|
Michael Fasham
Michael John Robert Fasham, FRS (29 May 1942 – 7 June 2008) was a British oceanographer and ecosystem modeller. He is best known for his pioneering work in the development of open ocean plankton ecosystem models. Early life and education Fasham was born in 1942 in Edgware in north London, and attended Kilburn Grammar School in Queen's Park. At the University of Birmingham he initially studied physics, obtaining his first degree in 1963, but moved to marine geology for his PhD, which was awarded in 1968. Career After his PhD, he joined the National Institute of Oceanography (NIO) in Wormley, and remained with this organisation and its successor institutes throughout his career. Here, together with NIO colleagues, Fasham developed one of the first shipborne computer systems. He also applied his experience in statistics to the biogeography of plankton, a field that was then largely descriptive. This led to a series of papers on plankton distribution, as well as the develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgware
Edgware () is a suburban town in northwest London. It was an ancient parish in the county of Middlesex east of the ancient Watling Street in what is now the London Borough of Barnet but it is now informally considered to cover a wider area, including parts of the boroughs of London Borough of Harrow, Harrow and London Borough of Brent, Brent. The district is located north-northwest of Charing Cross and has a generally suburban character. The urban-rural fringe includes some elevated woodland on a high gravel and sand ridge along the Hertfordshire border with Greater London. Edgware is principally a shopping and residential area, identified in the London Plan as one of the capital's 35 major centres, and one of the northern termini of the Northern line. It has a Edgware bus garage, bus garage, a shopping centre called the Broadwalk Centre, List of libraries in Barnet, a library, a community hospital, Edgware Community Hospital, and two streams, Silk Stream, Edgware Brook and Dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wormley, Surrey
Wormley is a village in the civil parish of Witley and Milford, in the Waverley district, in Surrey, England, around Witley station, off the A283 Petworth Road about SSW of Godalming. History Expansion from archetypal hamlet Wormley developed primarily as a result of the construction in the 19th century of Witley station, on the Portsmouth Direct line. King Edward's School, Witley once had its own station platform. Former businesses Cooper & Sons Ltd owned the Combelane walking stick factory; this was replaced by houses with small gardens and a light industrial estate. The Institute of Oceanographic Sciences Deacon Laboratory was here from 1952 to 1995, housed in the former Admiralty Signals Establishment building on Brook Road. The only public house, the ''Wood Pigeon'', closed in 2007. Architecture and gardens King Edward's School is a Grade II listed building, the school war memorial is also Grade II listed. Gertrude Jekyll designed the gardens at Tigbourne Court and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
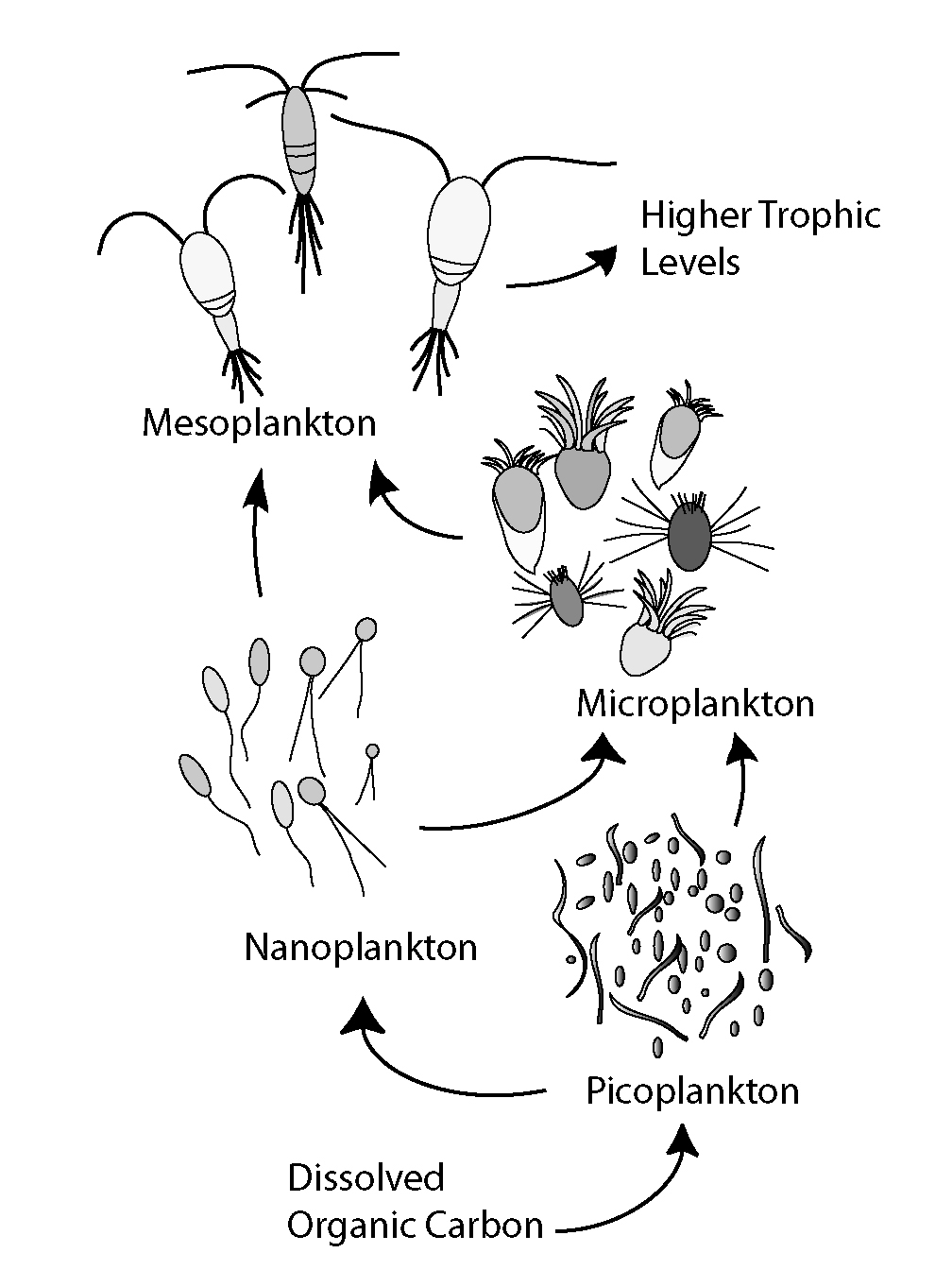
Microbial Loop
The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by phytoplankton-zooplankton-nekton. In soil systems, the microbial loop refers to soil carbon. The term microbial loop was coined by Farooq Azam, Tom Fenchel et al. in 1983 to include the role played by bacteria in the carbon and nutrient cycles of the marine environment. In general, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is introduced into the ocean environment from bacterial lysis, the leakage or exudation of fixed carbon from phytoplankton (e.g., mucilaginous exopolymer from diatoms), sudden cell senescence, sloppy feeding by zooplankton, the excretion of waste products by aquatic animals, or the breakdown or dissolution of organic particles from terrestrial plants and soils. Bacteria in the microbial loop decompose this particulate detritus t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton (cyanobacteria and microalgae), which are the plant-like component of the plankton community (the " phyto-" prefix comes from , although taxonomically ''not'' plants). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding), often generating biological energy and macromolecules through chlorophyllic carbon fixation using sunlightin other words, zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food, while phytoplankton can. As a result, zooplankton must acquire nutrients by feeding on other organisms such as phytoplankton, which are generally smaller t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal Environmental factor, factors. External factors—including climate—control the ecosystem's structure, but are not influenced by it. By contrast, internal factors control and are controlled by ecosystem processes; these include decomposition, the types of species present, root competition, shading, disturbance, and succession. While external factors generally determine which Resource (biology), resource inputs an ecosystem has, their availability within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors. Ecosystems are wikt:dynamic, dynamic, subject to periodic disturbances and always in the process of recovering from past disturbances. The tendency of an ecosystem to remain clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as earthworms and woodlice), or decomposer (such as fungi or bacteria). It is not the same as a food web. A food chain depicts relations between species based on what they consume for energy in trophic levels, and they are most commonly quantified in length: the number of links between a trophic consumer and the base of the chain. Food chain studies play an important role in many biological studies. Food chain stability is very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction or immense decreases of survival of a species. Many food chains and food webs contain a keystone species, a species that has a large impact on the surrounding environment and that can directly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeochemical Cycle
A biogeochemical cycle, or more generally a cycle of matter, is the movement and transformation of chemical elements and compounds between living organisms, the atmosphere, and the Earth's crust. Major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. In each cycle, the chemical element or molecule is transformed and cycled by living organisms and through various geological forms and reservoirs, including the atmosphere, the soil and the oceans. It can be thought of as the pathway by which a chemical substance Wiktionary:cycle, cycles (is turned over or moves through) the Biotic components, biotic compartment and the Abiotic, abiotic compartments of Earth. The biotic compartment is the biosphere and the abiotic compartments are the atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere. For example, in the carbon cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis, which converts it into organic compounds that are used by organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Flow (ecology)
Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. All living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. Each of the levels within the food chain is a trophic level. In order to more efficiently show the quantity of organisms at each trophic level, these food chains are then organized into trophic pyramids. The arrows in the food chain show that the energy flow is unidirectional, with the head of an arrow indicating the direction of energy flow; energy is lost as heat at each step along the way. The unidirectional flow of energy and the successive loss of energy as it travels up the food web are patterns in energy flow that are governed by thermodynamics, which is the theory of energy exchange between systems. Trophic dynamics relates to thermodynamics because it deals with the transfer and transformation of energy (originating externally from the sun via s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasham Ducklow McKelvie 1990
Fasham () is a city in, and the capital of, Rudbar-e Qasran District Rudbar-e Qasran District () is in Shemiranat County, Tehran province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, a ... of Shemiranat County, Tehran province, Tehran province, Iran. Demographics Population At the time of the 2006 National Census, the city's population was 6,895 in 2,019 households. The following census in 2011 counted 7,994 people in 2,509 households. The 2016 census measured the population of the city as 2,294 households. See also Notes References Cities in Tehran province Populated places in Shemiranat County {{Shemiranat-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |