|
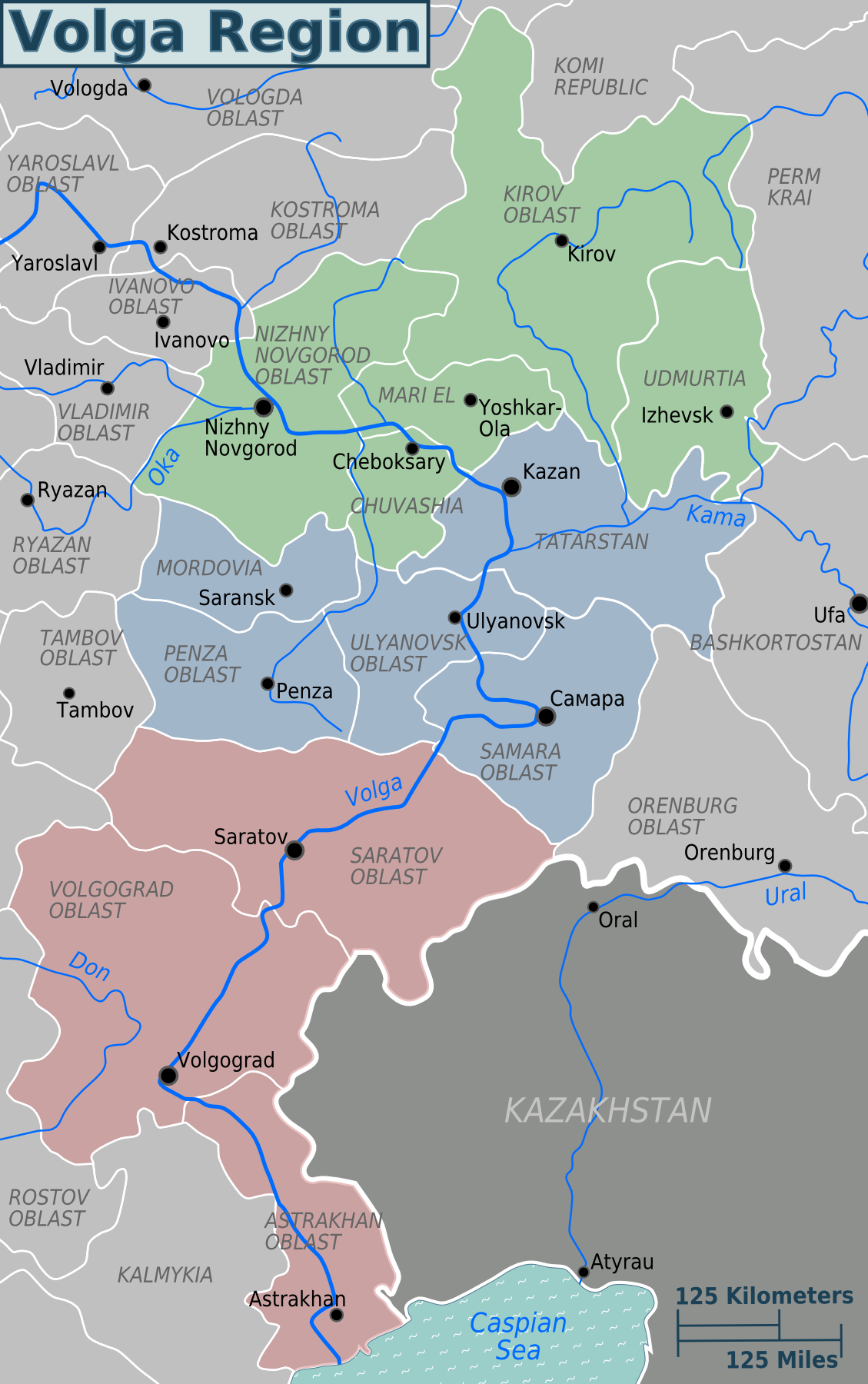
Middle Volga
The Volga region, known as the ( , ; rus, Поволжье, r=Povolžje, p=pɐˈvoɫʐje; ), is a historical region in Russia that encompasses the drainage basin of the Volga River, the longest river in Europe, in central and southern European Russia. The Volga region is culturally separated into three sections: * Upper Volga Region – from the Volga River's source in Tver Oblast to the mouth of the Oka River in Nizhny Novgorod; * Middle Volga Region – from the mouth of the Oka River to the mouth of the Kama River south of Kazan; * Lower Volga Region – from the mouth of the Kama River to the Volga Delta in the Caspian Sea, in Astrakhan Oblast. The geographic boundaries of the region are vague, and the term ''Volga region'' is used to refer primarily to the Middle and Lower sections, which are included in the Volga Federal District and Volga economic region. Geography The Volga Region is almost entirely within the East European Plain, with a notable distinction contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrachan Volgadelta
Astrakhan (, ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the Caspian Depression, from the Caspian Sea, with a population of 475,629 residents at the 2021 Census. At an elevation of below sea level, it is the lowest city in Russia. Astrakhan was formerly the capital of the Khanate of Astrakhan (a remnant of the Golden Horde) of the Astrakhan Tatars, and was located on the higher right bank of the Volga, from the present-day city. Situated on caravan and water routes, it developed from a village into a large trading centre, before being conquered by Timur in 1395 and captured by Ivan the Terrible in 1556 and in 1558 it was moved to its present site. The oldest economic and cultural center of the Lower Volga region, it is often called the southernmost outpost of Russia, and the Caspian capital. The city is a member of the Eurasian R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kostroma
Kostroma (, ) is a historic city and the administrative center of Kostroma Oblast, Russia. A part of the Golden Ring of Russian cities, it is located at the confluence of the rivers Volga and Kostroma. In the 2021 census, the population is 267,481. History Under the Rurikids The official founding year of the city is 1152 by Yury Dolgoruky.Official website of KostromaKostroma Today/ref> Since many scholars believe that early Eastern Slavs tribes arrived in modern-day Belarus, Ukraine and western Russia AD 400 to 600, Kostroma could be much older than previously thought. The city has the same name as the East Slavic goddess Kostroma. Like other towns of the Eastern Rus, Kostroma was sacked by the Mongols in 1238. It then constituted a small principality, under leadership of Prince Vasily of Kostroma, a younger brother of the famous Alexander Nevsky. Upon inheriting the grand ducal title in 1271, Vasily didn't leave the town for Vladimir, and his descendants ruled Kostroma f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl (; , ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl rivers. It is part of the Golden Ring, a group of historic cities northeast of Moscow that have played an important role in Russian history. The population of the city at the 2021 census was 577,279. History Reportedly the capital of an independent Principality of Yaroslavl from 1218, it was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Moscow in 1463. In the 17th century, it was Russia's second-largest city, and for a time (during the Polish occupation of Moscow in 1612), the country's de facto capital. Today, Yaroslavl is an important industrial center (petrochemical plant, tire manufacturing plant, diesel engines plant and many others). It developed at the confluence of major rivers, which were important for transportation and, later, for power. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rus' Khaganate
Rus' Khaganate (, ''Russkiy kaganat'', , ''Ruśkyj kahanat''), or Kaganate of Rus is a name applied by some modern historians to a hypothetical polity suggested to have existed during a poorly documented period in the history of Eastern Europe between 830 and the 890s. The fact that a few sparse contemporaneous sources appear to refer to the leader or leaders of Rus' people at this time with the word ''chacanus'', which might be derived from the title of ''khagan'' as used by groupings of Asian nomads, has led some scholars to suggest that his political organisation can be called a "k(h)aganate". Other scholars have disputed this, as it would have been unlikely for an organisation of Germanic immigrants from the north to adopt such a foreign title. Some historians have criticised the concept of a Rus' Khaganate, calling it a "historiographical phantom", and said that the society of 9th-century Rusʹ cannot be characterised as a state. Still other scholars identify these early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belaya River (Kama)
The Belaya ( ) is a river in Bashkortostan, Russia. Its source lies in the south-western Ural Mountains. It is long, and its drainage basin covers .«Река БЕЛАЯ» Russian State Water Registry Settlements along the Belaya include Beloretsk, , Ufa (at the with the river Ufa), and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaya Kokshaga River
The Malaya Kokshaga (, ''Izi Kakšan''; , literally Little Kokshaga) is a river in Mari El, a left tributary of the Volga. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . It originates in the northern part of the republic, passes through its capital, , and flows to the , |
Tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they flow, drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean, another river, or into an endorheic basin. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of . The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of . A confluence, where two or more bodies of water meet, usually refers to the joining of tributaries. The opposite to a tributary is a distributary, a river or stream that branches off from and flows away from the main stream. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.Ural Mountains , Encyclopædia Britannica on-line The mountain range forms part of the Boundaries between the continents of Earth, conventional boundary between the continents of Europe and Asia, marking the separation between European Russia and Siberia. Vaygach Island and the islands of Novaya Zemlya form a further continuation of the chain to the north into the Arctic Ocean. The average altitudes of the Urals are around , the highest point being Mount Narodnaya, which reaches a height of . The mountains lie within the Ural (region), Ural geographical region and significantl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Subjects Of Russia
The federal subjects of Russia, also referred to as the subjects of the Russian Federation () or simply as the subjects of the federation (), are the administrative division, constituent entities of Russia, its top-level political divisions. According to the Constitution of Russia, the federation consists of republics of Russia, republics, krais of Russia, krais, oblasts of Russia, oblasts, federal cities of Russia, cities of federal importance, an Jewish Autonomous Oblast, autonomous oblast, and autonomous okrugs of Russia, autonomous okrugs, all of which are equal subjects of the federation. Every federal subject has its own governor (Russia), head, a regional parliaments of Russia, parliament, and a constitutional court. Each subject has its own constitution or charter and legislation, although the authority of these organs differ. Subjects have equal rights in relations with federal government bodies. The subjects have equal representation – two delegates each – in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idel-Ural
Idel-Ural (, ), literally Volga-Ural, is a historical region in Eastern Europe, in what is today Russia. The name literally means ''Volga-Urals'' in the Tatar language. The frequently used Russian variant is ''Volgo-Uralye'' (). The term Idel-Ural is often used to designate 6 republics of Russia of this region: Bashkortostan, Chuvashia, Mari El, Mordovia, Tatarstan and Udmurtia, especially in Tatar-language literature or in the context of minority languages. Idel-Ural is at the center of the Volga Federal District (Поволжье, ''Povolzhye''). The major religions in the region are Islam and Orthodox Christianity. History Before being conquered by the Tsardom of Russia in the 16th century, the region was dominated by native Uralic tribes and a succession of Turkic-led empires, such as Volga Bulgaria, the Khazars, the Golden Horde and the Khanate of Kazan. At the time of Peter the Great's death, in the early 18th century, the region had been made up of roughly 1 million p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland. Definitions Upland and lowland are portions of a plain that are conditionally categorized by their elevation above the sea level. Lowlands are usually no higher than , while uplands are somewhere around to . On unusual occasions, certain lowlands such as the Caspian Depression lie below sea level. Uplands areas tend to spike into valleys and mountains, forming mountain ranges while lowland areas tend to be uniformly flat, although both can vary such as the Mongolian Plateau. Upland habitats are cold, clear and rocky whose rivers are fast-flowing in mountainous areas; lowland habitats are warm with slow-flowing rivers found in relatively flat lowland areas, with water that is frequently colored by sediment and organic matter. These classifications overlap with the geological definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |