|
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate Levels After A Single Intramuscular Injection Of Different Doses Of Medr
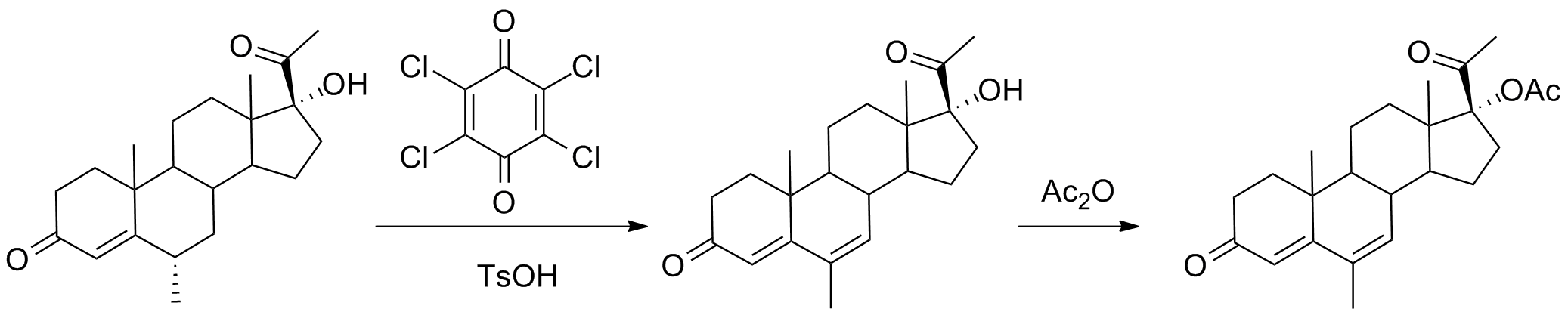
Medroxyprogesterone (MP), is a progestin which is not used medically. A derivative, medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), is used as a medication in humans, and is far more widely known in comparison. ''Medroxyprogesterone'' is sometimes used as a synonym for ''medroxyprogesterone acetate'', and what is almost always being referred to when the term is used is MPA and not medroxyprogesterone. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Compared to MPA, medroxyprogesterone is over two orders of magnitude less potent as a progestogen. Medroxyprogesterone is also notable in that it is a minor metabolite of MPA. In addition to its progestagenic activity, medroxyprogesterone is a weak antiandrogen ''in vitro'' on human androgen receptor. Chemistry Medroxyprogesterone, also known as 6α-methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesterone or as 6α-methyl-17α-hydroxypregn-4-en-3,20-dione, is a synthetic pregnane steroid and a derivative of progesterone. It is specifically a derivative of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side effects of progestogens include menstrual irregularities, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, acne, increased hair growth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Derivative
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is availa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diketones
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical (dialdehydes, diketones, diesters, ''etc.'') or unsymmetrical (keto-esters, keto-acids, ''etc.''). 1,2-Dicarbonyls 1,2-Dialdehyde The only 1,2-dialdehyde is glyoxal, . Like many alkyldialdehydes, glyoxal is encountered almost exclusively as its hydrate and oligomers thereof. These derivatives often behave equivalently to the aldehydes since hydration is reversible. Glyoxal condenses r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene Derivatives
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Drugs
Abandon, abandoned, or abandonment may refer to: Common uses * Abandonment (emotional), a subjective emotional state in which people feel undesired, left behind, insecure, or discarded * Abandonment (legal), a legal term regarding property ** Child abandonment, the extralegal abandonment of children ** Lost, mislaid, and abandoned property, legal status of property after abandonment and rediscovery * Abandonment (mysticism) Art, entertainment, and media Film * ''Abandon'' (film), a 2002 film starring Katie Holmes * ''Abandoned'' (1949 film), starring Dennis O'Keefe * ''Abandoned'' (1955 film), the English language title of the Italian war film ''Gli Sbandati'' * ''Abandoned'' (2001 film), a Hungarian film * ''Abandoned'' (2010 film), starring Brittany Murphy * ''Abandoned'' (2015 film), a television movie about the shipwreck of the ''Rose-Noëlle'' in 1989 * ''Abandoned'' (2022 film), starring Emma Roberts * ''The Abandoned'' (1945 film), a 1945 Mexican film * ''The A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Term
Trademark distinctiveness is an important concept in the law governing trademarks and service marks. A trademark may be eligible for registration, or registrable, if it performs the essential trademark function, and has distinctive character. Registrability can be understood as a continuum, with "inherently distinctive" marks at one end, "generic" and "descriptive" marks with no distinctive character at the other end, and "suggestive" and "arbitrary" marks lying between these two points. "Descriptive" marks must acquire distinctiveness through secondary meaning—consumers have come to recognize the mark as a source indicator—to be protectable. "Generic" terms are used to refer to the product or service itself and cannot be used as trademarks. The spectrum of distinctiveness In United States trademark law, Abercrombie & Fitch Co. v. Hunting World 537 F.2d 4 (2nd Cir. 1976) established the spectrum of trademark distinctiveness in the US, breaking trademarks into classes which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megestrol
Megestrol (, ) is a progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was never marketed and is not currently used clinically. Its acylated derivative megestrol acetate is also a progestogen, which, in contrast to megestrol itself, has been extensively used as a pharmaceutical drug. Synthesis See also * Megestrol acetate * Medroxyprogesterone * Medroxyprogesterone acetate Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), also known as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in injectable form and sold under the brand name Depo-Provera among others, is a hormonal medication of the progestin type. It is used as a method of bi ... References Tertiary alcohols Dienes Diketones Pregnanes Progestogens {{Genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyproterone
Cyproterone, also known by its developmental code name SH-80881, is a steroidal antiandrogen which was studied in the 1960s and 1970s but was never introduced for medical use. It is an analogue of cyproterone acetate (CPA), an antiandrogen, progestin, and antigonadotropin which was introduced instead of cyproterone and is widely used as a medication. Cyproterone and CPA were among the first antiandrogens to be developed. It is important to clarify that the term ''cyproterone'' is often used as a synonym and shorthand for ''cyproterone acetate'', and when the term occurs, what is almost always being referred to is, confusingly, CPA and not actually cyproterone. Cyproterone itself, unlike CPA, was never introduced for medical use and hence is not available as a medication. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Antiandrogenic activity Cyproterone is a potent antiandrogen, similarly to CPA. However, it has approximately three-fold lower potency as an antagonist of the androgen recep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlormadinone
Chlormadinone is a progestin which was never marketed. An acylated derivative, chlormadinone acetate Chlormadinone acetate (CMA), sold under the brand names Belara, Gynorelle, Lutéran, and Prostal among others, is a progestin and antiandrogen medication which is used in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, as a component of menopausal horm ..., is used clinically as a pharmaceutical drug. It was patented in 1958 and approved for medical use in 1963. While ''chlormadinone'' is sometimes used as a synonym for ''chlormadinone acetate'', what is almost always being referred to is chlormadinone acetate and not chlormadinone. See also * List of progestogens References Abandoned drugs Enones Chloroarenes Conjugated dienes Diketones Pregnanes Progestogens Tertiary alcohols {{Steroid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medrogestone
Medrogestone, sold under the brand name Colprone among others, is a progestin medication which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It is available both alone and in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth. Medrogestone is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. It has weak antiandrogenic, glucocorticoid, and antimineralocorticoid activity and no other important hormonal activity. Due to its progestogenic activity, medrogestone has antigonadotropic effects. Medrogestone was described as early as 1963 and was introduced for medical use by at least 1966. It has mostly been discontinued and remains available only in a few countries. Medical uses In the past, medrogestone was used in the treatment of endometrial cancer and in some regimens for breast cancer, and, in men, for benign prostatic hyper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |