|
Microfilm Reader
A microfilm reader is a device that uses a lens and source of light to magnify miniaturized text and accompanying images that have been printed on a roll of 16 mm film (100 cm or 215 cm in length) or 135 film, 35 mm film (100 cm in length), which is also known as Microform, microfilm or "roll film." Throughout the 20th century, many commercial organizations and government agencies used microfilm as the main medium to store large amounts of text from books, periodicals, and records until the advent of modern computers, which offered instant access to content and additional storage and cost-savings advantages over microfilm. The need and production of complementary microfilm readers therefore fell with the need for microfilm, but they are still used today to view stored content on microfilm that has yet to be converted into a digital format. History 19th century The development of the microfilm reader began when John Benjamin Dancer produced one of the first recorded microphotogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16 Mm Film
16 mm film is a historically popular and economical Film gauge, gauge of Photographic film, film. 16 mm refers to the width of the film (about inch); other common film gauges include 8 mm film, 8 mm and 35mm movie film, 35 mm. It is generally used for non-theatrical (e.g., industrial, educational, television) film-making, or for low-budget motion pictures. It also existed as a popular amateur or home movie-making format for several decades, alongside 8 mm film and later Super 8 film. Kodak, Eastman Kodak released the first 16 mm "outfit" in 1923, consisting of a Ciné-Kodak camera, Kodascope projector, tripod, screen and splicer, for US$335 (). RCA Records, RCA-Victor introduced a 16 mm sound movie projector in 1932, and developed an optical sound-on-film 16 mm camera, released in 1935. History Eastman Kodak introduced 16 mm film in 1923, as a less expensive alternative to 35mm movie film, 35 mm Film formats, film for amateurs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
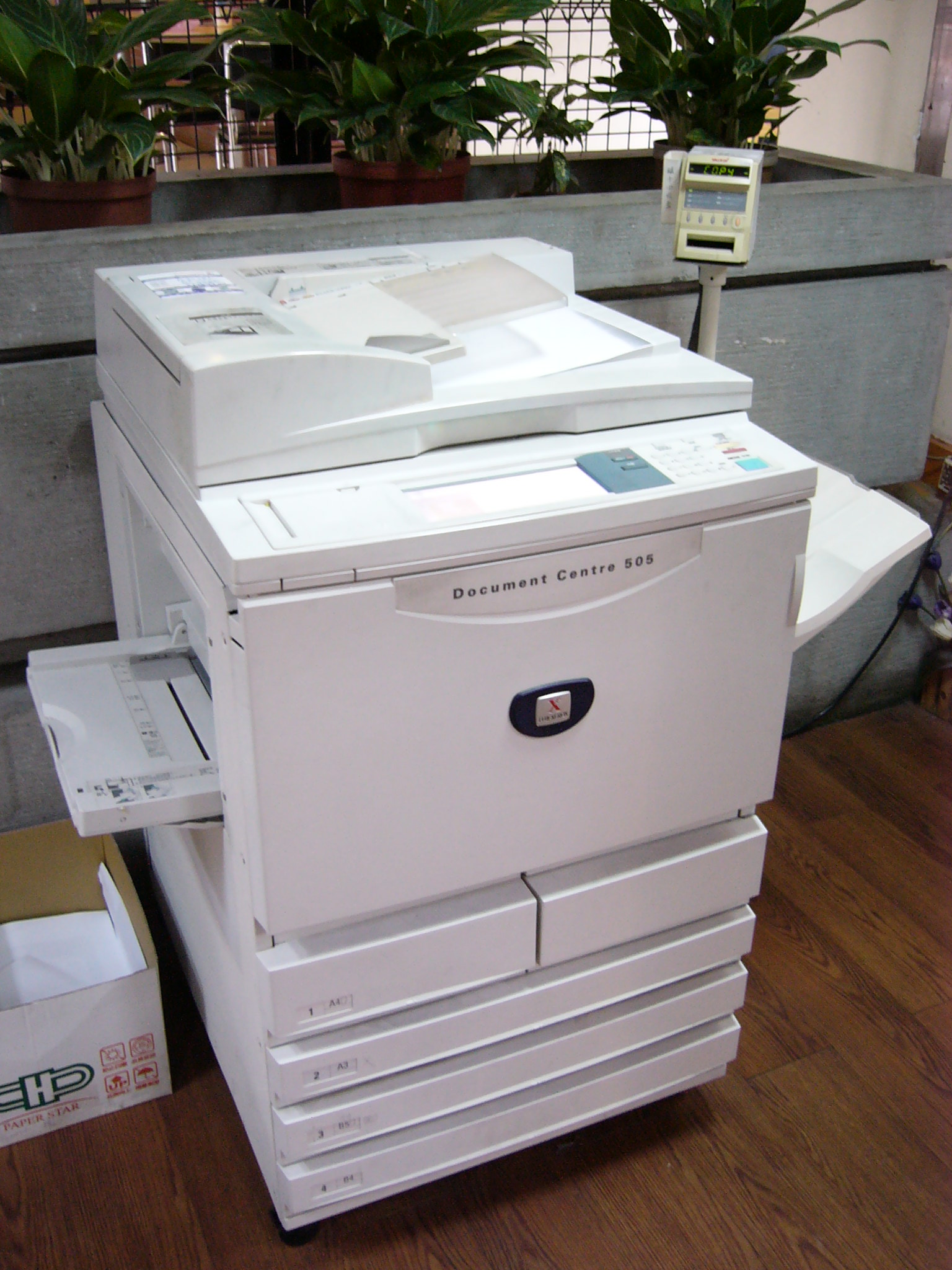
Photocopier
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called '' xerography'', a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles (a powder) onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying. Commercial xerographic office photocopying gradually replaced copies made by verifax, photostat, carbon paper, mimeograph machines, and other duplicating machines. Photocopying is widely used in the business, education, and government sectors. While there have been predictions that photocopiers will eventually become obsol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by the U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President Harry S. Truman signed the McMahon/Atomic Energy Act on August 1, 1946, transferring the control of atomic energy from military to civilian hands, effective on January 1, 1947. This shift gave the members of the AEC complete control of the plants, laboratories, equipment, and personnel assembled during the war to produce the atomic bomb. An increasing number of critics during the 1960s charged that the AEC's regulations were insufficiently rigorous in several important areas, including radiation protection standards, nuclear reactor safety, plant siting, and environmental protection. By 1974, the AEC's regulatory programs had come under such strong attack that the U.S. Congress decided to abolish the AEC. The AEC was abolished by the Energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
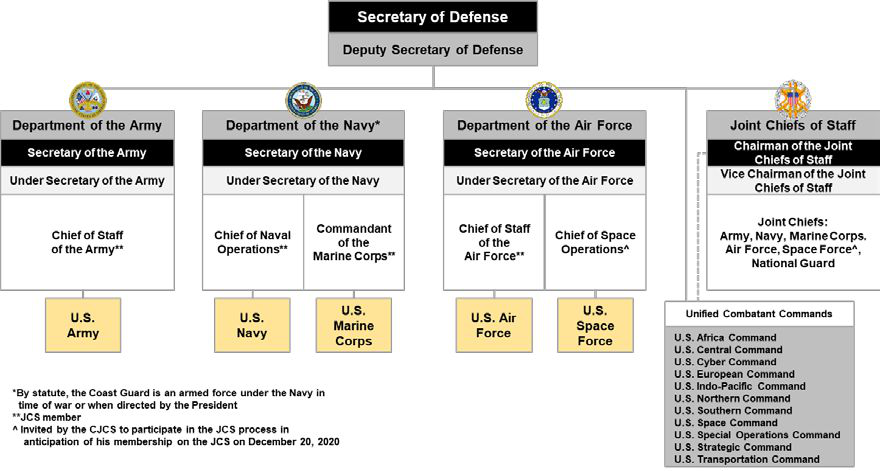
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcard
A microform is a scaled-down reproduction of a document, typically either photographic film or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the original document size. For special purposes, greater optical reductions may be used. Three formats are common: microfilm (reels), microfiche (flat sheets), and aperture cards. Microcards, also known as "micro-opaques", a format no longer produced, were similar to microfiche, but printed on cardboard rather than photographic film. Equipment is available that accepts a data stream from a computer; this exposes film to produce images as if the stream had been sent to a line printer and the listing had been microfilmed. The process is known as computer output microfilm or computer output microfiche (COM). History Using the daguerreotype process, John Benjamin Dancer was one of the first to produce microphotographs, in 1839. He achieved a reducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fremont Rider
Arthur Fremont Rider (May 25, 1885 – October 26, 1962) was an American writer, poet, editor, inventor, genealogist, and librarian. He studied under Melvil Dewey, of whom he wrote a biography for the American Library Association. Throughout his life he wrote in several genres including plays, poetry, short stories, non-fiction and an auto-biography which he wrote in the third-person. In the early 20th century he became a noted editor and publisher, working on such publications as ''Publishers Weekly'' and the ''Library Journal.'' In 1933 he became a librarian at Wesleyan University, eventually becoming director of the university's Olin Memorial Library and afterwards founding the Godfrey Memorial Library of genealogy and history in 1947. For his contributions to library science and as a librarian at Wesleyan University he was named one of the 100 Most Important Leaders of Library Science and the Library Profession in the twentieth century by the official publication of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
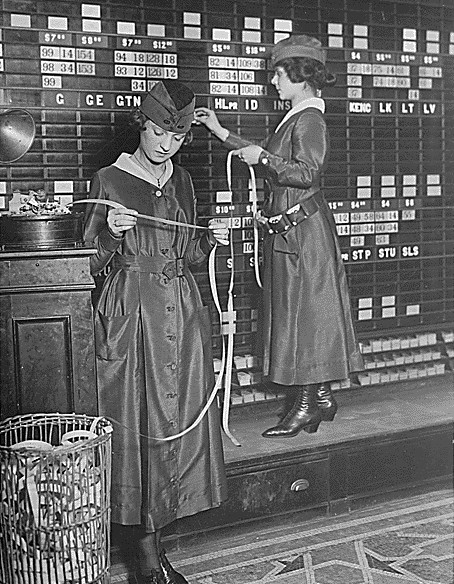
Ticker Tape
Ticker tape was the earliest electrical dedicated financial communications medium, transmitting stock price information over electrical telegraph, telegraph lines, in use from around 1870 to 1970. It consisted of a paper strip that ran through a machine called a stock ticker, which printed abbreviated company names as alphabetic symbols followed by numeric stock transaction price and volume information. The term "ticker" came from the sound made by the machine as it printed. The ticker tape revolutionized financial markets, as it relayed information from trading floors continuously and simultaneously across geographical distances. Paper ticker tape became obsolete in the 1960s, as television and computers were increasingly used to transmit financial information. The concept of the stock ticker lives on, however, in the scrolling electronic tickers seen on brokerage walls and on news and financial television channels. Ticker tape stock price telegraphs were invented in 1867 by E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition (literary Journal)
''transition'' was an experimental literary journal that featured surrealist, expressionist, and Dada art and artists. It was founded in 1927 by Maria McDonald and her husband Eugene Jolas and published in Paris, France. They were later assisted by editors Elliot Paul (April 1927 – March 1928), Robert Sage (October 1927 – Fall 1928), and James Johnson Sweeney (June 1936 – May 1938). After the Second World War, the publishing license of ''transition'' was transferred from the Jolases and McDonald to Georges Duthuit who capitalized the title to ''Transition'' (1948–1950) and changed its focus. Origins The literary journal was intended as an outlet for experimental writing and featured modernist, surrealist and other linguistically innovative writing and also contributions by visual artists, critics, and political activists. It ran until spring 1938. A total of 27 issues were produced. It was distributed primarily through Shakespeare and Company, the Paris bookstore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Brown (writer, Poet, Publisher)
Robert Carlton Brown II (June 14, 1886 – August 7, 1959) was an American writer and publisher in many forms from comic squibs to magazine fiction to advertising to avant-garde poetry to business news to cookbooks to political tracts to novelized memoirs to parodies and much more. Life and work In the first two decades of the twentieth century, Brown was a bestselling fiction writer and found great commercial success selling his stories to magazines, as well as novelizations of serialized magazines stories, including ''What Happened to Mary'' (1913) and ''The Remarkable Adventures of Christopher Poe'' (1913). He also published bohemian poetry when he and his second wife, Rose, became central figures in the Greenwich Village bohemian arts and culture scene. As part of his work with The Masses, Brown also became a fund-raising impresario staging balls and costume parties at Webster Hall. With the start of World War I, the Browns were forced into exile, first to Mexico for a y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |