|
Muckle–Wells Syndrome
Muckle–Wells syndrome (MWS) is a rare autosomal dominant disease which causes sensorineural deafness and recurrent hives, and can lead to amyloidosis. Individuals with MWS often have episodic fever, chills, and joint pain. As a result, MWS is considered a type of periodic fever syndrome. MWS is caused by a defect in the CIAS1 gene which creates the protein cryopyrin. MWS is closely related to two other syndromes, familial cold urticaria and neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease—in fact, all three are related to mutations in the same gene and subsumed under the term cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS). Sign and symptoms * Sensorineural deafness * Recurrent urticaria (hives) * Fevers * Chills * Arthralgia (painful joints) Causes Muckle-Wells syndrome occurs when a mutation in the ''NLRP3'' gene leads to increased activity of the protein NLRP3 (cryopyrin). This protein is partly responsible for the body's response to damage or infection. During th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Immunology
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms. Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders (such as autoimmune diseases, hypersensitivities, immune deficiency, and transplant rejection); and the physical, chemical, and physiological characteristics of the components of the immune system ''in vitro'', ''in situ'', and ''in vivo''. Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of medicine, particularly in the fields of organ transplantation, oncology, rheumatology, virology, bacteriology, parasitology, psychiatry, and dermatology. The term was coined by Russian biologist Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov, who advanced studies on immunology and received the Nobel Prize for his work in 1908 with Paul Ehrlich "in recognition of their work on immunity". He pinned small thorns i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
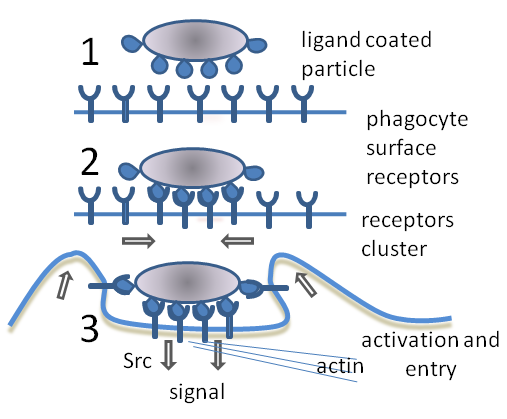
Innate Immune Cell
A non-specific immune cell is an immune cell (such as a macrophage, neutrophil, or dendritic cell) that responds to many antigens, not just one antigen. Non-specific immune cells function in the first line of defense against infection or injury. The innate immune system is always present at the site of infection and ready to fight the bacteria; it can also be referred to as the "natural" immune system. The cells of the innate immune system do not have specific responses and respond to each foreign invader using the same mechanism. The innate immune system There are two categories to which parts of the immune system are assigned: the non-specific, or innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The non-specific response is a generalized response to pathogen infections involving the use of several white blood cells and plasma proteins. Non-specific immunity, or innate immunity, is the immune system with which you were born, made up of phagocytes and barriers. Phagocytosis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Goldman
Howard Brian Goldman (born 1956) is a Canadian emergency physician, author, public speaker, and radio personality. Education and career He completed his undergraduate medical education at the University of Toronto in 1980. In July 1980, he began postgraduate medical education in family medicine. On 15 January 1982, Goldman obtained his Independent Practice Certificate from the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Ontario. He received his certification in family medicine from the College of Family Physicians of Canada (CFPC) in July 1984, followed by a certificate of advanced competency in emergency medicine from the CFPC in November 1985. He practices in the Schwartz Reisman Emergency Centre at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Goldman has been a regular medical columnist on CBC Radio One since 1999. Goldman was also awarded fellowship in the CFPC, thereby entitled to display the "FCPF" special designation, in addition to his current membership certification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Coat, Black Art
''White Coat, Black Art'' is a Canadian radio documentary series on CBC Radio One, hosted by physician Brian Goldman that examines the business and culture of medicine from an insider's perspective. Its name is a reference to the white coats that doctors wear, and to the ways that practicing medicine is still in some ways a "black art" rather than a science: mysterious, intuitive, and difficult to master. The series began as a summer series in 2007 and became a regular program on the network's schedule. The Canadian Medical Association awarded the program the 2011 Media Award for Health Reporting (Excellence in Radio Reporting / In-Depth). at the |
CBC Radio One
CBC Radio One is the English-language news and information radio network of the publicly owned Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. It is commercial-free and offers local and national programming. It is available on AM and FM to 98 percent of Canadians and overseas over the Internet, and through mobile apps. CBC Radio One is simulcast across Canada on Bell Satellite TV satellite channels 956 and 953, and Shaw Direct satellite channel 870. A modified version of Radio One, with local content replaced by additional airings of national programming, is available on Sirius XM channel 169. It is downlinked to subscribers via SiriusXM Canada and its U.S.-based counterpart, Sirius XM Satellite Radio. In 2010, Radio One reached 4.3 million listeners each week. It was the largest radio network in Canada. History CBC Radio began in 1936, and is the oldest branch of the corporation. In 1949, the facilities and staff of the Broadcasting Corporation of Newfoundland were transferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies are identical and can thus have monovalent affinity, binding only to a particular epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies are mixtures of antibodies derived from multiple plasma cell lineages which each bind to their particular target epitope. Artificial antibodies known as bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered which include two different antigen binding sites ( FABs) on the same antibody. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to almost any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canakinumab
Canakinumab, sold under the brand name Ilaris, is a medication for the treatment of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, active Still's disease, including adult-onset Still's disease, gout flares. It is a human monoclonal antibody targeted at interleukin-1 beta. It has no cross-reactivity with other members of the interleukin-1 family, including interleukin-1 alpha. Common side effects include infections (colds and upper respiratory tract infections), abdominal pain and injection-site reactions. Medical uses Canakinumab was approved for the treatment of cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2009, and by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in October 2009. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. CAPS is a spectrum of autoinflammatory syndromes including Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome (FCAS), Muckl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rilonacept
Rilonacept, sold under the brand name Arcalyst, is a medication used to treat cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes, including familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, and Muckle–Wells syndrome; deficiency of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; and recurrent pericarditis. Rilonacept is an interleukin 1 inhibitor. Rilonacept is a dimeric fusion protein consisting of the ligand-binding domains of the extracellular portions of the human interleukin-1 receptor component (IL-1R1) and IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) linked in-line to the fragment-crystallizable portion ( Fc region) of human IgG1 that binds and neutralizes IL-1. Rilonacept was given an orphan drug designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is used for the treatment of cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS), including familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, Muckle–Wells syndrome. Rilonacept is the first drug approved by the FDA to treat recurrent pericarditis. Rilona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 1
The Interleukin-1 family (IL-1 family) is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults. Discovery Discovery of these cytokines began with studies on the pathogenesis of fever. The studies were performed by Eli Menkin and Paul Beeson in 1943–1948 on the fever-producing properties of proteins released from rabbit peritoneal exudate cells. These studies were followed by contributions of several investigators, who were primarily interested in the link between fever and infection/inflammation. The basis for the term "interleukin" was to streamline the growing number of biological properties attributed to soluble factors from macrophages and lymphocytes. IL-1 was the name given to the macrophage product, whereas IL-2 was used to define the lymphocyte product. At the time of the assignment of these names, there was no amino acid sequence analysis known and the terms were used to define b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anakinra
Anakinra, sold under the brand name Kineret, is a biopharmaceutical medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes, familial Mediterranean fever, and Still's disease. It is a slightly modified recombinant version of the human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist protein. It is marketed by Swedish Orphan Biovitrum. Anakinra is administered by subcutaneous injection. Medical uses It is used as a second line treatment to manage symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis after treatment with a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) has failed. It can be used in combination with some DMARDs. It is administered subcutaneously to patients diagnosed with a cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome, including neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease. It is used to treat Schnitzler's syndrome (off label in the US). Its response rate is such that it has been suggested that "Treatment failures should lead to reconsider the diagnosis." Off labe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In certain types of arthritis, other organs such as the skin are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are several types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (most commonly seen in weightbearing joints) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs as an individual ages and often affects the hips, knees, shoulders, and fingers. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types of arthritis include gout, lupus, and septic arthritis. These are inflammatory based types of rheumatic disease. Early treatment for arthritis commonly includes resting the affected joint and conservative measures such as heating or icing. Weight Weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |