|
Millimeter Anisotropy EXperiment IMaging Array
The Millimeter Anisotropy eXperiment IMaging Array (MAXIMA) experiment was a balloon-borne experiment funded by the United States NSF, NASA, and Department of Energy, and operated by an international collaboration headed by the University of California, to measure the fluctuations of the cosmic microwave background. It consisted of two flights, one in August 1998 and one in June 1999. For each flight the balloon was started at the Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility in Palestine, Texas and flew to an altitude of 40,000 metres for over 8 hours. For the first flight it took data from about 0.3 percent of the sky of the northern region near the Draco constellation. For the second flight, known as MAXIMA-II, twice the area was observed, this time in the direction of Ursa Major. Initially planned together with the BOOMERanG experiment, it split off during the planning phase to take a less risky approach by reducing flying time as well as launching and landing on U.S. territory. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
University Of California
The University of California (UC) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university, research university system in the U.S. state of California. Headquartered in Oakland, California, Oakland, the system is composed of its ten campuses at University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, University of California, Davis, Davis, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, University of California, Merced, Merced, University of California, Riverside, Riverside, University of California, San Diego, San Diego, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, University of California, Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, and University of California, Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, along with numerous research centers and academic centers abroad. The system is the state's land-grant university. In 1900, UC was one of the founders of the Association of American Universities and since the 1970s seven of its campuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
CCD Camera
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. Overview In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Observational Cosmology
Observational cosmology is the study of the structure, the evolution and the origin of the universe through observation, using instruments such as telescopes and cosmic ray detectors. Early observations The science of physical cosmology as it is practiced today had its subject material defined in the years following the Shapley-Curtis debate when it was determined that the universe had a larger scale than the Milky Way galaxy. This was precipitated by observations that established the size and the dynamics of the cosmos that could be explained by Albert Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. In its infancy, cosmology was a speculative science based on a very limited number of observations and characterized by a dispute between steady state theorists and promoters of Big Bang cosmology. It was not until the 1990s and beyond that the astronomical observations would be able to eliminate competing theories and drive the science to the "Golden Age of Cosmology" which was heralde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Cosmic Microwave Background Experiments
This list is a compilation of experiments measuring the cosmic microwave background radiation, cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation anisotropies and polarization since the first detection of the CMB by Arno Allan Penzias, Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson, Wilson in 1964. There have been a variety of experiments to measure the cosmic microwave background radiation, CMB anisotropies and polarization since its first observation in 1964 by Arno Allan Penzias, Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson, Wilson. These include a mix of ground-, balloon- and space-based receivers. Some notable experiments in the list are Cosmic Background Explorer, COBE, which first detected the temperature anisotropies of the CMB, and showed that it had a black body spectrum; Degree Angular Scale Interferometer, DASI, which first detected the polarization signal from the CMB; Cosmic Background Imager, CBI, which made high-resolution observations and obtained the first E-mode polarization spectrum; WMAP; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Cosmic Inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the very early universe. Following the inflationary period, the universe continued to expand, but at a slower rate. The re-acceleration of this slowing expansion due to dark energy began after the universe was already over 7.7 billion years old (5.4 billion years ago). Inflation theory was developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s, with notable contributions by several theoretical physicists, including Alexei Starobinsky at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Alan Guth at Cornell University, and Andrei Linde at Lebedev Physical Institute. Starobinsky, Guth, and Linde won the 2014 Kavli Prize "for pioneering the theory of cosmic inflation". It was developed further in the early 1980s. It explains the origin of the large-scale structure of the cosmos. Quantum fluctuations in the microscopic inflationary region, magnified t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
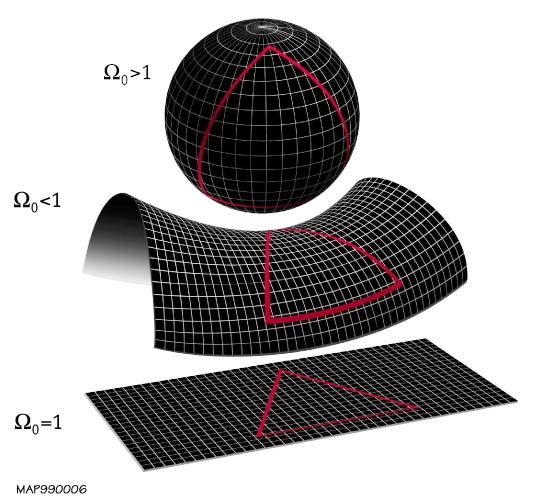 |
Shape Of The Universe
In physical cosmology, the shape of the universe refers to both its local and global geometry. Local geometry is defined primarily by its curvature, while the global geometry is characterised by its topology (which itself is constrained by curvature). General relativity explains how spatial curvature (local geometry) is constrained by gravity. The global topology of the universe cannot be deduced from measurements of curvature inferred from observations within the family of homogeneous general relativistic models alone, due to the existence of locally indistinguishable spaces with varying global topological characteristics. For example; a multiply connected space like a 3 torus has everywhere zero curvature but is finite in extent, whereas a flat simply connected space is infinite in extent (such as Euclidean space). Current observational evidence ( WMAP, BOOMERanG, and Planck for example) imply that the observable universe is spatially flat to within a 0.4% margin of error o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis (also known as primordial nucleosynthesis, and abbreviated as BBN) is a model for the production of light nuclei, deuterium, 3He, 4He, 7Li, between 0.01s and 200s in the lifetime of the universe. The model uses a combination of thermodynamic arguments and results from equations for the expansion of the universe to define a changing temperature and density, then analyzes the rates of nuclear reactions at these temperatures and densities to predict the nuclear abundance ratios. Refined models agree very well with observations with the exception of the abundance of 7Li. The model is one of the key concepts in standard cosmology. Elements heavier than lithium are thought to have been created later in the life of the Universe by stellar nucleosynthesis, through the formation, evolution and death of stars. Characteristics The Big Bang nucleosynthesis (BBN) model assumes a homogeneous plasma, at a temperature corresponding to 1 MeV, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Baryon
In particle physics, a baryon is a type of composite particle, composite subatomic particle that contains an odd number of valence quarks, conventionally three. proton, Protons and neutron, neutrons are examples of baryons; because baryons are composed of quarks, they belong to the hadron list of particles, family of particles. Baryons are also classified as fermions because they have half-integer Spin (physics), spin. The name "baryon", introduced by Abraham Pais, comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek word for "heavy" (βαρύς, ''barýs''), because, at the time of their naming, most known elementary particles had lower masses than the baryons. Each baryon has a corresponding antiparticle (antibaryon) where their corresponding antiquarks replace quarks. For example, a proton is made of two up quarks and one down quark; and its corresponding antiparticle, the antiproton, is made of two up antiquarks and one down antiquark. Baryons participate in the residual strong force, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Cosmic Background Radiation
Cosmic background radiation is electromagnetic radiation that fills all space. The origin of this radiation depends on the region of the spectrum that is observed. One component is the cosmic microwave background. This component is redshifted photons that have freely streamed from an epoch when the Universe became transparent for the first time to radiation. Its discovery and detailed observations of its properties are considered one of the major confirmations of the Big Bang. Background radiation is largely homogeneous and isotropic. A slight detectable anisotropy is present which correlates to galaxy filaments and voids. The discovery (by chance in 1965) of the cosmic background radiation suggests that the early universe was dominated by a radiation field, a field of extremely high temperature and pressure. There is background radiation observed across all wavelength regimes, peaking in microwave, but also notable in infrared and X-ray regimes. Fluctuations in cosmic backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Cosmic Microwave Background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope detects a faint background glow that is almost isotropic, uniform and is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other astronomical object, object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The accidental Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s. The CMB is landmark evidence of the Big Bang scientific theory, theory for the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang cosmological models, during the earliest periods, the universe was filled with an Opacity (optics), opaque fog of dense, hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
MAXIMA Map
Maxima may refer to: People * Maxima of Rome, early Christian saint and martyr * Maxima of Lisbon, early Christian saint and martyr * Queen Máxima of the Netherlands (born 1971) * Máxima Acuña, Peruvian activist * Maximilla, also known as Maxima, early Montanist figure Science and mathematics * Maxima and minima, the highest and lowest values of a function in calculus * Maxima (software), a free open-source computer algebra system * Millimeter Anisotropy eXperiment IMaging Array, a cosmic microwave background experiment Vehicles * Voith Maxima, a locomotive family built by Voith Turbo * Nissan Maxima, an automobile manufactured by Nissan Other uses * Maxima (music), a musical note value in mensural notation * ''Máxima'' (magazine), a Portuguese magazine * ''Maxima'', an Austrian magazine owned by BIPA, a health and beauty chain owned by REWE Group * Maxima (DC Comics), a character in the DC comics universe * Maxima (''The King of Fighters''), a character in ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris (Latinisation of names, Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude that fluctuates around 1.98, it is the brightest star in the constellation and is readily visible to the naked eye at night. The position of the star lies less than angular distance, 1° away from the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star. The stable position of the star in the northern celestial hemisphere, Northern Sky makes it useful for celestial navigation, navigation. As the closest Cepheid variable its distance is used as part of the cosmic distance ladder. The revised ''Hipparcos'' stellar parallax gives a distance to Polaris of about , while the successor mission Gaia (spacecraft), ''Gaia'' gives a distance of about . Although appearing to the naked eye as a single point of light, Polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |