|
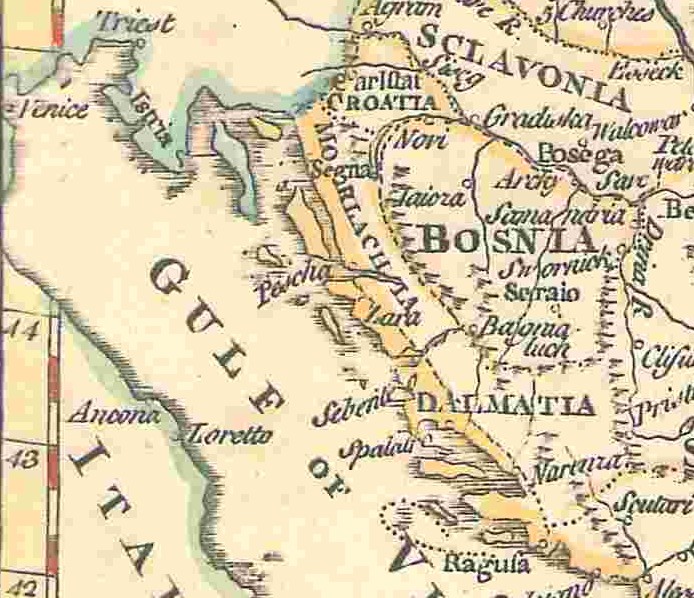
Morlachia
Morlachia (; ; ; ) was a vaguely defined region, named after the Morlachs, used on European maps between the 16th and the 19th centuries. Morlachia was located in modern-day Croatia between Istria and Dalmatia, being opposite to the island of Krk. The Morlachs were originally a Romance people related to modern Romanians before their Slavicisation. Overview In old topography, the toponym Morlachia was given great importance on maps, sometimes being placed at the same "level" or at a superior one than regions such as Bosnia or Croatia. This can be explained by the important geographical position Morlachia had, being located between the Ottoman Empire, the Republic of Venice and the Habsburg monarchy and its realms from the 16th to the 19th century. However, following the demise of Ottoman power in the region and the fall of the Republic of Venice in the latter century, Morlachia lost relevance and the Morlachs of the region became impoverished and eventually assimilated into the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morlachs
Morlachs ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Morlaci, Морлаци; ; ) is an exonym used for a rural Christian community in Herzegovina, Lika and the Dalmatian Hinterland. The term was initially used for a bilingual Vlach pastoralist community in the mountains of Croatia from the second half of the 14th until the early 16th century. Then, when the community straddled the Venetian– Ottoman border until the 17th century, it referred only to the Slavic-speaking people of the Dalmatian Hinterland, Orthodox and Catholic, on both the Venetian and Turkish side. The exonym ceased to be used in an ethnic sense by the end of the 18th century, and came to be viewed as derogatory, but has been renewed as a social or cultural anthropological subject. As the nation-building of the 19th century proceeded, the Vlach/Morlach population residing with the Croats and Serbs of the Dalmatian Hinterland espoused either a Croat or Serb ethnic identity, but preserved some common sociocultural outlines. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula) and north of the Danube. Although it has also been used to name present-day Romanians, the term "Vlach" today refers primarily to speakers of the Eastern Romance languages who live south of the Danube, in Albania, Bulgaria, northern Greece, North Macedonia and eastern Serbia. These people include the ethnic groups of the Aromanians, the Megleno-Romanians and, in Serbia, the Timok Romanians. The term also became a synonym in the Balkans for the social category of shepherds, and was also used for non-Romance-speaking peoples, in recent times in the western Balkans derogatively. The term is also used to refer to the ethnographic group of Moravian Vlachs who speak a Slavic language but originate from Romanians, as well as for Morlachs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberto Fortis
Alberto Fortis (9 or 11 November 1741 – 21 October 1803) was an Italian writer, naturalist and cartographer, citizen of Republic of Venice. Life His real name was Giovanni Battista Fortis (his religious name was ''Alberto'') and he was born in Padua on either 9 or 11 November 1741. He journeyed extensively in Venetian Dalmatia. His best-known work is ''Viaggio in Dalmazia'' (Journey to Dalmatia), originally published in 1774 and first published in London in 1778. The highlight of the book is the description of Morlachia, a historical region currently located in Croatia named after the Morlachs that inhabited the region. In his book, Fortis presented his literary discovery "Hasanaginica" as a Morlach (Vlach) ballad. Larry Wolff believed Fortis wrote the ballad as a poetry of South Slavs rather than a poetry of the Morlachs. Fortis believed that the Morlachs preserved their old customs and clothes. Their ethnographic traits were traditional clothing, use of the gusle musical ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Primorje-Gorski Kotar County
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imotski
Imotski () is a small town on the northeastern side of the Biokovo massif in the Dalmatian Hinterland of southern Croatia, near the border with Bosnia and Herzegovina. The town has a generally mild Mediterranean climate which makes it a popular tourist destination. Geography The town is located close to the border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, 10 km away from Posušje and 18 km from Grude. It is located 29 km away from the coast of Adriatic Sea ( Baška Voda). The nearest coastal town is Makarska, on the other side of the Biokovo massif. The town is located on the crossroad of D60 and D76 state roads and 20 km from the Sveti Ilija Tunnel. The A1 motorway is accessed at the Zagvozd Interchange, next to the D76 expressway. Imotski is known for its medieval fortress on the rocks of Blue Lake. Another phenomenon is the Red Lake which looks like an eye in the scenery. Both lakes are said to be connected with underground channels to the Adriatic Sea. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Alberta
The University of Alberta (also known as U of A or UAlberta, ) is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford, the first premier of Alberta, and Henry Marshall Tory, the university's first president. It was enabled through the ''Post-secondary Learning Act.'' The university is considered a "comprehensive academic and research university" (CARU), which means that it offers a range of academic and professional programs that generally lead to undergraduate and graduate level credentials. The university comprises four campuses in Edmonton, an Augustana Campus in Camrose, Alberta, Camrose, and a staff centre in downtown Calgary. The original north campus consists of 150 buildings covering 50 city blocks on the south rim of the North Saskatchewan River valley parks system, North Saskatchewan River valley, across and west from downtown Edmonton. About 37,000 students from Canada and 150 other countries partici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morlachism
Morlachism or Morlacchism (; or ) was a movement in Italian, Ragusan and Venetian literature that started in 1774 and lasted until the 1830s or 1840s. It consisted on the portrayal of the Morlachs (Vlachs from the Dalmatian Hinterland, now part of Croatia) and other inhabitants of Dalmatia and their beliefs, customs, way of living and many other aspects as understood and imagined by Italians, Ragusans, Venetians and other Europeans. Morlachism was initiated by Alberto Fortis's travel book '' Viaggio in Dalmazia'' ("Journey to Dalmatia") from 1774, which achieved great popularity in Western Europe. In 2014, Branislava Milić Brett, then professor at the University of Alberta, coined the term "Proto-Morlachism" (also referred to as "Pre-Morlachism") to refer to a purported earlier stage of Morlachism that lasted from the Middle Ages In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viaggio In Dalmazia
''Viaggio in Dalmazia'' ("Journey to Dalmatia"), also known by its full title ''Viaggio in Dalmazia dell'abate Alberto Fortis'' ("Journey to Dalmatia by Abbot Alberto Fortis"), is a 1774 book by the Venetian writer Alberto Fortis, published in the city of Venice. On it, Fortis recounted his journey to Dalmatia, a region now in Croatia. He described the region, its mineral resources and its inhabitants and their way of life, paying great attention to the native Morlachs. Fortis' book reached great popularity in Western Europe and increased the interest on Croatia and other South Slavic countries among ethnologists and anthropologists. Furthermore, ''Viaggio in Dalmazia'' would start a new movement in Italian, Ragusan and Venetian literature known as Morlachism, which consisted on the portrayal of the Morlachs and their customs, traditions and lifestyle by Italian and other Western European writers. This movement started in 1774 and lasted until the 1830s or 1840s. In 1776, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travel Book
Travel is the movement of people between distant geographical locations. Travel can be done by foot, bicycle, automobile, train, boat, bus, airplane, ship or other means, with or without luggage, and can be one way or round trip. Travel can also include relatively short stays between successive movements, as in the case of tourism. Etymology The origin of the word "travel" is most likely lost to history. The term "travel" may originate from the Old French word ''travail'', which means 'work'. According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, the first known use of the word ''travel'' was in the 14th century. It also states that the word comes from Middle English , (which means to torment, labor, strive, journey) and earlier from Old French (which means to work strenuously, toil). In English, people still occasionally use the words , which means struggle. According to Simon Winchester in his book ''The Best Travelers' Tales (2004)'', the words ''travel'' and ''travail'' both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's Dominant culture, majority group or fully adopts the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group. The melting pot model is based on this concept. A related term is cultural integration, which describes the process of becoming economically and socially integrated into another society while retaining elements of one’s original culture. This approach is also known as cultural pluralism, and it forms the basis of a cultural mosaic model that upholds the preservation of cultural rights. Another closely related concept is acculturation, which occurs through cultural diffusion and involves changes in the cultural patterns of one or both groups, while still maintaining distinct characteristics. There are various types of cultural assimilation, including full assimilation and forced assimilation. Full assimilation is common, as it occurs spontaneously. Assimilation can also invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice was dissolved and dismembered by the French general Napoleon Bonaparte and the Habsburg monarchy on 12 May 1797, ending approximately 1,100 years of its existence. It was the final action of Napoleon's Italian campaign of 1796–1797 before the War of the First Coalition formally ended in October. In 1796, General Napoleon had been sent by the newly formed French Republic to confront Austria, as part of the Italian front of the French Revolutionary Wars. He chose to go through Venice, which was officially neutral. Reluctantly, the Venetians allowed the formidable French army to enter their country so that it might confront Austria. However, the French covertly began supporting Jacobin revolutionaries within Venice, and the Venetian Senate began quiet preparations for war. The Venetian armed forces were depleted and hardly a match for the battle-tested French or even a local uprising. After the capture of Mantua on 2 February 1797, the French dropped a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |