|
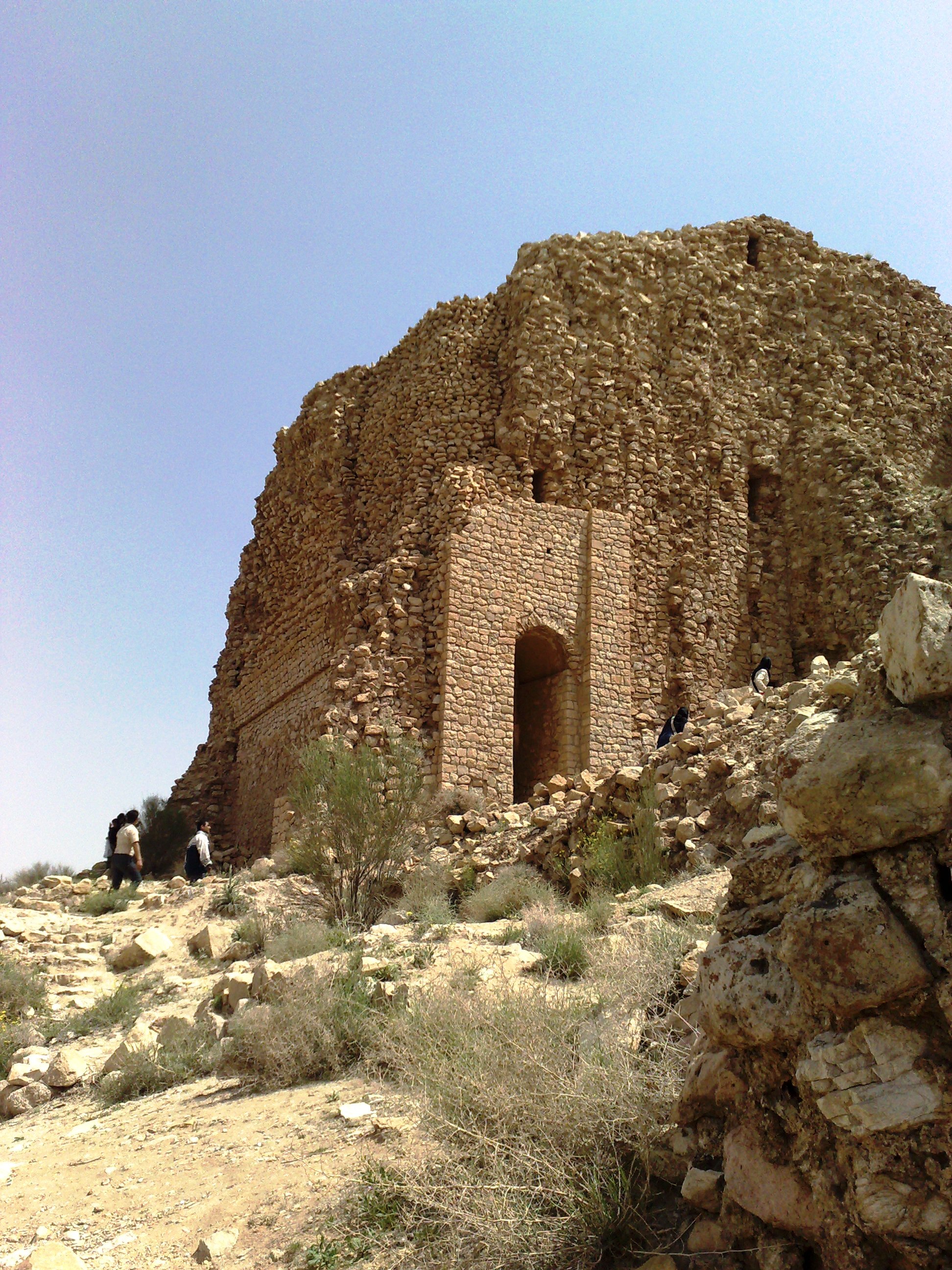
Minar (Firuzabad)
The Minar was a staged, tower-like structure built in the center of the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian circular city of Firuzabad, Fars, Gōr (modern Firuzabad, Iran). Several theories have been proposed for its purpose. Only the core of the structure remains today. Description and history The structure is known as ''Minar'' (, literally "pillar") or ''Minaret'' () in Persian language, New Persian, while the medieval Arabic-language Islamic sources referred to the structure as ''Terbal'' ( ''Ṭirbāl''). Similar structures, i.e., staged tower with an outside ramp, have been recorded by ancient historians, including a tower mentioned by Ammianus Marcellinus at the Nahar Malka (near the Sasanian capital Ctesiphon; he compared it to the Lighthouse of Alexandria), several towers at Pirisabora (Anbar (town), al-Anbar) mentioned by Zosimus (historian), Zosimus, and the Borsippa tower near Babylon. These in turn may have been based on the ziggurats of the ancient Near East. Ardashir I's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firuzabad, Fars
Firuzabad () is a city in the Central District (Firuzabad County), Central District of Firuzabad County, Fars province, Fars province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Firuzabad is south of Shiraz, Iran, Shiraz. The city is surrounded by a mud wall and ditch. The original ancient city of Gor, dating back to the Achaemenid period, was destroyed by Alexander the Great. Centuries later, Ardashir I, the founder of the Sassanid Empire, revived the city before it was ransacked during the Muslim conquest of Persia, Arab Muslim invasion of the seventh century. It was again revived by the Buyids under Fanna Khusraw, but was eventually abandoned in the Qajar Iran, Qajar era and was replaced by a nearby town, which is now Firuzabad. Its only surviving structure is the central core, an ancient Minar (Firuzabad), tower. History Gor dates back to the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid era. It was situated in a low-lying area of the region, so, during his invasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zosimus (historian)
Zosimus ( ; 490s–510s) was a Greek historian who lived in Constantinople during the reign of the eastern Roman Emperor Anastasius I (491–518). According to Photius, he was a ''comes'', and held the office of "advocate" of the imperial treasury. Zosimus was also known for condemning Constantine’s rejection of the traditional polytheistic religion. Little more is known about the life of Zosimus except that he was Greek and a pagan. He was not a contemporary of the events of his books. ''Historia Nova'' Zosimus' ''Historia Nova'' (Ἱστορία Νέα, "New History") is written in Greek in six books and covers the period from 238 to 410 A.D. It was written at the end of the fifth century. For the period from 238 to 270, he apparently uses Dexippus; for the period from 270 to 404, Eunapius; and after 407, Olympiodorus. His dependence on his sources is made clear by the change in tone and style between the Eunapian and Olympiodoran sections, and by the gap left in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Iranica
''Encyclopædia Iranica'' is a project whose goal is to create a comprehensive and authoritative English-language encyclopedia about the history, culture, and civilization of Iranian peoples from prehistory to modern times. Scope The ''Encyclopædia Iranica'' is dedicated to the study of Iranian civilization in the wider Middle East, the Caucasus, Southeastern Europe, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. The academic reference work will eventually cover all aspects of Iranian history and culture as well as all Iranian languages and literatures, facilitating the whole range of Iranian studies research from archeology to political sciences. It is a project founded by Ehsan Yarshater in 1973 and currently carried out at Columbia University's Center for Iranian Studies. It is considered the standard encyclopedia of the academic discipline of Iranistics. The scope of the encyclopedia goes beyond modern Iran (also known as ''"Persia"'') and encompasses the entire Iranian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and meditation. Walking around a stupa in a clockwise direction, known as '' pradakhshina'', has been an important ritual and devotional practice in Buddhism since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate, or drum, with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas, there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have, or had, ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkh
Balkh is a town in the Balkh Province of Afghanistan. It is located approximately to the northwest of the provincial capital city Mazar-i-Sharif and approximately to the south of the Amu Darya and the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border. In 2021–2022, the National Statistics and Information Authority reported that the town had 138,594 residents. Listed as the List of cities in Afghanistan, eighth largest settlement in the country, unofficial 2024 estimates set its population at around 114,883 people. Historically, the site of present-day Balkh was held in considerably high regard due to its religious and political significance in Ariana. A hub of Zoroastrianism and Buddhism, the ancient city was also known to the Ancient Iran, Persians as Zariaspa and to the Ancient Greece, Greeks as Bactra, giving its name to Bactria. As such, it was famously known as the capital of Bactria or Tokharistan. The Italian explorer and writer Marco Polo described Balkh as "a noble city and a great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Al-Jazira (caliphal province), Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled from AD 943 to 969.Ludwig W. Adamec (2009), ''Historical Dictionary of Islam'', p.137. Scarecrow Press. . His famous work, written in 977, is called ''Surat Al-Ard'' (; "The face of the Earth"). The date of his death, known from his writings, was after Anno Hegirae, AH 368/AD 978. Biography Details known of Ibn Hawqal's life are extrapolated from his book. He spent the last 30 years of his life traveling to remote parts of Asia and Africa, and writing about different things he saw during his journey. One journey brought him 20° south of the equator along the East African coast where he discovered large populations in regions the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek writers had deemed uninhabitable. Ṣūrat al-’Arḍ Ibn Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Al-Balkhi
''Fārsnāma'' (, "The Book of Fars") is a local Persian-language history and geography of Fars province, Persia, written between 1105 and 1116 during the Seljuk period. It is attributed to the otherwise unknown Ibn al-Balkhi (), a native of Fars who flourished in the 12th century. His ancestors were from Balkh in Khorasan, as his ''nisba'' suggests. The work was commissioned by Seljuk ruler Muhammad I Tapar (1105–1118). Roughly speaking, the first two-thirds of the book consists of information about the pre-Islamic Iranian rulers of Fars, as well as the Arab conquest of the province. The final third of the work consists of information on the province's geography. The critical edition published by Reynold A. Nicholson and Guy Le Strange Guy Le Strange (24 July 1854 – 24 December 1933) was a British Orientalist noted especially for his work in the field of the historical geography of the pre-modern Middle Eastern and Eastern Islamic lands, and his editing of Persian geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istakhri
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al-Istakhri () (also ''Estakhri'', , i.e. from the Iranian city of Istakhr, b. – d. 346 AH/AD 957) was a 10th-century travel author and Islamic geographer who wrote valuable accounts in Arabic of the many Muslim territories he visited during the Abbasid era of the Islamic Golden Age. There is no consensus regarding his origin. Some sources describe him as Persian, while others state he was Arab. IV:222b-223b. The ''Encyclopedia Iranica'' states: "Biographical data are very meager. From his ''nesbas'' (attributive names) he appears to have been a native of Eṣṭaḵr in Fārs, but it is not known whether he was Persian". VIII(6):646-647 (I have used the updated online version). Istakhri's account of windmills is the earliest known. Istakhri met the celebrated traveller-geographer Ibn Hawqal, while travelling, and Ibn Hawqal incorporated the work of Istakhri in his book ''Kitab al-Surat al-Ard''. Works Istakhri's two surviving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
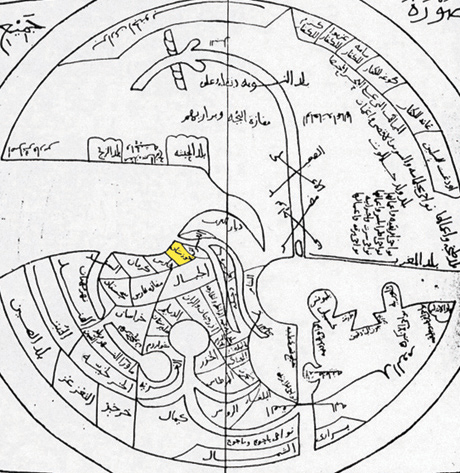
Circular Plan
Several ancient cities of Mesopotamia and Greater Persia, Persia are known to have had a circular plan. List of circular cities See also * Iranian architecture#City design References {{DEFAULTSORT:Circular cities Lists of cities City plans History of urban planning Architecture in Iran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th century by modern Western geographers and was originally applied to the Ottoman Empire, but today has varying definitions within different academic circles. The term ''Near East'' was used in conjunction with the ''Middle East'' and the ''Far East'' (China and beyond), together known as the "three Easts"; it was a separate term from the ''Middle East'' during earlier times and official British usage. As of 2024, both terms are used interchangeably by politicians and news reporters to refer to the same region. ''Near East'' and ''Middle East'' are both Eurocentrism, Eurocentric terms. According to the National Geographic Society, the terms ''Near East'' and ''Middle East'' denote the same territories and are "generally accepted as comprisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |