer people than in rich. According to John Mayn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Quesnay
François Quesnay (; 4 June 1694 – 16 December 1774) was a French economist and physician of the Physiocratic school. He is known for publishing the " Tableau économique" (Economic Table) in 1758, which provided the foundations of the ideas of the Physiocrats. This was perhaps the first work attempting to describe the workings of the economy in an analytical way, and as such can be viewed as one of the first important contributions to economic thought. His ''Le Despotisme de la Chine'', written in 1767, describes Chinese politics and society, and his own political support for enlightened despotism. Life Quesnay was born at Méré near Versailles, the son of an advocate and small landed proprietor. Apprenticed at the age of sixteen to a surgeon, he soon went to Paris, studied medicine and surgery there, and, having qualified as a master-surgeon, settled down to practice at Mantes. In 1737 he was appointed perpetual secretary of the academy of surgery founded by François ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tableau économique
The Tableau économique () or ''Economic Table'' is an economic model first described by French economist François Quesnay in 1758, which laid the foundation of the Physiocratic school of economics.Henry William Spiegel (1983) ''The Growth of Economic Thought'', Revised and Expanded Edition, Duke University Press. p.189 Quesnay believed that trade and industry were not sources of wealth, and instead in his 1758 manuscript ''Tableau économique'' (Economic Table) argued that agricultural surpluses, by flowing through the economy in the form of rent, wages, and purchases were the real economic movers. The model The model Quesnay created consisted of three economic movers. The "Proprietary" class consisted of only landowners. The "Productive" class consisted of all agricultural laborers. The "Sterile" class is made up of artisans and merchants. The flow of production and/or cash between the three classes started with the Proprietary class because they own the land and they buy fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Dynamics
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the ( equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. But the concept of ''equilibrium'' in economics also applies to imperfectly competitive markets, where it takes the form of a Nash equilibrium. Understanding economic equilib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmut Lütkepohl
Helmut Lütkepohl (born 26 July 1951) is a German econometrician specializing in time series analysis. Since January 2012, he has been Bundesbank Professor in the field of "Methods of Empirical Economics" at the Free University of Berlin and Dean of the Graduate Center at the German Institute for Economic Research. Education and career After a diplom (1977) and doctorate (1981) from Bielefeld University, Lütkepohl was a Visiting Assistant Professor at the University of California, San Diego (1984–85). He became Professor of Statistics at the University of Kiel in 1987, and later moved on to become Professor of Econometrics at Humboldt University of Berlin.http://www.diw.de/documents/dokumentenarchiv/17/diw_01.c.414305.de/diwcvlong_en_hluetkepohl_jan2013.pdf Lütkepohl has been on the editorial boards of several scientific journals like ''Econometric Theory'', ''Journal of Econometrics'', ''Journal of Applied Econometrics'', '' Macroeconomic Dynamics'', '' Empirical Economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impulse Response
In signal processing and control theory, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse (). More generally, an impulse response is the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change. In both cases, the impulse response describes the reaction of the system as a function of time (or possibly as a function of some other independent variable that parameterizes the dynamic behavior of the system). In all these cases, the dynamic system and its impulse response may be actual physical objects, or may be mathematical systems of equations describing such objects. Since the impulse function contains all frequencies (see the Fourier transform of the Dirac delta function, showing infinite frequency bandwidth that the Dirac delta function has), the impulse response defines the response of a linear time-invariant system for all frequencies. Mathematical consideratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogenous (economics)
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell. In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism. For example, estradiol is an endogenous estrogen hormone produced within the body, whereas ethinylestradiol Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ... is an exogenous synthetic estrogen, commonly used in birth control pills. References External links *{{Wiktionary-inline, endogeny Biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Statics
In economics, comparative statics is the comparison of two different economic outcomes, before and after a change in some underlying exogenous parameter. As a type of ''static analysis'' it compares two different equilibrium states, after the process of adjustment (if any). It does not study the motion towards equilibrium, nor the process of the change itself. Comparative statics is commonly used to study changes in supply and demand when analyzing a single market, and to study changes in monetary or fiscal policy when analyzing the whole economy. Comparative statics is a tool of analysis in microeconomics (including general equilibrium analysis) and macroeconomics. Comparative statics was formalized by John R. Hicks (1939) and Paul A. Samuelson (1947) (Kehoe, 1987, p. 517) but was presented graphically from at least the 1870s. For models of stable equilibrium rates of change, such as the neoclassical growth model, comparative dynamics is the counterpart of com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricardian Equivalence
The Ricardian equivalence proposition (also known as the Ricardo–de Viti–Barro equivalence theorem) is an economic hypothesis holding that consumers are forward-looking and so internalize the government's budget constraint when making their consumption decisions. This leads to the result that, for a given pattern of government spending, the method of financing such spending does not affect agents' consumption decisions, and thus, it does not change aggregate demand. Introduction Governments can finance their expenditures by creating new money, by levying taxes, or by issuing bonds. Since bonds are loans, they must eventually be repaid—presumably by raising taxes in the future. The choice is therefore "tax now or tax later." Suppose that the government finances some extra spending through deficits; i.e. it chooses to tax later. According to the hypothesis, taxpayers will anticipate that they will have to pay higher taxes in future. As a result, they will save, rather than sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |