|
Martin Pring
Martin Pring (1580–1626) was an English explorer from Bristol, England who in 1603 at the age of 23 was captain of an expedition to North America to assess commercial potential; he explored areas of present-day Maine, New Hampshire, and Cape Cod in Massachusetts. In the process, he named what is now Plymouth Harbor 'Whitson Bay' and a nearby hill 'Mount Aldworth' after the two Bristol merchants who provided him with ships and supplies. The harbour was later renamed by the Pilgrim fathers. Pring and his crew were the first known Europeans to ascend the Piscataqua River. It is thought that Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano explored this part of the New England coast in 1524-25 looking for a route to the Far East, but he did not make landfall until he reached the St. Lawrence River further north. In 1606 Pring returned to America and mapped the Maine coast. Later he became a ship's master, sailing for the East India Company (EIC) and exploring in East Asia. He also prevented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a Venetia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes Plimouth) was, from 1620 to 1691, the first permanent English colony in New England and the second permanent English colony in North America, after the Jamestown Colony. It was first settled by the passengers on the '' Mayflower'', at a location that had previously been surveyed and named by Captain John Smith. The settlement served as the capital of the colony and developed as the town of Plymouth, Massachusetts. At its height, Plymouth Colony occupied most of the southeastern portion of Massachusetts. Many of the people and events surrounding Plymouth Colony have become part of American folklore, including the American tradition of Thanksgiving and the monument of Plymouth Rock. Plymouth Colony was founded by a group of Puritan Separatists initially known as the Brownist Emigration, who came to be known as the Pilgrims. It was the second successful colony to be founded by the English in the United States after Jamestown in Virginia, and it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes flushed, and may begin to sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections—such as influenza, the common cold, meningitis, urinary tract infections, appendicitis, Lassa, COVID-19, and malaria. Non-infectious cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bay (New Hampshire)
Great Bay is a tidal estuary located in Strafford and Rockingham counties in eastern New Hampshire, United States. The bay occupies over , not including its several tidal river tributaries. Its outlet is at Hilton Point in Dover, New Hampshire, where waters from the bay flow into the Piscataqua River, thence proceeding southeast to the Atlantic Ocean near Portsmouth. The northern end of the bay, near its outlet, is referred to as Little Bay. Geography Located within the Gulf of Maine watershed, the Great Bay Estuary is a drowned river valley composed of high-energy tidal waters, deep channels and fringing mudflats. The entire estuary extends inland from the mouth of the Piscataqua River between Kittery, Maine, and New Castle, New Hampshire through Little Bay into Great Bay proper at Furber Strait, a distance of . The Great Bay Estuary is a tidally-dominated system and is the drainage confluence of three major rivers, the Lamprey, Squamscott, and Winnicut. Four additional rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontoon
A spontoon, sometimes known by the variant spelling espontoon or as a half-pike, is a type of European polearm that came into being alongside the pike. The spontoon was in common use from the mid-17th century to the early 19th century, but it was used to a much lesser extent as a military weapon and ceremonial implement until the late 19th century. Description Unlike the pike, which was an extremely long weapon (typically ), the spontoon measured only in overall length. Generally, this weapon featured a more elaborate head than the typical pike. The head of a spontoon often had a pair of blades or lugs on each side, giving the weapon the look of a military fork, or a trident. There were also spontoon-style axes which used the same shaped blades mounted on the side of the weapon with a shorter handle. Italians might have been the first to use the spontoon, and, in its early days, the weapon was used for combat, before it became more of a symbolic item. After the musket replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of . The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of . A confluence, where two or more bodies of water meet, usually refers to the joining of tributaries. The opposite to a tributary is a distributary, a river or stream that branches off from and flows away from the main stream. PhysicalGeography.net, Michael Pidwirny & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
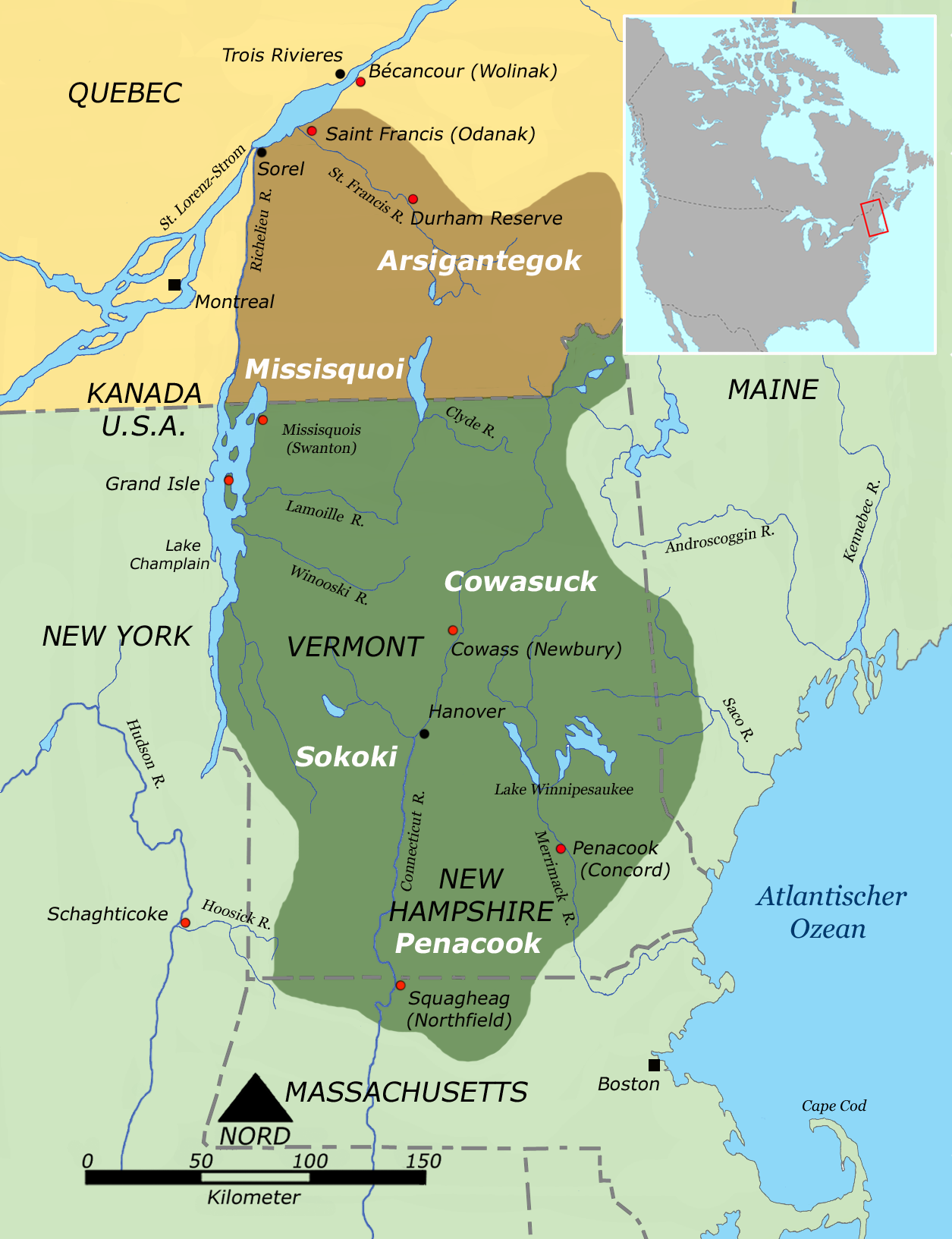
Abenaki People
The Abenaki (Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was predominantly spoken in Maine, while the Western Abenaki language was spoken in Quebec, Vermont, and New Hampshire. While Abenaki peoples have shared cultural traits, they did not historically have a centralized government. They came together as a post-contact community after their original tribes were decimated by colonization, disease, and warfare. Names The word ''Abenaki'' and its syncope, ''Abnaki,'' are both derived from ''Wabanaki'', or ''Wôbanakiak,'' meaning "People of the Dawn Land" in the Abenaki language. While the two terms are often confused, the Abenaki are one of several tribes in the Wabanaki Confederacy. The name is spelled several ways including Abnaki, Abinaki, and Alnôbak. ''Wôbanakiak'' is derived from ''wôban'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Ethnic Groups
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) count 87 distinct "''peoples of Europe''", of which 33 form the majority population in at least one sovereign state, while the remaining 54 constitute ethnic minorities. The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of 770 million Europeans.Christoph Pan, Beate Sibylle Pfeil (2002), Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als2006 reprint by Springer(Amazon, no preview) . The Russians are the most populous among Europeans, with a population of roughly 120 million. There are no universally accepted and precise definitions of the terms "ethnic group" and "nationality". In the context of European ethnography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world. Most existing estuaries formed during the Holocene epoch with the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when the sea level began to rise about 10,000–12,000 years ago. Estuaries are typically classified according to their geomorphological features or to water-circulation patterns. They can have many different names, such as bays, harbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York River (Maine)
The York River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 30, 2011 stream in southeast Maine, United States. It is tidal for over half of its length. It rises at York Pond in Eliot, and conjoined by brooks and creeks, feeds the tidal section. The York River flows southeast to the Atlantic Ocean at York Harbor in the town of York. The Abenaki name for the York River is ''Agamenticus'', which means "Beyond-the-hill-little-cove". According to Eben Norton Horsford, Agamenticus "described the site of the mouth of Little York River to one approaching it from the ''north'', as it lay behind the hill called by the Indians "Sassanows" (the modern Agamenticus). Little York River, a short tidal river, was the "Beyond-the-hill-little-cove." Legislation On May 23, 2013, Rep Chellie Pingree introduced the York River Wild and Scenic River Study Act of 2013 (H.R. 2197; 113th Congress) would have required the National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennebunk River
The Kennebunk River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed June 30, 2011 river in York County, Maine Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ... in the United States. It drains a settled rural area southwest of Portland, Maine, Portland, emptying into the Atlantic Ocean. It rises in central York County, at the junction of Carlisle Brook and Lords Brook in the town of Lyman, Maine, Lyman. Lords Brook issues from Kennebunk Pond in Lyman. The Kennebunk River flows generally southeast, passing under Interstate 95 in Maine, Interstate 95 and U.S. Route 1. It flows past the town center of Kennebunkport, Maine, Kennebunkport, where it becomes navigable, and enters the Atlantic in Kennebunkport, approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saco River
The Saco River (Abenaki: ''Sαkóhki'') is a river in northeastern New Hampshire and southwestern Maine in the United States. It drains a rural area of of forests and farmlands west and southwest of Portland, emptying into the Atlantic Ocean at Saco Bay, from its source.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed June 30, 2011 It supplies drinking water to roughly 250,000 people in thirty-five towns; and historically provided transportation and water power encouraging development of the cities of Biddeford and Saco and the towns of Fryeburg and Hiram. The name "Saco" comes from the Eastern Abenaki word '' ɑkohki', meaning "land where the river comes out". ''The Jesuit Relations'', ethnographic documents from the 17th century, refer to the river as ''Chouacoet''. Course The river rises at Saco Lake in Crawford Notch in the White Mountains and flows generally south-southeast through Bartlett and Conway in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |