|
Methanobacteriales
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteriales are an order of the Methanobacteria. Species within this order differ from other methanogens in that they can use fewer catabolic substrates and have distinct morphological characteristics, lipid compositions, and RNA sequences. Their cell walls are composed of pseudomurein. Most species are Gram-positive with rod-shaped bodies and some can form long filaments. Most of them use formate to reduce carbon dioxide, but those of the genus ''Methanosphaera'' use hydrogen to reduce methanol to methane. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanothermaceae
In taxonomy, the Methanothermaceae are a family of microbes within the order Methanobacteriales.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Methanothermaceae Data extracted from the See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny National Center for ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * * * Scientific books Scientific databases External links Archaea taxonomic families Euryarchaeota {{Euryarchaeota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanobacteriaceae
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteriaceae are a family of the Methanobacteriales. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny National Center for ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * * Scientific books Scientific databases External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q6823582 Archaea taxonomic families Euryarchaeota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea Taxonomic Orders
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
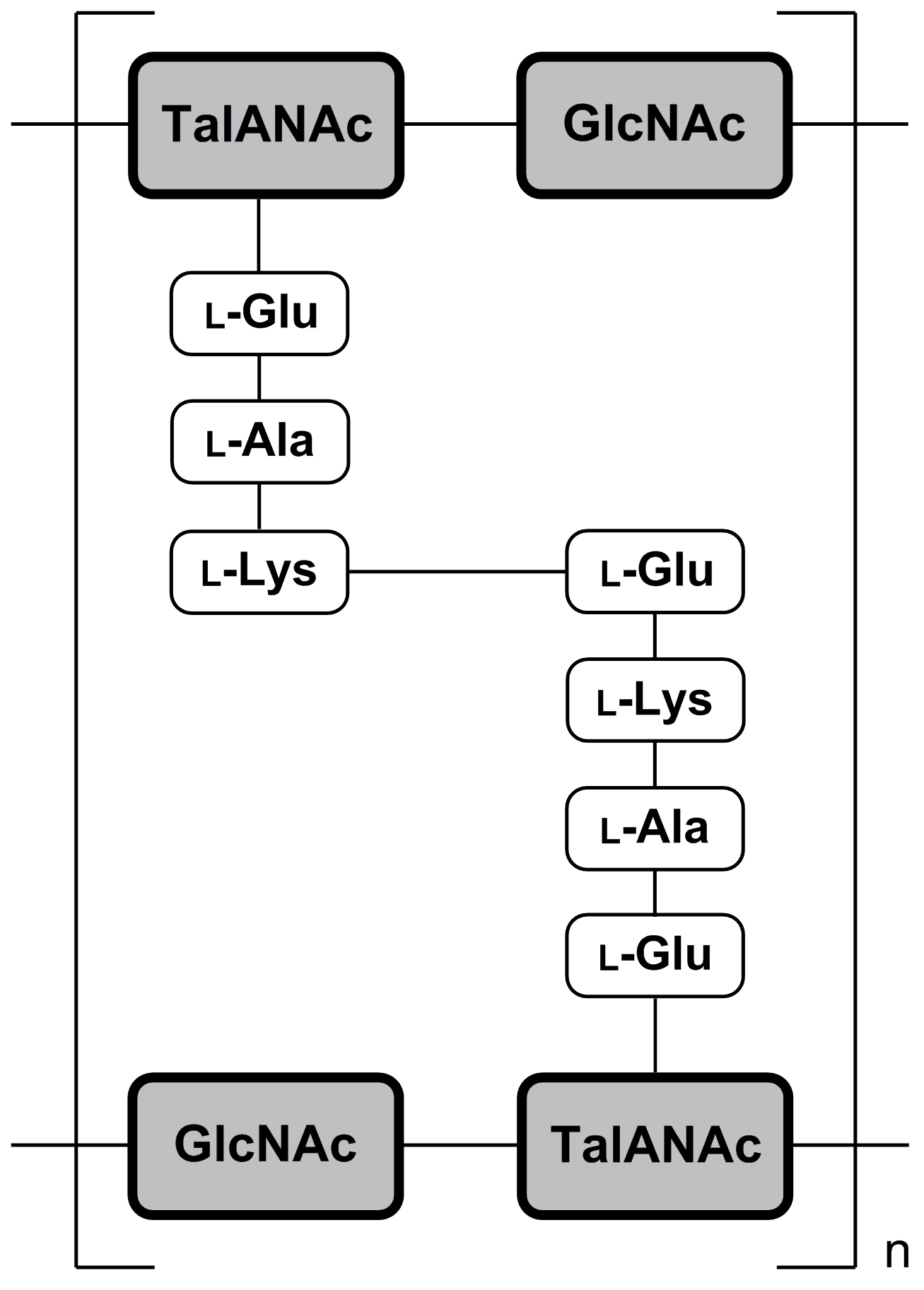
Pseudomurein
Pseudopeptidoglycan (also known as pseudomurein;White, David. (1995) ''The Physiology and Biochemistry of Prokaryotes'', pages 6, 12-21. (Oxford: Oxford University Press). . PPG hereafter) is a major cell wall component of some Archaea that differs from bacterial peptidoglycan in chemical structure, but resembles bacterial peptidoglycan in function and physical structure. Pseudopeptidoglycan, in general, is only present in a few methanogenic archaea. The basic components are N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid (bacterial peptidoglycan containing ''N''-acetylmuramic acid instead), which are linked by β-1,3-glycosidic bonds. Lysozyme, a host defense mechanism present in human secretions (e.g. saliva and tears) breaks β-1,4-glycosidic bonds to degrade peptidoglycan. However, because pseudopeptidoglycan has β-1,3-glycosidic bonds, lysozyme is ineffective. It was thought from these large differences in cell wall chemistry that archaeal cell walls and bacterial cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archaea Genera
This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy was initially used to decorate the genome tree via tax2tree. The 16S rRNA-based Greengenes taxonomy is used to supplement the taxonomy particularly in regions of the tree with no cultured representatives. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is used as the primary taxonomic authority for establishing naming priorities. Taxonomic ranks are normalised using phylorank and the taxonomy manually curated to remove polyphyletic groups. Cladogram was taken from the GTDB release 07-RS207 (8th April 2022). The position of clades with a "question mark" are based on the additional phylogeny of the 16S rRNA-based LTP_12_2021 by The All-Species Living Tree Project. Phylum " Altar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanobacterium
In taxonomy, ''Methanobacterium'' is a genus of the Methanobacteriaceae family of Archaea.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Methanobacterium Data extracted from the Despite the name, this genus belongs not to the bacterial domain but the archaeal domain (for instance, they lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls). Methanobacterium are nonmotile and live without oxygen. Some members of this genus can use formate to reduce methane; others live exclusively through the reduction of carbon dioxide with hydrogen. They are ubiquitous in some hot, low-oxygen environments, such as anaerobic digestors, their wastewater, and hot springs. Examples of Methanobacterium Species ''Methanobacterium bryantii'' is part of the syntrophic ''Methanobacillus omelianskii'' culture. ''Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum'' Marburg can undergo natural genetic transformation, the transfer of DNA from one cell to another. Genetic transformation in archaeal species, generally, appears to be an adaptation for rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanosphaera
In taxonomy, ''Methanosphaera'' is a genus of microbes within the family Methanobacteriaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Methanosphaera Data extracted from the It was distinguished from other genera within Methanobacteriaceae in 1985 on the basis of the oligonucleotide sequence of its 16S RNA. Like other archaea within Methanobacteriaceae, those of ''Methanosphaera'' are methanogens, but while most use formate to reduce carbon dioxide, those of ''Methanosphaera'' use hydrogen to reduce methanol to methane. See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny National Center for ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * * * Scientific books Scientific databases External links Archaea genera Euryarchaeota {{Euryarchaeota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanobacteria
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteria are a class of the Euryarchaeota. Several of the classes of the Euryarchaeota are methanogens and the Methanobacteria are one of these classes. Applications Methanobacteria can be used in biomass conversion as well as energy production through Anaerobic digestion (AD) process. Microbial community is used in Anaerobic digestion(AD) to convert organic wastes into clean energy by reducing chemical and biological oxygen demand in the wastes. Solid-state anaerobic digestion, which contains six genera of methanogens including Methanobacteria, can ferment rice straw and then produce methane. Since conventional treatment is burning rice straw in field, applying Methanobacteria to waste disposal process can reduce the air pollution caused by straw burning and also alleviate energy shortage problem, especially in rural areas. During biomethanation process, insoluble organic material and higher molecular mass compounds will first be transformed into simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants and many humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching in ruminants and flatulence in humans. In marine sediments, the biological production of methane, also termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted, below the top layers. Moreover, methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Others are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface. Physical description Methanogens are coccoid (spherica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Taxonomy Database
The Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB) is an online database that maintains information on a proposed nomenclature of prokaryotes, following a phylogenomic approach based on a set of conserved single-copy proteins. In addition to breaking up paraphyletic groups, this method also reassigns taxonomic ranks algorithmically, creating new names in both cases. Information for archaea was added in 2020, along with a species classification based on average nucleotide identity. Each update incorporates new genomes as well as human adjustments to the taxonomy. An open-source tool called GTDB-Tk is available to classify draft genomes into the GTDB hierarchy. The GTDB system, via GTDB-Tk, has been used to catalogue not-yet-named bacteria in the human gut microbiome and other metagenomic sources. The GTDB is incorporated into the '' Bergey's Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria'' in 2019 as its phylogenomic resource. See also * PhyloCode * National Center for Biotechnology Infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Taxonomy
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)