|
Mount Alayta
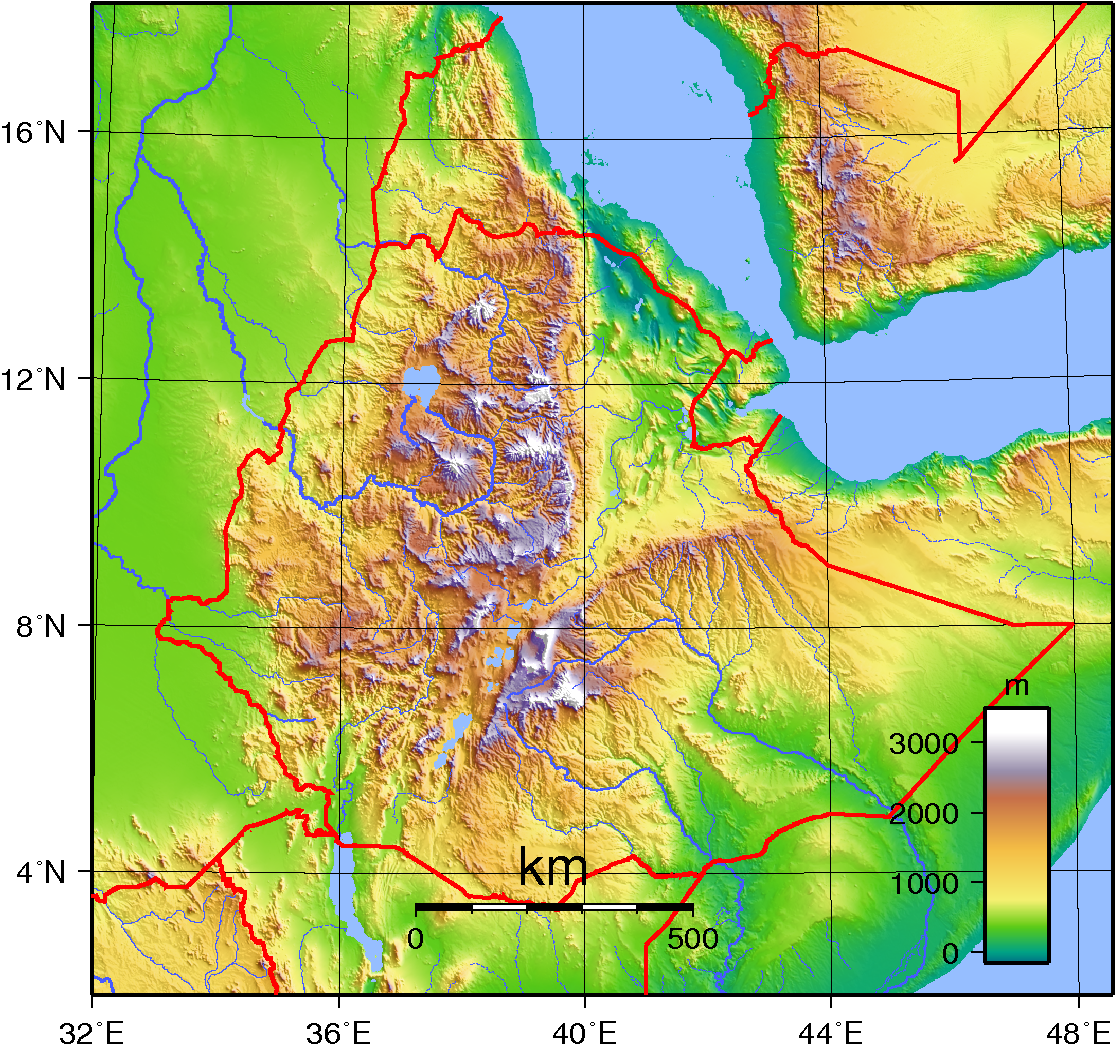
Mount Alayta is an active shield volcano in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. It is part of the Afar Triangle (Afar Depression), a highly active volcanic region which includes the adjacent Afdera (volcano), Mount Afdera. Mount Alayta covers an area of 2,700 square kilometers southwest of Lake Afrera. A chain of younger craters are aligned along a north-northwest axis in the basaltic-to-trachytic shield along the east side of the shield volcano, which extends to the western flank of Mount Afdera. The Alayta Lavafeld was formed from a series of north-south fissures. In two areas on the southern side of the volcanic complex, fumaroles can be observed. Two historical eruptions that were formerly attributed to Mount Afdera are believed to have originated from Alayta. One of those eruptions, between June and August 1907, produced a large lava flow from a vent on its southeastern flank. Its most recent eruption was in 1915. See also *Erta Ale *Geography of Ethiopia References Afar Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Ethiopia
This is a list of volcanoes in Ethiopia. It includes both active and extinct vents. See also * Geography of Ethiopia * Lists of volcanoes References {{Global Volcanism Program Volcanoes Ethiopia Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afar Depression
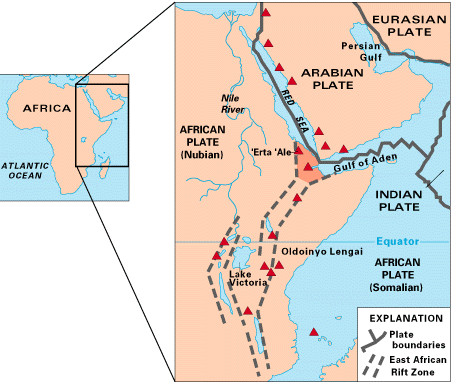
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; that is, the earliest of the human clade, and it is thought by some paleontologists to be the cradle of the evolution of humans. The Depression overlaps the borders of Eritrea, Djibouti and the entire Afar Region of Ethiopia; and it contains the lowest point in Africa, Lake Assal, Djibouti, at below sea level. The Awash River is the main waterflow into the region, but it runs dry during the annual dry season, and ends as a chain of saline lakes. The northern part of the Afar Depression is also known as the Danakil Depression. The lowlands are affected by heat, drought, and minimal air circulation, and contain the hottest places (year-round average temperatures) of anywhere on Earth. The Afar Triangle is bordered as follows (see the topog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afar Region
The Afar Region (; aa, Qafar Rakaakayak; am, አፋር ክልል), formerly known as Region 2, is a regional state in northeastern Ethiopia and the homeland of the Afar people. Its capital is the planned city of Semera, which lies on the paved Awash–Assab highway. The Afar Triangle, the northern part of which is the Danakil Depression, is part of the Great Rift Valley of Ethiopia, and is located in the north of the region. It has the lowest point in Ethiopia and one of the lowest in Africa. The southern part of the region consists of the valley of the Awash River, which empties into a string of lakes along the Ethiopian–Djibouti border. Other notable landmarks include the Awash National Park. Demographics Based on the 2017 projections by the Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), the Afar Regional State has a population of 1,812,002, consisting of 991,000 men and 821,002 women; urban inhabitants number 346,000 of the population, a further 1,466,000 were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, north, Djibouti to the Djibouti–Ethiopia border, northeast, Somalia to the Ethiopia–Somalia border, east and northeast, Kenya to the Ethiopia–Kenya border, south, South Sudan to the Ethiopia–South Sudan border, west, and Sudan to the Ethiopia–Sudan border, northwest. Ethiopia has a total area of . As of 2022, it is home to around 113.5 million inhabitants, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, 13th-most populous country in the world and the List of African countries by population, 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African Plate, Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield Volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more viscous lava erupted from a stratovolcano. Repeated eruptions result in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes are found wherever fluid low-silica lava reaches the surface of a rocky planet. However, they are most characteristic of ocean island volcanism associated with hot spots or with continental rift volcanism. They include the largest volcanoes on earth, such as Tamu Massif and Mauna Loa. Giant shield volcanoes are found on other planets of the Solar System, including Olympus Mons on Mars and Sapas Mons on Venus. Etymology The term 'shield volcano' is taken from the German term ''Schildvulkan'', coined by the Austrian geologist Eduard Suess in 1888 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afar Triangle
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; that is, the earliest of the human clade, and it is thought by some paleontologists to be the cradle of the evolution of humans. The Depression overlaps the borders of Eritrea, Djibouti and the entire Afar Region of Ethiopia; and it contains the lowest point in Africa, Lake Assal, Djibouti, at below sea level. The Awash River is the main waterflow into the region, but it runs dry during the annual dry season, and ends as a chain of saline lakes. The northern part of the Afar Depression is also known as the Danakil Depression. The lowlands are affected by heat, drought, and minimal air circulation, and contain the hottest places (year-round average temperatures) of anywhere on Earth. The Afar Triangle is bordered as follows (see the topo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afdera (volcano)
Afdera is an isolated stratovolcano in northeastern Ethiopia, located at the intersection of three fault systems between the Erta Ale, Tat Ali, and Alayta mountain ranges. There have been reports of the volcano erupting in 1907 and 1915 but morphological evidence cannot substantiate these claims. The reported eruptions were probably from the Mount Alayta volcano to the west. See also *List of volcanoes in Ethiopia *List of stratovolcanoes A list of stratovolcanoes follows below. Africa Cameroon * Mount Cameroon Democratic Republic of Congo * Mount Nyiragongo, Goma; designated as a Decade Volcano ** It contains an active lava lake inside its crater which overflowed due to ... References Mountains of Ethiopia Stratovolcanoes of Ethiopia Afar Region {{Afar-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Afrera
Lake Afrera (in Italian Lake Giuletti) is a hypersaline lake in northern Ethiopia. Located in Kilbet Rasu, Afar Region, it is one of the lakes of the Danakil Depression. According to its entry in Lakenet, it has a surface area of , although another source states the area is .Robert Mepham, R. H. Hughes, and J. S. Hughes''A directory of African wetlands'' (Cambridge: IUCN, UNEP and WCMC, 1992), p. 168 An unconfirmed report gives its depth as ; the lake is fed by underground streams. It is also known as Lake Giulietti, the name Raimondo Franchetti gave it after the Italian explorer Giuseppe Maria Giulietti was slain by Afars southwest of the lake. Another name for this body of water is Lake Egogi (or Egogi Bad), which is the name L. M. Nesbitt's Afar guide gave it when the Italian explorer became the first European to see it in 1928. The single island in Lake Afrera, Franchetti Island (also known as "Deset"), located in the southern part of the lake, is considered the lowest-lyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erta Ale
Erta Ale (or Ertale or Irta'ale; Amharic: ኤርታሌ) is a continuously active basaltic shield volcano in the Afar Region of northeastern Ethiopia. It is situated in the Afar Depression, a barren desert area. Erta Ale is the most active volcano in Ethiopia. Geology Erta Ale is high, with one or sometimes two active lava lakes at the summit which occasionally overflow on the south side of the volcano. It is notable for holding the longest-existing lava lake, present since the early years of the twentieth century (1906). Volcanoes with lava lakes are very rare: there are only eight in the world. ''Erta Ale'' means "smoking mountain" in the local Afar language and its southernmost pit is known locally as "the gateway to Hell". In 2009, it was mapped by a team from the BBC using three-dimensional laser techniques, in order for the mapping team to maintain a distance and avoid the lakes' searingly hot temperatures. Erta Ale is centered over the East African Rift system, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Ethiopia
Ethiopia is located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Sudan and South Sudan to the west, and Kenya to the south. Ethiopia has a high central plateau that varies from above sea level, with the highest mountain reaching . Elevation is generally highest just before the point of descent to the Great Rift Valley, which splits the plateau diagonally. A number of rivers cross the plateau; notably the Blue Nile rising from Lake Tana. The plateau gradually slopes to the lowlands of the Sudan on the west and the Somali-inhabited plains to the east. Ethiopia's westernmost locality is Pibor River opposite the Sudanese village of Denjok. Its easternmost locality lies along the eastern border of Dollo Zone opposite Puntland and Galmudug states. Physical features Geography Between the valley of the Upper Nile and Ethiopia's border with Sudan and South Sudan is a region of elevated plateaus from which rise the various tablel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fissure Vents
A fissure vent, also known as a volcanic fissure, eruption fissure or simply a fissure, is a linear volcanic vent through which lava erupts, usually without any explosive activity. The vent is often a few metres wide and may be many kilometres long. Fissure vents can cause large flood basalts which run first in lava channels and later in lava tubes. After some time, the eruption tends to become focused at one or more spatter cones. Small fissure vents may not be easily discernible from the air, but the crater rows (see Laki) or the canyons (see Eldgjá) built up by some of them are. The dikes that feed fissures reach the surface from depths of a few kilometers and connect them to deeper magma reservoirs, often under volcanic centers. Fissures are usually found in or along rifts and rift zones, such as Iceland and the East African Rift. Fissure vents are often part of the structure of shield volcanoes. Iceland In Iceland, volcanic vents, which can be long fissures, ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)