|
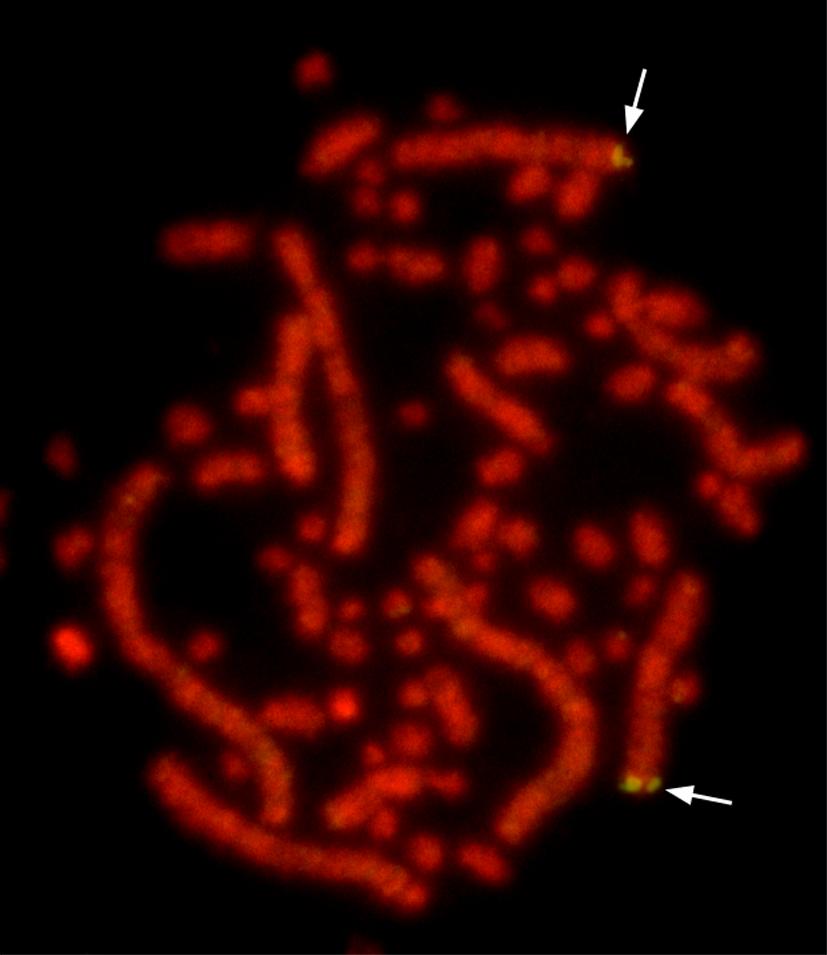
Micronucleus
Micronucleus is the name given to the small nucleus that forms whenever a chromosome or a fragment of a chromosome is not incorporated into one of the daughter nuclei during cell division. It usually is a sign of genotoxic events and chromosomal instability. Micronuclei are commonly seen in cancerous cells and may indicate genomic damage events that can increase the risk of developmental or degenerative diseases. Micronuclei form during anaphase from lagging acentric chromosome or chromatid fragments caused by incorrectly repaired or unrepaired DNA breaks or by nondisjunction of chromosomes. This incorrect segregation of chromosomes may result from hypomethylation of repeat sequences present in pericentromeric DNA, irregularities in kinetochore proteins or their assembly, dysfunctional spindle apparatus, or flawed anaphase checkpoint genes. Micronuclei can contribute to genome instability by promoting a catastrophic mutational event called chromothripsis. Many micronucleus assays h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micronuclei And Nuclear Abnormalities In Peripheral Blood Erythrocytes Of Penguins Pygoscelis Papua 1
Micronucleus is the name given to the small nucleus that forms whenever a chromosome or a fragment of a chromosome is not incorporated into one of the daughter nuclei during cell division. It usually is a sign of genotoxic events and chromosomal instability. Micronuclei are commonly seen in cancerous cells and may indicate genomic damage events that can increase the risk of developmental or degenerative diseases. Micronuclei form during anaphase from lagging acentric chromosome or chromatid fragments caused by incorrectly repaired or unrepaired DNA breaks or by nondisjunction of chromosomes. This incorrect segregation of chromosomes may result from hypomethylation of repeat sequences present in pericentromeric DNA, irregularities in kinetochore proteins or their assembly, dysfunctional spindle apparatus, or flawed anaphase checkpoint genes. Micronuclei can contribute to genome instability by promoting a catastrophic mutational event called chromothripsis. Many micronucleus assays h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some obligate and opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species range in size from as little as 10 µm in some colpodeans to as much as 4 mm in length in some g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromothripsis
Chromothripsis is a mutational process by which up to thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements occur in a single event in localised and confined genomic regions in one or a few chromosomes, and is known to be involved in both cancer and congenital diseases. It occurs through one massive genomic rearrangement during a single catastrophic event in the cell's history. It is believed that for the cell to be able to withstand such a destructive event, the occurrence of such an event must be the upper limit of what a cell can tolerate and survive. The chromothripsis phenomenon opposes the conventional theory that cancer is the gradual acquisition of genomic rearrangements and somatic mutations over time. The simplest model as to how these rearrangements occur is through the simultaneous fragmentation of distinct chromosomal regions (breakpoints show a non-random distribution) and then subsequent imperfect reassembly by DNA repair pathways or aberrant DNA replication mechanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
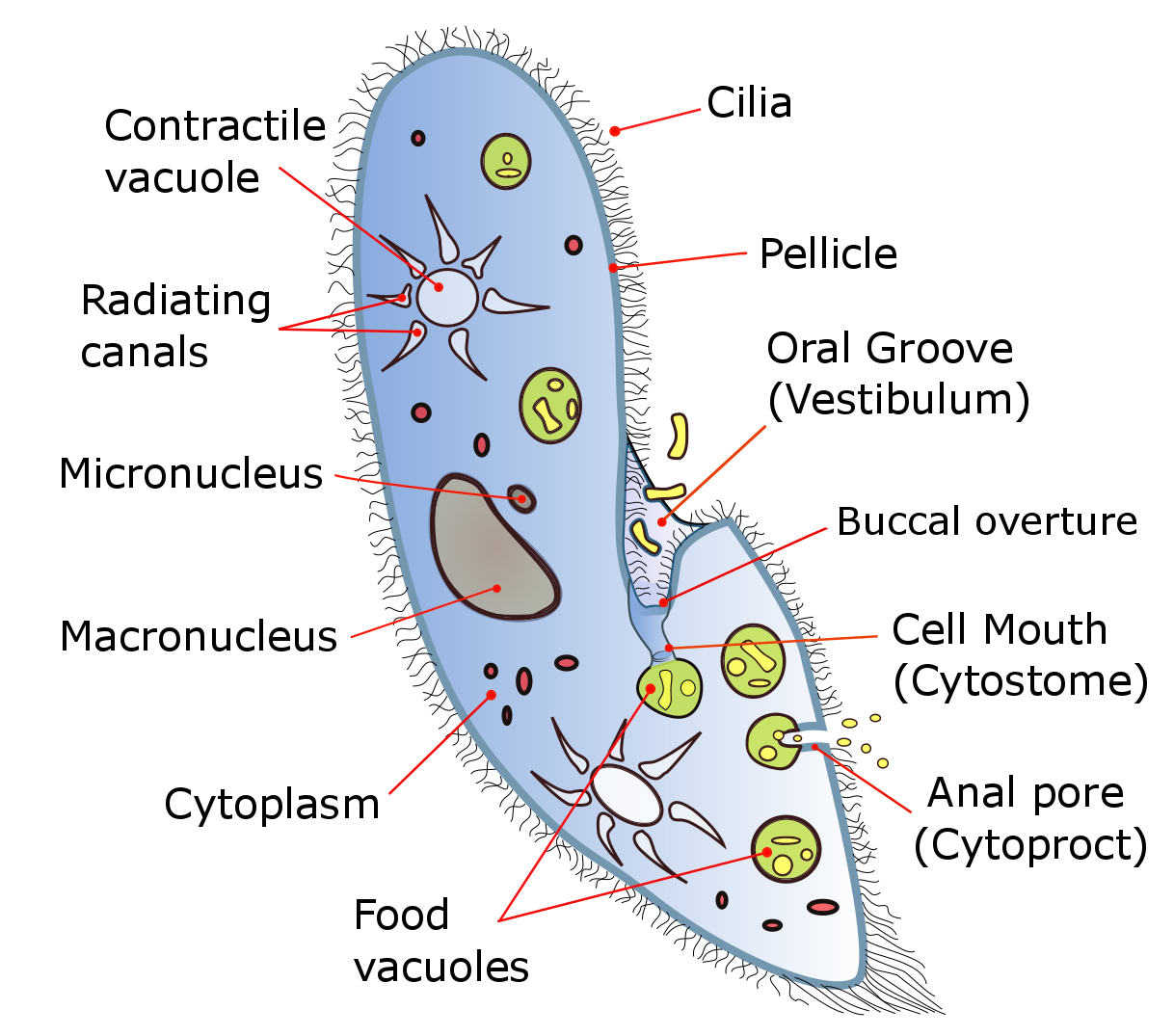
Paramecium
'' ''Paramecium'' ( , ; also spelled ''Paramoecium'') is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. ''Paramecia'' are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and are often very abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to conjugate and divide, it has been widely used in classrooms and laboratories to study biological processes. Its usefulness as a model organism has caused one ciliate researcher to characterize it as the "white rat" of the phylum Ciliophora. Historical background ''Paramecia'' were among the first ciliates to be seen by microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were probably known to the Dutch pioneer of protozoology, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, and were clearly described by his contemporary Christiaan Huygens in a letter of 1678. The earliest known illustration of a Paramecium was published anonymously in Philosophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochalasin B
Cytochalasin B, the name of which comes from the Greek ''cytos'' (cell) and ''chalasis'' (relaxation), is a cell-permeable mycotoxin. It was found that substoichimetric concentrations of cytochalasin B (CB) strongly inhibit network formation by actin filaments. Due to this, it is often used in cytological research. It inhibits cytoplasmic division by blocking the formation of contractile microfilaments. It inhibits cell movement and induces nuclear extrusion. Cytochalasin B shortens actin filaments by blocking monomer addition at the fast-growing end of polymers. Cytochalasin B inhibits glucose transport and platelet aggregation. It blocks adenosine-induced apoptotic body formation without affecting activation of endogenous ADP-ribosylation in leukemia HL-60 cells. It is also used in cloning through nuclear transfer. Here enucleated recipient cells are treated with cytochalasin B. Cytochalasin B makes the cytoplasm of the oocytes more fluid and makes it possible to aspirate the nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancerous Micronuclei
Cancerous micronuclei is a type of micronucleus that is associated with cancerous cells. History Theodor Boveri originally observed the fact that abnormal nuclear morphologies commonly occur in cancer. Micronuclei are also referred to Howell-Jolly bodies; discovered by hematologists William Henry Howell and Justin Marie Jolly in erythrocytes. Micronucleus induction by a chemical was first reported in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells treated with colchicine. The effect of environmental stressors on the expression of micronuclei was first analyzed in root tip cells under ionizing radiation. It can be inferred that nuclear abnormalities are a result of various molecular mechanisms. These events can ultimately lead to cell death. Description Characteristics Micronuclei are characterized in the cells that have some sort of DNA damage. This includes damage caused by radiation, harmful chemicals, and random mutations that occur throughout the genome. Micronuclei are small bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macronuclei
A macronucleus (formerly also meganucleus) is the larger type of nucleus in ciliates. Macronuclei are polyploid and undergo direct division without mitosis. It controls the non-reproductive cell functions, such as metabolism. During conjugation, the macronucleus disintegrates, and a new macronucleus is formed by karyogamy of the micronuclei. The macronucleus contains hundreds to thousands of chromosomes, each present in many copies. The macronucleus lacks a mechanism to precisely partition this complex genome equally during nuclear division; thus, how the cell manages to maintain a balanced genome after generations of divisions is unknown. See also *Micronucleus Micronucleus is the name given to the small nucleus that forms whenever a chromosome or a fragment of a chromosome is not incorporated into one of the daughter nuclei during cell division. It usually is a sign of genotoxic events and chromosomal i ... References . Cell nucleus Ciliate biology {{Cilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macronucleus
A macronucleus (formerly also meganucleus) is the larger type of nucleus in ciliates. Macronuclei are polyploid and undergo direct division without mitosis. It controls the non-reproductive cell functions, such as metabolism. During conjugation, the macronucleus disintegrates, and a new macronucleus is formed by karyogamy of the micronuclei. The macronucleus contains hundreds to thousands of chromosomes, each present in many copies. The macronucleus lacks a mechanism to precisely partition this complex genome equally during nuclear division; thus, how the cell manages to maintain a balanced genome after generations of divisions is unknown. See also *Micronucleus Micronucleus is the name given to the small nucleus that forms whenever a chromosome or a fragment of a chromosome is not incorporated into one of the daughter nuclei during cell division. It usually is a sign of genotoxic events and chromosomal i ... References . Cell nucleus Ciliate biology {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microchromosome
A microchromosome (μChr) is a type of very small chromosome which is a typical component of the karyotype of birds, some reptiles, fish, and amphibians; they have yet to be found in mammals. They are less than 20 Mb in size; chromosomes which are greater than 40 Mb in size are known as macrochromosomes (MChrs), while those between 20 and 40 Mb are classified as intermediate chromosomes. Microchromosomes are characteristically very small and often cytogenetically indistinguishable in a karyotype. While originally thought to be insignificant fragments of chromosomes, in species where they have been studied they have been found to be rich in genes and high in GC content. In chickens, microchromosomes have been estimated to contain between 50 and 75% of all genes. The presence of microchromosomes makes ordering and identifying chromosomes into a coherent karyotype particularly difficult. During metaphase, they appear merely as 0.5-1.5 μm long specks. Their small size and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .σπλήν Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', on Perseus Digital Library The spleen plays very important roles in regard to red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the . It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood, which can be valuable in case of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetochore
A kinetochore (, ) is a disc-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. The kinetochore assembles on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubule polymers from the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis. The term kinetochore was first used in a footnote in a 1934 Cytology book by Lester W. Sharp and commonly accepted in 1936. Sharp's footnote reads: "The convenient term ''kinetochore'' (= movement place) has been suggested to the author by J. A. Moore", likely referring to John Alexander Moore who had joined Columbia University as a freshman in 1932. Monocentric organisms, including vertebrates, fungi, and most plants, have a single centromeric region on each chromosome which assembles a single, localized kinetochore. Holocentric organisms, such as nematodes and some plants, assemble a kinetochore along the entire length of a chromosome. K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |