|
Monostatic Radar
Bistatic radar is a radar system comprising a transmitter and receiver that are separated by a distance comparable to the expected target distance. Conversely, a conventional radar in which the transmitter and receiver are co-located is called a monostatic radar. A system containing multiple spatially diverse monostatic or bistatic radar components with a shared area of coverage is called '' multistatic radar''. Many long-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems use semi-active radar homing, which is a form of bistatic radar. Types Pseudo-monostatic radars Some radar systems may have separate transmit and receive antennas, but if the angle subtended between transmitter, target and receiver (the bistatic angle) is close to zero, then they would still be regarded as monostatic or pseudo-monostatic. For example, some very long range HF radar systems may have a transmitter and receiver which are separated by a few tens of kilometres for electrical isolation, but as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bistatic Radar
Bistatic radar is a radar system comprising a transmitter and receiver that are separated by a distance comparable to the expected target distance. Conversely, a conventional radar in which the transmitter and receiver are co-located is called a monostatic radar. A system containing multiple spatially diverse monostatic or bistatic radar components with a shared area of coverage is called '' multistatic radar''. Many long-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems use semi-active radar homing, which is a form of bistatic radar. Types Pseudo-monostatic radars Some radar systems may have separate transmit and receive antennas, but if the angle subtended between transmitter, target and receiver (the bistatic angle) is close to zero, then they would still be regarded as monostatic or pseudo-monostatic. For example, some very long range HF radar systems may have a transmitter and receiver which are separated by a few tens of kilometres for electrical isolation, but as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Cross Section
Radar cross-section (RCS), also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected. An object reflects a limited amount of radar energy back to the source. The factors that influence this include: *the material with which the target is made; *the size of the target relative to the wavelength of the illuminating radar signal; *the absolute size of the target; *the incident angle (angle at which the radar beam hits a particular portion of the target, which depends upon the shape of the target and its orientation to the radar source); *the reflected angle (angle at which the reflected beam leaves the part of the target hit; it depends upon incident angle); *the polarization of the transmitted and the received radiation with respect to the orientation of the target. While important in detecting targets, strength of emitter and distance are not factors that affect the calculation of an RCS becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNSS Reflectometry
GNSS reflectometry (or GNSS-R) involves making measurements from the reflections from the Earth of navigation signals from Global Navigation Satellite Systems such as GPS. The idea of using reflected GNSS signal for earth observation became more and more popular in the mid-1990s at NASA Langley Research Center and is also known as ''GPS reflectometry''. Research applications of GNSS-R are found in * Altimetry * Oceanography (Wave Height and Wind Speed) * Cryosphere monitoring * Soil moisture monitoring GNSS reflectometry is passive sensing that takes advantage of and relies on separate active sources - the satellites generating the navigation signals. For this, the GNSS receiver measures the signal delay from the satellite (the pseudorange measurement) and the rate of change of the range between satellite and observer (the Doppler measurement). The surface area of the reflected GNSS signal also provides the two parameters time delay and frequency change. As a result, the Del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLidar
The CLidar is a scientific instrument used for measuring particulates (aerosols) in the lower atmosphere. CLidar stands for camera lidar, which in turn is a portmanteau of "light" and "radar". It is a form of remote sensing and used for atmospheric physics. Description In this technique a very wide-angle lens images light scattered from a laser beam onto a CCD (Charge-coupled device) camera. The camera is positioned hundreds of meters away from the (usually vertically-pointed) laser beam. The geometry of the CLidar is shown in the figure. It is important in the analysis that the optics, the wide-angle lens in this case, accurately maps equal angles onto an equal number of pixels throughout the 100 degree field-of-view. image:CLidarDiagram2008.jpg Example In the second figure, an image from the CCD camera is shown which is analyzed by adding up the individual pixels at each altitude. The camera was 122 meters from the vertically pointed, circularly-polarized laser beam. The bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
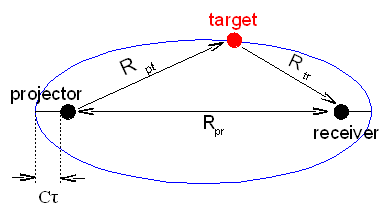
Bistatic Sonar
Bistatic sonar is a sonar configuration in which transmitter and receiver are separated by a distance large enough to be comparable to the distance to the target. Most sonar systems are ''monostatic'', in that the transmitter and receiver are located in the same place. A configuration with multiple receivers is called ''multistatic''. Bistatic vs monostatic Propagation (transmission) loss This is a loss in sound level which happens while the sound pulse travels from projector to target and from target to receiver. There are 3 different mechanisms causing transmission Loss: spherical (or cylindrical in shallow water) spreading, absorbing and scattering by ocean media inhomogeneities. Transmission loss (TL) is proportional to range, (the farther the sound travels the more the loss), and to sound frequency. In monostatic sonar the sound first travels from projector to target, then the same way back from target to receiver, so two-way loss is just 2TL, where TL is one-way loss. In bist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathering, transport, and deposition of exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Imaging
Imaging radar is an application of radar which is used to create two-dimensional images, typically of landscapes. Imaging radar provides its light to illuminate an area on the ground and take a picture at radio wavelengths. It uses an antenna and digital computer storage to record its images. In a radar image, one can see only the energy that was reflected back towards the radar antenna. The radar moves along a flight path and the area illuminated by the radar, or footprint, is moved along the surface in a swath, building the image as it does so. Digital radar images are composed of many dots. Each pixel in the radar image represents the radar backscatter for that area on the ground: brighter areas represent high backscatter, darker areas represents low backscatter. The traditional application of radar is to display the position and motion of typically highly reflective objects (such as aircraft or ships) by sending out a radiowave signal, and then detecting the direction and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Range Rate
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the distance or range between the two points. It is equivalent to the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity onto the relative direction connecting the two points. In astronomy, the point is usually taken to be the observer on Earth, so the radial velocity then denotes the speed with which the object moves away from the Earth (or approaches it, for a negative radial velocity). Formulation Given a differentiable vector \mathbf \in \mathbb^3 defining the instantaneous position of a target relative to an observer. Let with \mathbf \in \mathbb^3, the instantaneous velocity of the target with respect to the observer. The magnitude of the position vector \mathbf is defined as The quantity range rate is the time derivative of the magnitude ( norm) of \mathbf, expressed as Substituting () into () : \f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave. Therefore, each wave takes slightly less time to reach the observer than the previous wave. Hence, the time between the arrivals of successive wave crests at the observer is reduced, causing an inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |