|
MIASE
The minimum information about a simulation experiment (MIASE){{cite journal, author1=D. Waltemath , author2=Richard Adams , author3=Daniel A. Beard , author4=rank T. Bergmann , author5=Upinder S. Bhalla , author6=Randall Britten , author7=Vijayalakshmi Chelliah , author8=Michael T. Cooling , author9=Jonathan Cooper , author10=Edmund J. Crampin , author11=Alan Garny , author12=Stefan Hoops , author13=Michael Hucka , author14=Peter Hunter , author15=Edda Klipp , author16=Camille Laibe , author17=Andrew K. Miller , author18=Ion Moraru , author19=David Nickerson , author20=Poul Nielsen , author21=Macha Nikolski , author22=Sven Sahle , author23=Herbert M. Sauro , author24=Henning Schmidt , author25=Jacky L. Snoep , author26=Dominic Tolle , author27=Olaf Wolkenhauer , author28=Nicolas Le Novère , title=Minimum Information About a Simulation Experiment (MIASE). , journal=PLOS Computational Biology , year= 2011 , volume= 7 , issue= 4 , doi=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001122 , pmid=21552546 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miase 170
The minimum information about a simulation experiment (MIASE){{cite journal, author1=D. Waltemath , author2=Richard Adams , author3=Daniel A. Beard , author4=rank T. Bergmann , author5=Upinder S. Bhalla , author6=Randall Britten , author7=Vijayalakshmi Chelliah , author8=Michael T. Cooling , author9=Jonathan Cooper , author10=Edmund J. Crampin , author11=Alan Garny , author12=Stefan Hoops , author13=Michael Hucka , author14=Peter Hunter , author15=Edda Klipp , author16=Camille Laibe , author17=Andrew K. Miller , author18=Ion Moraru , author19=David Nickerson , author20=Poul Nielsen , author21=Macha Nikolski , author22=Sven Sahle , author23=Herbert M. Sauro , author24=Henning Schmidt , author25=Jacky L. Snoep , author26=Dominic Tolle , author27=Olaf Wolkenhauer , author28=Nicolas Le Novère , title=Minimum Information About a Simulation Experiment (MIASE). , journal=PLOS Computational Biology , year= 2011 , volume= 7 , issue= 4 , doi=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001122 , pmid=21552546 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Information Standards
Minimum information standards are sets of guidelines and formats for reporting data derived by specific high-throughput methods. Their purpose is to ensure the data generated by these methods can be easily verified, analysed and interpreted by the wider scientific community. Ultimately, they facilitate the transfer of data from journal articles (unstructured data) into databases (structured data) in a form that enables data to be mined across multiple data sets. Minimal information standards are available for a vast variety of experiment types including microarray (MIAME), RNAseq ( MINSEQE), metabolomics (MSI) and proteomics ( MIAPE). Minimum information standards typically have two parts. Firstly, there is a set of reporting requirements – typically presented as a table or a checklist. Secondly, there is a data format. Information about an experiment needs to be converted into the appropriate data format for it to be submitted to the relevant database. In the case of MIAME, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Information Standards
Minimum information standards are sets of guidelines and formats for reporting data derived by specific high-throughput methods. Their purpose is to ensure the data generated by these methods can be easily verified, analysed and interpreted by the wider scientific community. Ultimately, they facilitate the transfer of data from journal articles (unstructured data) into databases (structured data) in a form that enables data to be mined across multiple data sets. Minimal information standards are available for a vast variety of experiment types including microarray (MIAME), RNAseq ( MINSEQE), metabolomics (MSI) and proteomics ( MIAPE). Minimum information standards typically have two parts. Firstly, there is a set of reporting requirements – typically presented as a table or a checklist. Secondly, there is a data format. Information about an experiment needs to be converted into the appropriate data format for it to be submitted to the relevant database. In the case of MIAME, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BioPAX
BioPAX (Biological Pathway Exchange) is a RDF/OWL-based standard language to represent biological pathways at the molecular and cellular level. Its major use is to facilitate the exchange of pathway data. Pathway data captures our understanding of biological processes, but its rapid growth necessitates development of databases and computational tools to aid interpretation. However, the current fragmentation of pathway information across many databases with incompatible formats presents barriers to its effective use. BioPAX solves this problem by making pathway data substantially easier to collect, index, interpret and share. BioPAX can represent metabolic and signaling pathways, molecular and genetic interactions and gene regulation networks. BioPAX was created through a community process. Through BioPAX, millions of interactions organized into thousands of pathways across many organisms, from a growing number of sources, are available. Thus, large amounts of pathway data are availab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CellML
CellML is an XML based markup language for describing mathematical models. Although it could theoretically describe any mathematical model, it was originally created with the Physiome Project in mind, and hence used primarily to describe models relevant to the field of biology. This is reflected in its name CellML, although this is simply a name, not an abbreviation. CellML is growing in popularity as a portable description format for computational models, and groups throughout the world are using CellML for modelling or developing software tools based on CellML. CellML is similar to Systems Biology Markup Language SBML but provides greater scope for model modularity and reuse, and is not specific to descriptions of biochemistry. History The CellML language grew from a need to share models of cardiac cell dynamics among researchers at a number of sites across the world. The original working group formed in 1998 consisted of David Bullivant, Warren Hedley, and Poul Nielsen; all th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
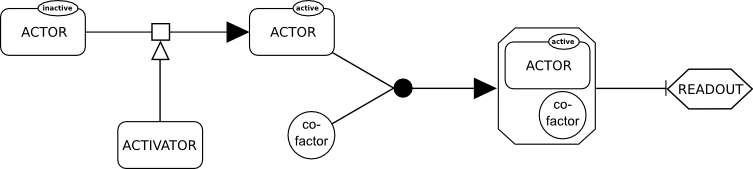
SBGN
The Systems Biology Graphical Notation (SBGN) is a standard graphical representation intended to foster the efficient storage, exchange and reuse of information about signaling pathways, metabolic networks, and gene regulatory networks amongst communities of biochemists, biologists, and theoreticians. The system was created over several years by a community of biochemists, modelers and computer scientists. SBGN is made up of three orthogonal languages for representing different views of biological systems: ''Process Descriptions'', ''Entity Relationships'' and ''Activity Flows''. Each language defines a comprehensive set of symbols with precise semantics, together with detailed syntactic rules regarding the construction and interpretation of maps. Using these three notations, a life scientist can represent in an unambiguous way networks of interactions (for example biochemical interactions). These notations make use of an idea and symbols similar to that used by electrical and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Biology Ontology
The Systems Biology Ontology (SBO) is a set of controlled, relational vocabularies of terms commonly used in systems biology, and in particular in computational modeling. SBO is part of thBioModels.neteffort. Motivation The rise of Systems Biology, seeking to comprehend biological processes as a whole, highlighted the need to not only develop corresponding quantitative models, but also to create standards allowing their exchange and integration. This concern drove the community to design common data format such as SBML and CellML. SBML is now largely accepted and used in the field. However, as important as the definition of a common syntax is, it is also necessary to make clear the semantics of models. SBO is an attempt to provide the means of annotating models with terms that indicate the intended semantics of an important subset of models in common use in computational systems biology. The development of SBO was first discussed at the 9th SBML Forum Meeting in Heidelberg Oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Biology
Systems biology is the computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach ( holism instead of the more traditional reductionism) to biological research. Particularly from the year 2000 onwards, the concept has been used widely in biology in a variety of contexts. The Human Genome Project is an example of applied systems thinking in biology which has led to new, collaborative ways of working on problems in the biological field of genetics. One of the aims of systems biology is to model and discover emergent properties, properties of cells, tissues and organisms functioning as a system whose theoretical description is only possible using techniques of systems biology. These typically involve metabolic networks or cell signaling networks. Overview Systems biology can be considered from a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |