|
Microprobe
A microprobe is an instrument that applies a stable and well-focused beam of charged particles (electrons or ions) to a sample. Types When the primary beam consists of accelerated electrons, the probe is termed an electron microprobe, when the primary beam consists of accelerated ions, the term ion microprobe is used. The term microprobe may also be applied to optical analytical techniques, when the instrument is set up to analyse micro samples or micro areas of larger specimens. Such techniques include micro Raman spectroscopy, micro infrared spectroscopy and micro LIBS. All of these techniques involve modified optical microscopes to locate the area to be analysed, direct the probe beam and collect the analytical signal. A laser microprobe is a mass spectrometer that uses ionization by a pulsed laser and subsequent mass analysis of the generated ions. Uses Scientists use this beam of charged particles to determine the elemental composition of solid materials (minerals, glas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Microprobe
An electron microprobe (EMP), also known as an electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA) or electron micro probe analyzer (EMPA), is an analytical tool used to non-destructively determine the chemical composition of small volumes of solid materials. It works similarly to a scanning electron microscope: the sample is bombarded with an electron beam, emitting x-rays at wavelengths characteristic to the elements being analyzed. This enables the abundances of elements present within small sample volumes (typically 10-30 cubic micrometers or less) to be determined,Wittry, David B. (1958). "Electron Probe Microanalyzer"US Patent No 2916621 Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office when a conventional accelerating voltage of 15-20 kV is used. The concentrations of elements from lithium to plutonium may be measured at levels as low as 100 parts per million (ppm), material dependent, although with care, levels below 10 ppm are possible. The ability to quantify lithium by EPMA became a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Microscopy
A microprobe is an instrument that applies a stable and well-focused beam of charged particles (electrons or ions) to a sample. Types When the primary beam consists of accelerated electrons, the probe is termed an electron microprobe, when the primary beam consists of accelerated ions, the term ion microprobe is used. The term microprobe may also be applied to optical analytical techniques, when the instrument is set up to analyse micro samples or micro areas of larger specimens. Such techniques include micro Raman spectroscopy, micro infrared spectroscopy and micro LIBS. All of these techniques involve modified optical microscopes to locate the area to be analysed, direct the probe beam and collect the analytical signal. A laser microprobe is a mass spectrometer that uses ionization by a pulsed laser and subsequent mass analysis of the generated ions. Uses Scientists use this beam of charged particles to determine the elemental composition of solid materials (minerals, glasses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Microprobe Mass Spectrometer
A laser microprobe mass spectrometer (LMMS), also laser microprobe mass analyzer (LAMMA), laser ionization mass spectrometer (LIMS), or laser ionization mass analyzer (LIMA) is a mass spectrometer that uses a focused laser for microanalysis. It employs local ionization by a pulsed laser and subsequent mass analysis of the generated ions. Methods In laser microprobe mass analysis, a highly focused laser beam is pulsed on a micro sample usually with a volume of approximately 1 microliter. The resulting ions generated by this laser are then analyzed with time-of-flight mass spectrometry to give composition, concentration, and in the case of organic molecules structural information. Unlike other methods of microprobe analysis which involve ions or electrons, the LMMS microproble fires an ultraviolet pulse in order to create ions. Advantages LMMS is relatively simple to operate compared to other methods. Furthermore, its strengths include its ability to analyze biological materials to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherford Backscattering
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample. Geiger–Marsden experiment Rutherford backscattering spectrometry is named after Lord Rutherford, a physicist sometimes referred to as the father of nuclear physics. Rutherford supervised a series of experiments carried out by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden between 1909 and 1914 studying the scattering of alpha particles through metal foils. While attempting to eliminate "stray particles" they believed to be caused by an imperfection in their alpha source, Rutherford suggested that Marsden attempt to measure backscattering from a gold foil sample. According to the then-dominant plum-pudding model of the atom, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focused Ion Beam
Focused ion beam, also known as FIB, is a technique used particularly in the semiconductor industry, materials science and increasingly in the biological field for site-specific analysis, deposition, and ablation of materials. A FIB setup is a scientific instrument that resembles a scanning electron microscope (SEM). However, while the SEM uses a focused beam of electrons to image the sample in the chamber, a FIB setup uses a focused beam of ions instead. FIB can also be incorporated in a system with both electron and ion beam columns, allowing the same feature to be investigated using either of the beams. FIB should not be confused with using a beam of focused ions for direct write lithography (such as in proton beam writing). These are generally quite different systems where the material is modified by other mechanisms. Ion beam source Most widespread instruments are using liquid metal ion sources (LMIS), especially gallium ion sources. Ion sources based on elemental gold an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Press
The CRC Press, LLC is an American publishing group that specializes in producing technical books. Many of their books relate to engineering, science and mathematics. Their scope also includes books on business, forensics and information technology. CRC Press is now a division of Taylor & Francis, itself a subsidiary of Informa. History The CRC Press was founded as the Chemical Rubber Company (CRC) in 1903 by brothers Arthur, Leo and Emanuel Friedman in Cleveland, Ohio, based on an earlier enterprise by Arthur, who had begun selling rubber laboratory aprons in 1900. The company gradually expanded to include sales of laboratory equipment to chemists. In 1913 the CRC offered a short (116-page) manual called the ''Rubber Handbook'' as an incentive for any purchase of a dozen aprons. Since then the ''Rubber Handbook'' has evolved into the CRC's flagship book, the ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics''. In 1964, Chemical Rubber decided to focus on its publishing ventures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoelectromechanical Systems
Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) are a class of devices integrating electrical and mechanical functionality on the nanoscale. NEMS form the next logical miniaturization step from so-called microelectromechanical systems, or MEMS devices. NEMS typically integrate transistor-like nanoelectronics with mechanical actuators, pumps, or motors, and may thereby form physical, biological, and chemical sensors. The name derives from typical device dimensions in the nanometer range, leading to low mass, high mechanical resonance frequencies, potentially large quantum mechanical effects such as zero point motion, and a high surface-to-volume ratio useful for surface-based sensing mechanisms. Applications include accelerometers and sensors to detect chemical substances in the air. History Background As noted by Richard Feynman in his famous talk in 1959, " There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom," there are many potential applications of machines at smaller and smaller sizes; by building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microelectromechanical Systems
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), also written as micro-electro-mechanical systems (or microelectronic and microelectromechanical systems) and the related micromechatronics and microsystems constitute the technology of microscopic devices, particularly those with moving parts. They merge at the nanoscale into nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) and nanotechnology. MEMS are also referred to as micromachines in Japan and microsystem technology (MST) in Europe. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometers in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre (i.e., 0.02 to 1.0 mm), although components arranged in arrays (e.g., digital micromirror devices) can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data (an integrated circuit chip such as microprocessor) and several components that interact with the surroundings (such as microsensors). Because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STIM
STIM, ''Svenska Tonsättares Internationella Musikbyrå'' (Swedish Performing Rights Society), is a Swedish collecting society for songwriters, composers and music publisher. Its role is to act as an agent for its members in order to collect license fees whenever their musical works are performed in public, broadcast or transmitted, and to pay out performing royalties. STIM was founded in 1923, a few years before Sveriges Radio Sveriges Radio AB (, "Sweden's Radio") is Sweden's national publicly funded radio broadcaster. Sveriges Radio is a public limited company, owned by an independent foundation, previously funded through a licensing fee, the level of which is d ... began regular broadcasting. Initially an organization for collecting concert fees for composers of classical music, it has since expanded to all genres of music, and license fees from broadcasters have become an important source of income. The organization now has more than 71,000 members. In 2003–2007 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
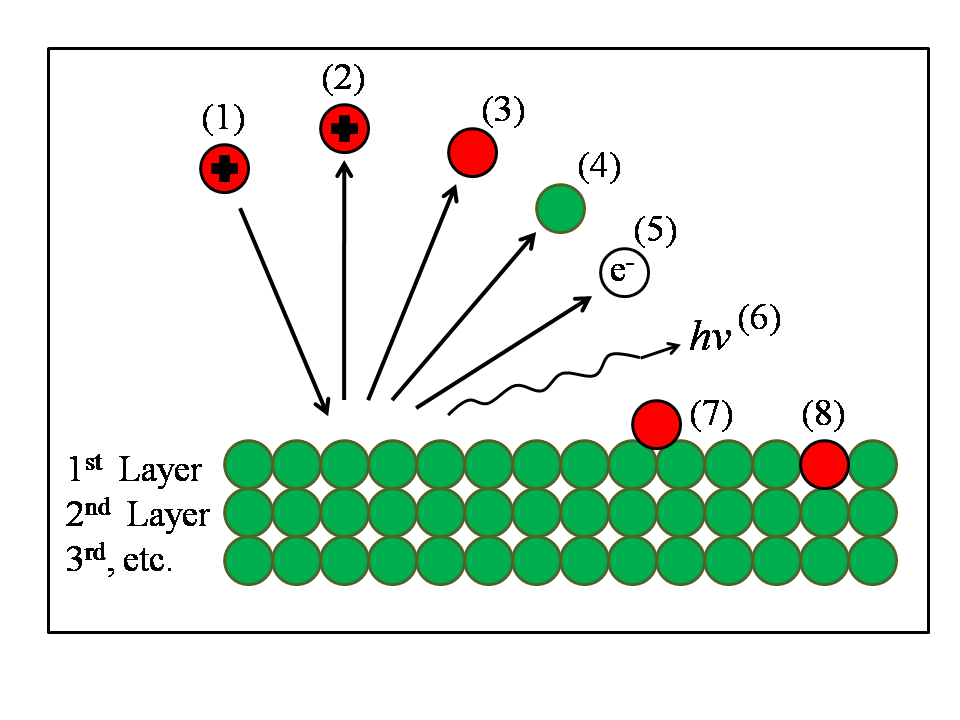
Ion Beam Analysis
Ion beam analysis ("IBA") is an important family of modern analytical techniques involving the use of MeV ion beams to probe the composition and obtain elemental depth profiles in the near-surface layer of solids. All IBA methods are highly sensitive and allow the detection of elements in the sub-monolayer range. The depth resolution is typically in the range of a few nanometers to a few ten nanometers. Atomic depth resolution can be achieved, but requires special equipment. The analyzed depth ranges from a few ten nanometers to a few ten micrometers. IBA methods are always quantitative with an accuracy of a few percent. Channeling allows to determine the depth profile of damage in single crystals. *RBS: Rutherford backscattering is sensitive to heavy elements in a light matrix *EBS: ''Elastic (non-Rutherford) backscattering spectrometry'' can be sensitive even to light elements in a heavy matrix. The term ''EBS'' is used when the incident particle is going so fast that it exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIXE
Particle-induced X-ray emission or proton-induced X-ray emission (PIXE) is a technique used for determining the elemental composition of a material or a sample. When a material is exposed to an ion beam, atomic interactions occur that give off EM radiation of wavelengths in the x-ray part of the electromagnetic spectrum specific to an element. PIXE is a powerful yet non-destructive elemental analysis technique now used routinely by geologists, archaeologists, art conservators and others to help answer questions of provenance, dating and authenticity. The technique was first proposed in 1970 by Sven Johansson of Lund University, Sweden, and developed over the next few years with his colleagues Roland Akselsson and Thomas B Johansson. Recent extensions of PIXE using tightly focused beams (down to 1 μm) gives the additional capability of microscopic analysis. This technique, called microPIXE, can be used to determine the distribution of trace elements in a wide range of samples. A r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |