|
Megarid
:''This is also the ancient Greek name of a small island off Naples, site of the Castel dell'Ovo.'' Megaris () was a small but populous state of ancient Greece, west of Attica and north of Corinthia, whose inhabitants were adventurous seafarers, credited with deceitful propensities. The capital, Megara, was famous for white marble and fine clay. Mount Geraneia dominated the center of the region. The island of Salamis was originally under the control of Megara, before it was lost to Athens in the late 7th century BCE. Province The province of Megaris or Megarida ( or ) was one of the provinces of the East Attica Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Aspropyrgos, Eleusis, Mandra-Eidyllia and Megara Megara (; , ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castel Dell'Ovo
Castel dell'Ovo ("Egg Castle") is a seafront castle in Naples, located on the former island of Megaride, now a peninsula, on the Gulf of Naples in Italy. The castle's name comes from a legend about the Roman Republic, Roman poet Virgil, who had a reputation in the Middle Ages as a great sorcerer and predictor of the future. In the legend, Virgil put a magical egg into the foundations to support the fortifications. It remains there along with his bones, and had this egg been broken, the castle would have been destroyed and a series of disastrous events for Naples would have followed. The castle is located between the districts of San Ferdinando, Naples, San Ferdinando and Chiaia, facing Mergellina across the sea. History during the Roman era The Castel dell'Ovo is the oldest castle in Naples. The island of Megaride was where Greek colonists of Magna Graecia from Cumae founded the original nucleus of the city in the 6th century BC. Its location offers an excellent view of the Naples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaris (Naples)
:''This is also the ancient Greek name of Megaris (Naples), a small island off Naples, site of the Castel dell'Ovo.'' Megaris () was a small but populous Sovereign state, state of ancient Greece, west of Attica and north of Corinthia, whose inhabitants were adventurous seafarers, credited with deceitful propensities. The capital, Megara, was famous for white marble and fine clay. Mount Geraneia dominated the center of the region. The island of Salamis Island, Salamis was originally under the control of Megara, before it was lost to Classical Athens, Athens in the late 7th century BCE. Province The province of Megaris or Megarida ( or ) was one of the provinces of Greece, provinces of the East Attica Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Aspropyrgos, Eleusis, Mandra-Eidyllia and Megara. It was abolished in 2006. References Sources * Ancient Megara, Ancient Greek geography Provinces of Greece Historical regions Historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
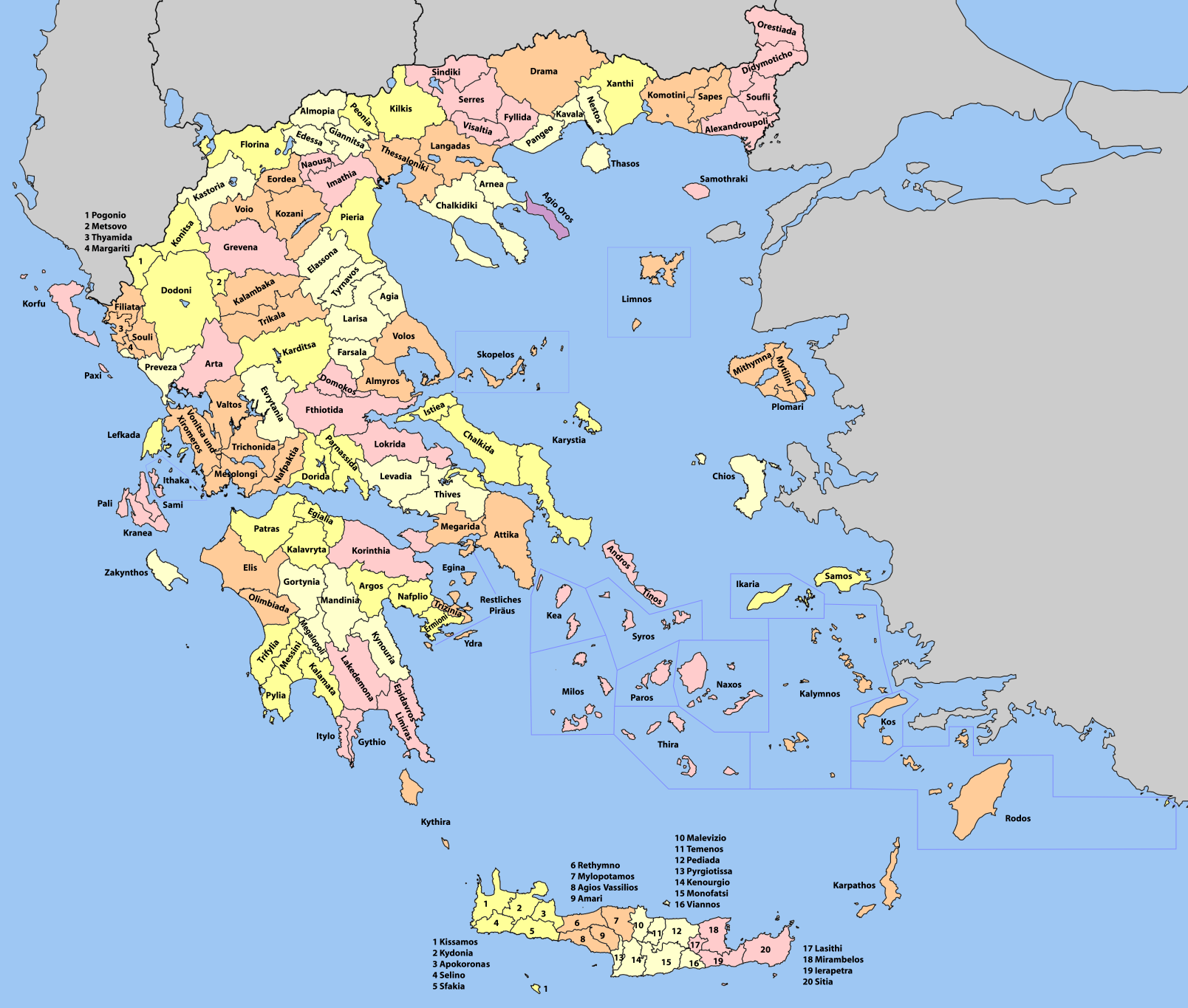
Provinces Of Greece
The provinces of Greece (, "eparchy") were sub-divisions of some the country's prefectures of Greece, prefectures. From 1887, the provinces were abolished as actual administrative units, but were retained for some state services, especially financial and educational services, as well as for electoral purposes. Before the Second World War, there were 139 provinces, and after the war, with the addition of the Dodecanese, Dodecanese Islands, their number grew to 148. According to the Article 7 of the Code of Prefectural Self-Government (Presidential Decree 30/1996), the provinces constituted a "particular administrative district" within the wider "administrative district" of the prefectures. The provinces were finally abolished after the 2006 Greek local elections, 2006 local elections, in line with Law 2539/1997, as part of the wide-ranging administrative reform known as the "Kapodistrias reform, Kapodistrias Project", and replaced by enlarged Municipalities and communities of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Geography
;Pre-Hellenistic Classical Greece *Homer *Anaximander (died ) *Hecataeus of Miletus (died ) *Massaliote Periplus (6th century BC) *Scylax of Caryanda (6th century BC) *Herodotus (died ) ;Hellenistic period *Pytheas (died ) *''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' (3rd or 4th century BC) *Megasthenes (died ) *Autolycus of Pitane (died ) *Dicaearchus (died ) *Deimakos (3rd century BC) *Timosthenes (floruit, fl. 270s BC) *Eratosthenes (c. 276–194 BC) *Scymnus (floruit, fl. 180s BC) *Hipparchus (c. 190–120 BC) *Agatharchides (2nd century BC) *Posidonius (c. 135–51 BC) *Pseudo-Scymnus (c. 90 BC) *Diodorus Siculus (c. 90–30 BC) *Alexander Polyhistor (1st century BC) ;Roman Empire period *''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' *Strabo (63 BC – AD 24) *Pomponius Mela (fl. 40s AD) *Isidore of Charax (1st century AD) *Mucianus (1st century AD) *Pliny the Elder (AD 23 – 79), ''Natural History (Pliny), Natural History'' *Marinus of Tyre (AD 70 – 130)Hubert Cancik and Helmuth Schneider (ed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Megara
Megara (; , ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken by Athens. Megara was one of the four districts of Attica, embodied in the four mythic sons of King Pandion II, of whom Nisos was the ruler of Megara. Megara was also a trade port, its people using their ships and wealth as a way to gain leverage on armies of neighboring poleis. Megara specialized in the exportation of wool and other animal products including livestock such as horses. It possessed two harbors, Pagae to the west on the Corinthian Gulf, and Nisaea to the east on the Saronic Gulf of the Aegean Sea. History Late Bronze Mycenaean period In the Late Bronze Age, Megara features prominently as a small kingdom in the myths and legends of Homer. Megara emerged between two fortified ports, Nisaea on the Saronic Gulf and Pagae on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandra-Eidyllia
Mandra-Eidyllia () is a municipality in the West Attica regional unit, Attica, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Mandra. The municipality has an area of 426.197 km2. Municipality The municipality Mandra–Eidyllia was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 4 former municipalities, that became municipal units: *Erythres *Mandra *Oinoi *Vilia Vilia (; formerly Eidyllia, Ειδυλλία) is a village and a former municipality of West Attica, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Mandra-Eidyllia, of which it is a municipal unit. Its population w ... References External links * Municipalities of Attica Populated places in West Attica {{Attica-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleusis
Elefsina () or Eleusis ( ; ) is a suburban city and Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Athens metropolitan area. It belongs to West Attica regional unit of Greece. It is located in the Thriasio Plain, at the northernmost end of the Saronic Gulf. North of Elefsina are Mandra, Greece, Mandra and Magoula, Attica, Magoula, while Aspropyrgos is to the northeast. It is the site of the Eleusinian Mysteries and the birthplace of Aeschylus. Today, Elefsina is a major industrial centre, with the largest oil refinery in Greece as well as the home of the Aeschylia Festival, the longest-lived arts event in the Attica Region. On 11 November 2016, Elefsina was named the European Capital of Culture for 2021, which became effective in 2023 due to the COVID-19 pandemic postponement. Etymology The word ''Eleusis'' first appears in the ''Orphic Hymn to Eleusinian Demeter'': «Δήμητρος Ελευσινίας, θυμίαμα στύρακα». Also Hesychius of Alexand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspropyrgos
Aspropyrgos (, ) is a western suburb, in the Athens metropolitan area and a municipality in the West Attica regional unit in the Thriasio Plain, Attica, Greece. The municipality had a population of 31,381 at the 2021 census. It has an area of 101.983 km2. Etymology The name 'Aspropyrgos' is derived from the Greek words , meaning 'white', and , meaning 'castle' or 'tower'. Geography Aspropyrgos is located 15 km northwest of the city center of Athens in the Thriasio Plain. It is 5 km northeast of Elefsina, near the Saronic Gulf coast. Mount Parnitha forms its northern border, and the Aigaleo hills its southeastern border. The Elefsina Military Airbase lies to its west. The main street is Dimokratias ('Democracy') Avenue. Aspropyrgos can be accessed from the A6 motorway (Elefsina - Athens International Airport) and the A65 motorway (Ano Liosia - Aspropyrgos). It is also accessible through A6 exit 4. (The industrial area is in the southeastern part of Aspropy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Greece
The provinces of Greece (, "eparchy") were sub-divisions of some the country's prefectures of Greece, prefectures. From 1887, the provinces were abolished as actual administrative units, but were retained for some state services, especially financial and educational services, as well as for electoral purposes. Before the Second World War, there were 139 provinces, and after the war, with the addition of the Dodecanese, Dodecanese Islands, their number grew to 148. According to the Article 7 of the Code of Prefectural Self-Government (Presidential Decree 30/1996), the provinces constituted a "particular administrative district" within the wider "administrative district" of the prefectures. The provinces were finally abolished after the 2006 Greek local elections, 2006 local elections, in line with Law 2539/1997, as part of the wide-ranging administrative reform known as the "Kapodistrias reform, Kapodistrias Project", and replaced by enlarged Municipalities and communities of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
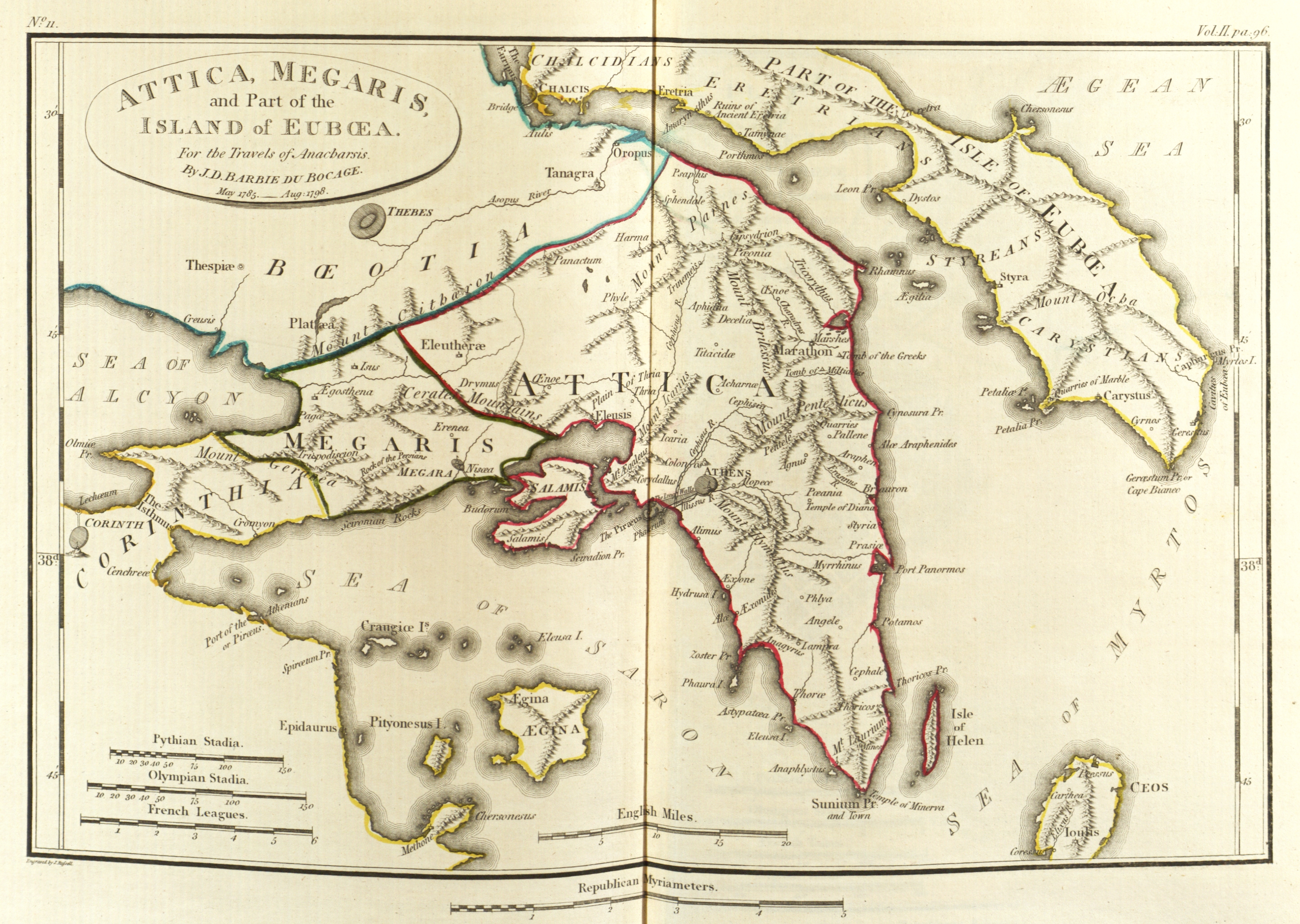
Map Of Attica And Megaris
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Athens
The city of Athens (, ''Athênai'' ; Modern Greek: Αθήναι, ''Athine'' ) during the classical period of ancient Greece (480–323 BC) was the major urban centre of the notable '' polis'' ( city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Isagoras. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions, it remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC (aftermath of Lamian War). The peak of Athenian hegemony was achieved in the 440s to 430s BC, known as the Age of Pericles. In the classical period, Athens was a centre for the arts, learning, and philosophy, the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum, Athens was also the birthplace of Socrates, Plato, Pericles, Aristophanes, Sophocles, and many other prominent philosophers, writers, and politici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamis Island
Salamis ( ; ) or Salamina () is the largest Greece, Greek island in the Saronic Gulf, about from the coast of Athens' port of Piraeus and about west of Athens center. The chief city, Salamina (city), Salamina, lies in the west-facing core of the crescent on Salamis Bay, which opens into the Saronic Gulf. On the eastern side of the island its main port, Paloukia, connects the island with Perama in the western part of Athens urban area through a frequent ferry line and is the second largest port in Greece in terms of passengers, after the port of Piraeus. Etymology The traditional etymology of Salamis derives it from the eponymous nymph Salamis (mythology), Salamis, the mother of Cychreus, the legendary first king of the island. A more modern theory considers "Salamis" to come from the root ''sal'' 'salt' and ''-amis'' 'middle'; thus ''Salamis'' would be the place amid salt water. A theory presented by Martin Bernal in his book Black Athena, which has been overwhelmingly rejecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |