|
MacBook (Retina)
The MacBook is a brand of Mac notebook computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc. that use Apple's macOS operating system since 2006. It replaced the PowerBook and iBook brands during the Mac transition to Intel processors, announced in 2005. The current lineup consists of the MacBook Air (2008–present) and the MacBook Pro (2006–present). Two different lines simply named "MacBook" existed from 2006 to 2012 and 2015 to 2019. Overview The MacBook family was initially housed in designs similar to the iBook and PowerBook lines which preceded them, now making use of a unibody aluminum construction first introduced with the MacBook Air. This new construction also has a black plastic keyboard that was first used on the MacBook Air, which itself was inspired by the sunken keyboard of the original polycarbonate MacBooks. The now standardized keyboard brings congruity to the MacBook line, with black keys on a metallic aluminum body. The lids of the MacBook family are held cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touch ID
Touch ID is an electronic fingerprint recognition feature designed and released by Apple Inc. that allows users to unlock devices, make purchases in the various Apple digital media stores (iTunes Store, App Store, and Apple Books Store), and authenticate Apple Pay online or in apps. It can also be used to lock and unlock password-protected notes on iPhone and iPad. Touch ID was first introduced in iPhones with 2013's iPhone 5S, In 2015, Apple introduced a faster second-generation Touch ID in the iPhone 6S; a year later in 2016, it made its laptop debut in the MacBook Pro integrated on the right side of the Touch Bar. Touch ID has been used on all iPads since the iPad Air 2 was introduced in 2014. In MacBooks, each user account can have up to three fingerprints, and a total of five fingerprints across the system. Fingerprint information is stored locally in a secure enclave on the Apple A7 and later chips, not in the cloud, a design choice intended to secure fingerprint inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transportation Security Administration
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) that has authority over the security of transportation systems within, and connecting to the United States. It was created as a response to the September 11 attacks to improve airport security procedures and consolidate air travel security under a dedicated federal administrative law enforcement agency. The TSA develops broad policies to protect the U.S. transportation system, including highways, railroads, buses, mass transit systems, ports, pipelines, and intermodal freight facilities. It fulfills this mission in conjunction with other federal agencies and state partners. However, the TSA's primary focus is on airport security and the prevention of aircraft hijacking. It is responsible for screening passengers and baggage at more than 450 U.S. airports, employing screening officers in airports, armed Federal Air Marshals on planes, mobile teams of dog ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radeon RX 5000 Series
The Radeon RX 5000 series is a series of graphics processors developed by AMD, based on their RDNA architecture. The series is targeting the mainstream mid to high-end segment and is the successor to the Radeon RX Vega series. The launch occurred on July 7, 2019. It is manufactured using TSMC's 7 nm FinFET semiconductor fabrication process. Architecture The Navi GPUs are the first AMD GPUs to use the new RDNA architecture, whose compute units have been redesigned to improve efficiency and instructions per clock (IPC). It features a multi-level cache hierarchy, which offers higher performance, lower latency, and less power consumption compared to the previous series. Navi also features an updated memory controller with GDDR6 support. The encoding stack has changed from using Unified Video Decoder and Video Coding Engine, to using Video Core Next. VCN was previously used in the GCN 5th generation (Vega) implementation in Raven Ridge, though not utilized in other Vega p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radeon RX Vega Series
The Radeon RX Vega series is a series of graphics processors developed by AMD. These GPUs use the Graphics Core Next (GCN) 5th generation architecture, codenamed Vega, and are manufactured on 14 nm FinFET technology, developed by Samsung Electronics and licensed to GlobalFoundries. The series consists of desktop graphics cards and APUs aimed at desktops, mobile devices, and embedded applications. The lineup was released on 14 August 2017. It included the RX Vega 56 and the RX Vega 64, priced at $399 and $499 respectively. These were followed by two mobile APUs, the Ryzen 2500U and Ryzen 2700U, in October 2017. February 2018 saw the release of two desktop APUs, the Ryzen 3 2200G and the Ryzen 5 2400G, and the Ryzen Embedded V1000 line of APUs. In September 2018 AMD announced several Vega APUs in their Athlon line of products. Later in January 2019, the Radeon VII was announced based on the 7nm FinFET node manufactured by TSMC. History The Vega microarchitecture was AMD's h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD Polaris
Graphics Core Next (GCN) is the codename for a series of microarchitectures and an instruction set architecture that were developed by AMD for its GPUs as the successor to its TeraScale microarchitecture. The first product featuring GCN was launched on January 9, 2012. GCN is a reduced instruction set SIMD microarchitecture contrasting the very long instruction word SIMD architecture of TeraScale. GCN requires considerably more transistors than TeraScale, but offers advantages for general-purpose GPU (GPGPU) computation due to a simpler compiler. GCN graphics chips were fabricated with CMOS at 28 nm, and with FinFET at 14 nm (by Samsung Electronics and GlobalFoundries) and 7 nm (by TSMC), available on selected models in AMD's Radeon HD 7000, HD 8000, 200, 300, 400, 500 and Vega series of graphics cards, including the separately released Radeon VII. GCN was also used in the graphics portion of Accelerated Processing Units (APUs), such as those in the PlayStation 4 and Xbox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactured its own processors, the company later outsourced its manufacturing, a practice known as going fabless, after GlobalFoundries was spun off in 2009. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, graphics processors, and FPGAs for servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded system applications. History First twelve years Advanced Micro Devices was formally incorporated by Jerry Sanders, along with seven of his colleagues from Fairchild Semiconductor, on May 1, 1969. Sanders, an electrical engineer who was the director of marketing at Fairchild, had, like many Fairchild executives, grown frustrated with the increasing lack of support, opportunity, and flexibility within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esc Key
On computer keyboards, the Esc key (named ''Escape key'' in the international standard series ISO/IEC 9995) is a key used to generate the escape character (which can be represented as ASCII code 27 in decimal, Unicode U+001B, or ). The escape character, when sent from the keyboard to a computer, often is interpreted by software as "stop", and when sent from the computer to an external device (including many printers since the 1980s, computer terminals and Linux consoles, for example) marks the beginning of an escape sequence to specify operating modes or characteristics generally. It is now generally placed at the top left corner of the keyboard, a convention dating at least to the original IBM PC keyboard, though the key itself originated decades earlier with teletypewriters. Symbol The keyboard symbol for the ESC key (which may be used when the usual Latin lettering "Esc" is not preferred for labelling the key) is standardized in ISO/IEC 9995-7 as symbol 29, and in IS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function Keys
A function key is a key on a computer or terminal keyboard that can be programmed so as to cause an operating system command interpreter or application program to perform certain actions, a form of soft key. On some keyboards/computers, function keys may have default actions, accessible on power-on. Function keys on a terminal may either generate short fixed sequences of characters, often beginning with the escape character (ASCII 27), or the characters they generate may be configured by sending special character sequences to the terminal. On a standard computer keyboard, the function keys may generate a fixed, single byte code, outside the normal ASCII range, which is translated into some other configurable sequence by the keyboard device driver or interpreted directly by the application program. Function keys may have abbreviations or pictographic representations of default actions printed on/besides them, or they may have the more common "F-number" designations. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB4
USB4 (aka: USB 4.0) is a specification by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), which was released in version 1.0 on 29 August 2019. The USB4 protocol is based on the Thunderbolt 3 protocol; the Thunderbolt 3 specification was donated to the USB-IF by Intel Corp. The USB4 architecture can share a single high-speed link with multiple end-device types dynamically, best serving each transfer by data type and application. In contrast to prior USB protocol standards, USB4 ''mandates'' the exclusive use of the Type-C connector, and ''mandates'' the use of USB PD for power delivery. USB4 products must support 20 Gbit/s throughput and can support 40 Gbit/s throughput, but due to tunneling even nominal 20 Gbit/s can result in higher effective data rates in USB4, compared to USB 3.2, when sending mixed data. In contrast to USB 3.2, it allows tunneling of DisplayPort and PCI Express. Support of interoperability with Thunderbolt 3 products is required for USB4 hosts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderbolt (interface)
Thunderbolt is the brand name of a hardware interface for the connection of external peripherals to a computer. It has been developed by Intel, in collaboration with Apple. It was initially marketed under the name Light Peak, and first sold as part of an end-user product on 24 February 2011. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express (PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) into two serial signals, and additionally provides DC power, all in one cable. Up to six peripherals may be supported by one connector through various topologies. Thunderbolt 1 and 2 use the same connector as Mini DisplayPort (MDP), whereas Thunderbolt 3 and 4 reuse the USB-C connector from USB. Description Thunderbolt controllers multiplex one or more individual data lanes from connected PCIe and DisplayPort devices for transmission via two duplex Thunderbolt lanes, then de-multiplex them for use by PCIe and DisplayPort devices on the other end. A single Thunderbolt port supports up to six Thunderbolt devices via hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
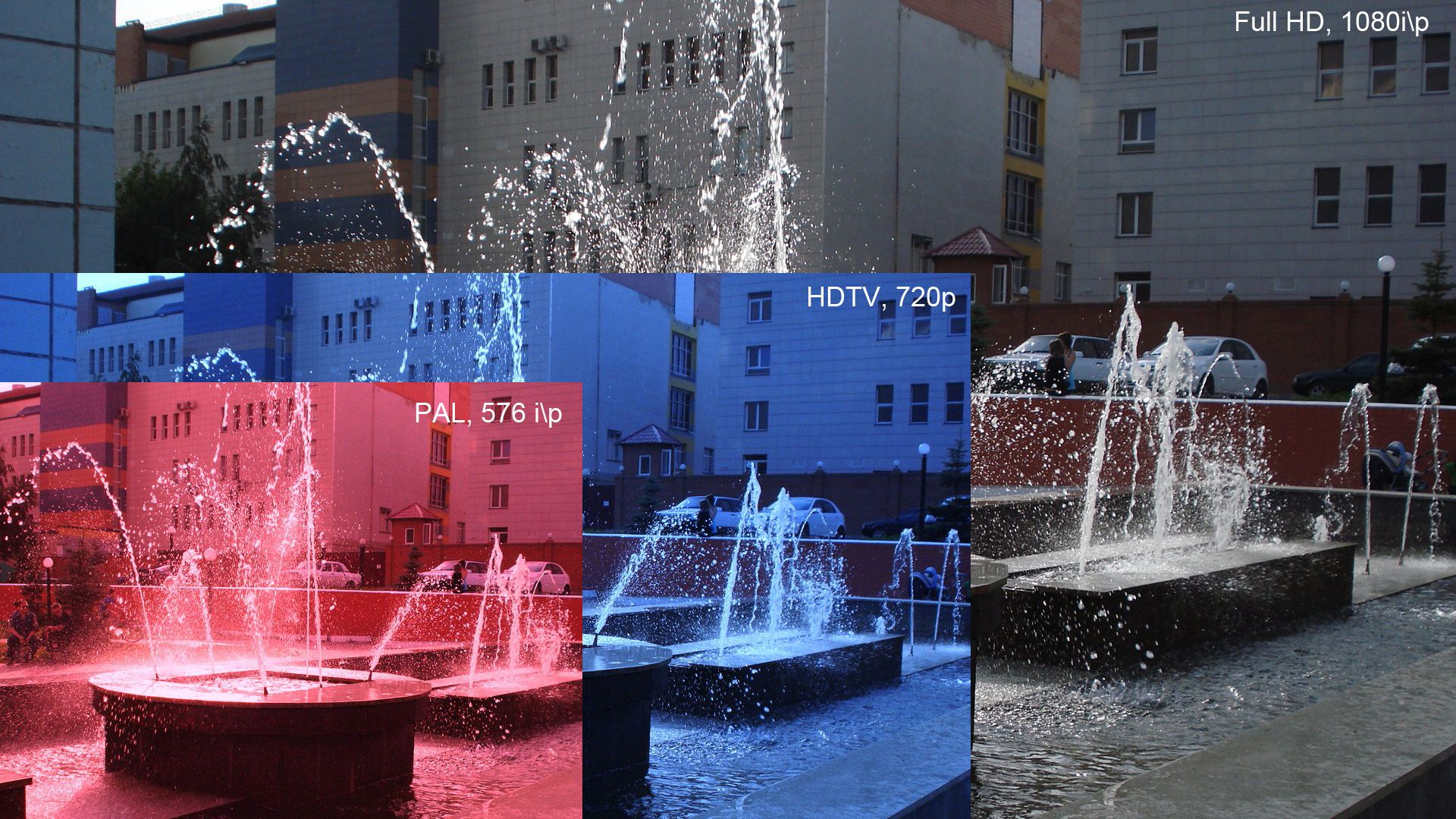
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |