|
Mengisa Language
Leti, or Mangisa, is a Bantu language of Cameroon, spoken by the Mengisa people. Most Mengisa have switched to the Eton language, though a number of them continue to use Leti as a secret ritual language. A smaller number speak Leti as their mother tongue. Leti is quite close to Tuki and may be a dialect.Hammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices It is also closely related to Eton. Mengisa is spoken in the northern part of Sa'a commune (in Lekié Lekié is a department of Centre Region in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 2,989 km and had a total population of 354,864. The capital of the department lies at Monatélé. It is named after the Lekié River. Subdivisions The ... department, Central Region). References Ritual languages Mbam languages Languages of Cameroon {{mbam-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea, and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka people (Cameroon and Gabon), Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese discoveries, Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area ''Rio dos Camarões'' (''Shrimp River''), which became ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Language
A second language (L2) is a language spoken in addition to one's first language (L1). A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a foreign language. A speaker's dominant language, which is the language a speaker uses most or is most comfortable with, is not necessarily the speaker's first language. For example, the Canadian census defines first language for its purposes as "What is the language that this person first learned at home in childhood and still understands?", recognizing that for some, the earliest language may be lost, a process known as language attrition. This can happen when young children start school or move to a new language environment. Second-language acquisition The distinction between acquiring and learning was made by Stephen Krashen as part of his monitor theory. According to Krashen, the ''acquisition'' of a language is a natural process; whereas ''learning'' a language is a conscious one. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic–Congo Languages
The Atlantic–Congo languages make up the largest demonstrated family of languages in Africa. They have characteristic noun class systems and form the core of the Niger–Congo family hypothesis. They comprise all of Niger–Congo apart from Mande, Dogon, Ijoid, Siamou, Kru, the Katla and Rashad languages (previously classified as Kordofanian), and perhaps some or all of the Ubangian languages. Hans Gunther Mukanovsky's "Western Nigritic" corresponded roughly to modern Atlantic–Congo. In the infobox, the languages which appear to be the most divergent are placed at the top. The Atlantic branch is defined in the narrow sense (as Senegambian), while the former Atlantic branches Mel and the isolates Sua, Gola and Limba are split out as primary branches; they are mentioned next to each other because there is no published evidence to move them; Volta–Congo is intact apart from Senufo and Kru. ''Glottolog'', based primarily on Güldemann (2018), has a more limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
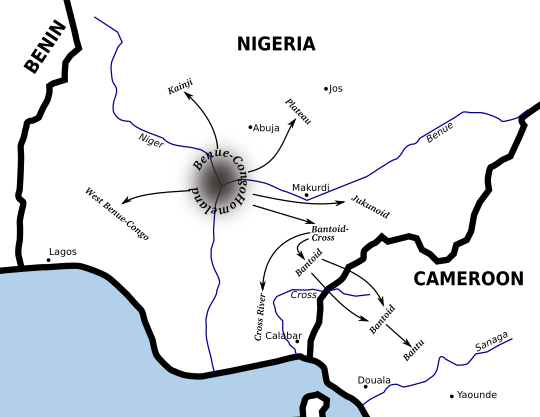
Benue–Congo Languages
Benue–Congo (sometimes called East Benue–Congo) is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. Subdivisions Central Nigerian (or Platoid) contains the Plateau languages, Plateau, Jukunoid languages, Jukunoid and Kainji languages, Kainji families, and Bantoid–Cross combines the Bantoid languages, Bantoid and Cross River languages, Cross River groups. Bantoid is only a collective term for every subfamily of Bantoid–Cross except Cross River, and this is no longer seen as forming a valid branch, however one of the subfamilies, Southern Bantoid, is still considered valid. It is Southern Bantoid which contains the Bantu languages, which are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa. This makes Benue–Congo one of the largest subdivisions of the Niger–Congo language family, both in number of languages, of which ''Ethnologue'' counts 976 (2017), and in speakers, numbering perhaps 350 million. Benue–Congo also includes a few minor Languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Bantoid Languages
Southern Bantoid (or South Bantoid) is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon (though the affiliation of some branches is uncertain). Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by ''Ethnologue'', though many of these are mutually intelligible. History Southern Bantoid was first introduced by Williamson in a proposal that divided Bantoid into North and South branches. The unity of the North Bantoid group was subsequently called into question, and Bantoid itself may be polyphyletic A polyphyletic group is an assemblage that includes organisms with mixed evolutionary origin but does not include their most recent common ancestor. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as Homoplasy, homoplasies ..., but the work did establish Southern Banto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages, depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" versus "dialect"."Guthrie (1967–71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mbam Languages
The Mbam languages are a group of Bantu languages The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, South ... spoken in Cameroon. *Sanaga (A60): Tuki (Bacenga), Leti/ Mengisa, Mbwasa *West Mbam (A40): Bati (A60), Nomaande (Mandi)– Tunen (Aling'a, Banen)– Tuotomb– Yambeta, Nyokon *Yambasa (A60): Nubaca, Mbule, Nugunu, Elip– Mmaala– Yangben References Southern Bantoid languages {{SBantoid-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ki Language
The Ki language, ''Tuki'' (Baki, Oki), is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon. It is spoken by 26,000 people in the Central Province of Cameroon, in the Lekie division and in the Mbam and Kim division, along the Sanaga river.Biloa, E. (2013). Syntax of Tuki : A Cartographic Approach. John Benjamins Publishing Company. The dialects are Kombe (Tukombe), Cenga (Tocenga), Tsinga (Tutsingo), Bundum, Njo (Tonjo), Ngoro (Tu Ngoro), Mbere (Tumvele) and possibly Leti/MengisaHammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices and Mbwasa. Phonology Tuki distinguishes six phonetic vowels. It distinguishes between long and short vowels. The consonants are as follows. Grammar As in most Bantu languages The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mengisa People
Leti, or Mangisa, is a Bantu language of Cameroon, spoken by the Mengisa people. Most Mengisa have switched to the Eton language, though a number of them continue to use Leti as a secret ritual language. A smaller number speak Leti as their mother tongue. Leti is quite close to Tuki and may be a dialect.Hammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices It is also closely related to Eton. Mengisa is spoken in the northern part of Sa'a commune (in Lekié Lekié is a department of Centre Region in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 2,989 km and had a total population of 354,864. The capital of the department lies at Monatélé. It is named after the Lekié River. Subdivisions The ... department, Central Region). References Ritual languages Mbam languages Languages of Cameroon {{mbam-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eton Language
Eton, or Ìtón, is a Bantu language spoken by the Eton people of Cameroon.Velde, Mark L. O. Van de. ''A Grammar of Eton'', p. 3 It is mutually intelligible with Ewondo, a fact which may have delayed its study for some time. Eton speakers inhabit the Lekié department of the Centre Region of Cameroon, an area north of the capital Yaoundé bounded in the north by the Sanaga River. Ethnologue cites four dialects of Eton, but its speakers generally distinguish two, a northern and a southern dialect, the latter of which is closer to the Ewondo language. The Mengisa people have largely switched to Eton. A small number continue to speak their ancestral language, Leti. It is not clear if the ISO code for "Mengisa" refers to Eton or Leti; ''Ethnologue'' classifies Mengisa with Eton, but the code is likely based on Guthrie, who classified it with Leti.Hammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices Phonology Eton is a tone langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Language
A sacred language, liturgical language or holy language is a language that is cultivated and used primarily for religious reasons (like church service) by people who speak another, primary language in their daily lives. Some religions, or parts of them, regard the language of their sacred texts as in itself sacred. These include Ecclesiastical Latin in Roman Catholicism, Hebrew in Judaism, Arabic in Islam, Avestan in Zoroastrianism, Sanskrit in Hinduism, and Punjabi in Sikhism. By contrast Buddhism and Christian denominations outside of Catholicism do not generally regard their sacred languages as sacred in themselves. Concept A sacred language is often the language which was spoken and written in the society in which a religion's sacred texts were first set down; these texts thereafter become fixed and holy, remaining frozen and immune to later linguistic developments. (An exception to this is Lucumí, a ritual lexicon of the Cuban strain of the Santería religion, with no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sa'a, Cameroon
Sa'a is a town located in the Centre Province of Cameroon, within the Lekie division. Sa'a is a small town composed of two main ethnic groups: Eton and Manguissa. Both ethnic groups speak the Eton and Manguissa languages, which are very similar, and people from the two ethnic groups can converse without the need of a translator. A small community of around 50 to 60 people has begun to practice Judaism in Sa'a, but they have not yet formally converted. This group of former Christians is known as Beth Yeshourun. They have begun to collect materials in order to construct a synagogue. The Cameroonian author Severin Cecile Abega was born in Sa'a. See also *Communes of Cameroon The Divisions of Cameroon are the third-level units of administration in Cameroon. They are organised by divisions and sub divisions of each province (now Regions). As of 2005 (and since 1996) there are 2 urban communities (Douala and Ya ... * History of the Jews in Cameroon References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |