|
Masidwola
Masidwola (, meaning "of the Masid (Pashtun tribe), Mehsuds"), Mehsudi, or Maseedwola is a dialect of Waziristani. Phonology Rozi Khan Burki claims that in Waziristani is that the phonemes [ʃ] and [ʂ], along with their voiced counterparts, [ʒ] and [ʐ], have merged into the phonemes [ɕ] and [ʑ], both of which also exist in the nearby Ormuri or Ormuri, Warmuri language of Burkis of Kaniguram, South Waziristan. But Pashto linguists such as Josef Elfenbein, Anna Boyle or Yousaf Khan Jazab have not noted this in Waziri Phonology. See also *Waneci NotesLinguist List*Lorimer, John Gordon (1902). ''Grammar and Vocabulary of Waziri Pashto''. References {{Iranian languages Pashto dialects Languages of Afghanistan Languages of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Waziristan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashto Dialects
Pashto dialects ( də Pəx̌tó žәbgóṭi) can be divided into two large varieties: Northern Pashto and Southern Pashto. Each of the two varieties of Pashto is further divided into a number of dialects. Northern Pashto is spoken in eastern Afghanistan, and central, northern and eastern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (including Peshawar). Southern Pashto is spoken to the south of it, in southern and western Afghanistan (including Kandahar), southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and northern Balochistan (including Quetta). 'Ethnologue' divides Pashto into Northern, Southern and Central Pashto, and Wanetsi. Overview According to David Neil MacKenzie, a consonant shift took place in the northern parts of Pashtunistan in several phases in the medieval era. During the shift, the retroflex fricative ''ṣ̌'' changed to ''x̌'' or to ''x'' , while ''ẓ̌'' changed to ''ǵ'' or to ''g'' . That is supported by the linguist Georg Morgenstierne's assertion that the Pashto script developed in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
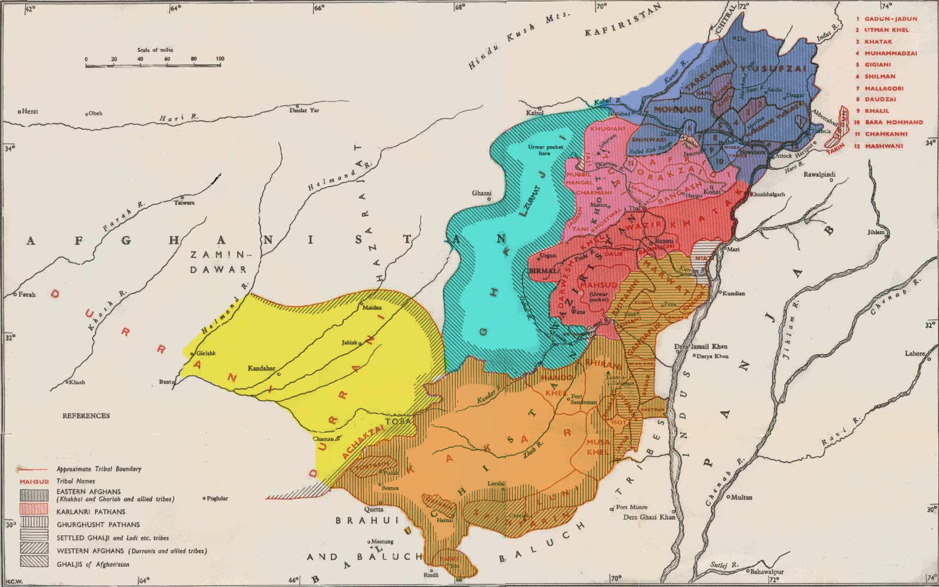
Waziristani
Waziristāní (), also known as Wazirwóla (, meaning "of the Wazir (Pashtun tribe), Wazirs") and Wazirí, is a central Pashto dialect spoken in North Waziristan and South Waziristan. Waziristani differs in pronunciation and to a much lesser degree in grammar from the other varieties of Pashto. The Waziristani dialect is similar to the dialect spoken around Urgun (eastern Paktika province) and the Bannuchi dialect of Bannu. John Gordon Lorimer (civil servant), Lorimer states: Waziristani Pashto is spoken by various tribes, and it is also called ''Masidwola dialect, Masidwola'' by the Mahsuds and ''Dāwaṛwóla'' by the Dawari, Dāwaṛ. In the Dāwaṛi variety of Wazrisitani the word for هګۍ [haɡəɪ] is يييې [jije]. The standard Pashto word for "boy", "هلک" [halək], is rarely heard in Waziristani, instead, "وېړکی" [weṛkai] meaning "little one" is used [from standard: وړوکی -waṛúkai] . The word "ləshki" [ləʃki] is used instead of the standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaniguram
Kānīgūram () is a town in the South Waziristan region of Pakistan. Kaniguram's population mainly consists of the Ormur or Burki tribes of Pashtuns. It is also the hometown of the sixteenth-century Pashtun revolutionary leader and warrior-poet Bayazid Pir Roshan, who wrote the first known book of Pashto language. According to the 2017 Census, Kaniguram has population of 13,809. Today the locals in this town speak the Ormuri as well as the Waziristani (Maseedwola) dialect of Pashto. Demographics The Burki tribe has primarily inhabited Kaniguram. This place has been their tribe's focal point for over 800 years. Kaniguram has historically been remained off limits to outsiders except for the Burki and, more recently, the Mahsuds. Common store-front signs are "Burki knives" and "Burki pharmacy" and are indicative of the Burki's dominant position in Kaniguram despite being significantly outnumbered by Mahsuds. Relations between the Burki/Urmar and the Mahsuds are as complex as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population as of 2023. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is List of cities in Pakistan by population, its largest city and financial centre. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country by area. Bounded by the Arabian Sea on the south, the Gulf of Oman on the southwest, and the Sir Creek on the southeast, it shares land borders with India to the east; Afghanistan to the west; Iran to the southwest; and China to the northeast. It shares a maritime border with Oman in the Gulf of Oman, and is separated from Tajikistan in the northwest by Afghanistan's narrow Wakhan Corridor. Pakistan is the site of History of Pakistan, several ancient cultures, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's capital and largest city. Demographics of Afghanistan, Afghanistan's population is estimated to be between 36 and 50 million. Ancient history of Afghanistan, Human habitation in Afghanistan dates to the Middle Paleolithic era. Popularly referred to as the graveyard of empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waziristan
Waziristan (Persian language, Persian, Pashto, Ormuri, , ) is a mountainous region of the Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The Waziristan region administratively splits among three districts: North Waziristan, Lower South Waziristan District, and Upper South Waziristan District. Waziristan region, consisted of three districts, covers around and is mainly populated by the Burki, Wazir (Pashtun tribe), Mehsud, The Wolves, & Wazir Pashtun tribe, who speak the Waziri dialect of the Pashto language. Etymology The name "Waziristan" is associated with the ancestor of the Pashtun tribes, Mahsud, Mehsud (The Wolves), named Wazir. Both tribes descended from him and are predominantly settled in the Waziristan region. Overview and history Waziristan lies between the Tochi River, Kurram River and the Gomal River. It borders the Kurram Agency in the north, Bannu District, Bannu in the northeast, Tank, Pakistan, Tank in the east, Frontier Region Dera Ismail Khan, Dera Ismail Kha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Iranian Languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also known as Indo-Iranic languages or collectively the Aryan languages) constitute the largest branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.7 billion speakers worldwide, predominantly in South Asia, West Asia and parts of Central Asia. Indo-Iranian languages are divided into three major branches: Indo-Aryan, Iranian, and Nuristani languages. The Badeshi language remains unclassified within the Indo-Iranian branch. The largest Indo-Iranian language is the Hindustani language (Hindi-Urdu)."Hindi" L1: 322 million (2011 Indian census), including perhaps 150 million speakers of other languages that reported their language as "Hindi" on the census. L2: 274 million (2016, source unknown). Urdu L1: 67 million (2011 & 2017 censuses), L2: 102 million (1999 Pakistan, source unknown, and 2001 Indian census): ''Ethnologue'' 21. . . The areas with Indo-Iranian languages stretch from Europe ( Romani) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Languages
The Iranian languages, also called the Iranic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau. The Iranian languages are grouped in three stages: Old Iranian (until 400 BCE), Middle Iranian (400 BCE – 900 CE) and New Iranian (since 900 CE). The two directly attested Old Iranian languages are Old Persian (from the Achaemenid Empire) and Old Avestan (the language of the Avesta). Of the Middle Iranian languages, the better understood and recorded ones are Middle Persian (from the Sasanian Empire), Parthian (from the Parthian Empire), and Bactrian (from the Kushan and Hephthalite empires). Number of speakers , '' Ethnologue'' estimates that there are 86 languages in the group. Terminology and grouping Etymology The term ''Iran'' derives directly from Middle Persian , first attested in a third-century inscription at Naqsh-e Rostam, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Iranian Languages
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages, having emerged during the Iranian languages#Middle Iranian, Middle Iranian era (4th century BC to 9th century AD). The Avestan, Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle-era Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian dialects, the Middle-era Eastern Iranian dialects preserve word-final syllables. The largest living Eastern Iranian language is Pashto, with at least 90 million speakers between the Amu Darya, Oxus River in Afghanistan and the Indus River in Pakistan. The second-largest living Eastern Iranian language is Ossetian language, Ossetic, with roughly 600,000 speakers across Ossetia (split between Georgia (country), Georgia and Russia). All other languages of the Eastern Iranian subgroup have fewer than 200,000 speakers combined. Most living Eastern Iranian languages are spoken in a contiguous area: southern and eastern Afghanistan and the adjacent parts of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ormuri
Ormuri (Ormuri: اورموړی Pashto: اورموړی) also known as ''Baraki, Ormur, Ormui or Bargista '' is an Eastern Iranian language spoken in the Waziristan region of Pakistan. It is primarily spoken by the Burki people in the town of Kaniguram in South Waziristan. A small number of speakers are also found in Logar, Afghanistan. The language belongs to the Eastern-Iranian language group. The extremely small number of speakers makes Ormuri an endangered language that is considered to be in a "threatened" state. Ormuri is notable for its unusual sound inventory, which includes a voiceless alveolar trill that does not exist in the surrounding Pashto. Ormuri also has voiceless and voiced alveolo-palatal fricatives (the voiceless being contrastive with the more common voiceless palato-alveolar fricative), which also exist in the Waziristani dialect of Pashto, but could have been adopted from Ormuri due to its close proximity.. Originally published in ''Pakistan Journal of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waneci
Waṇetsi (), commonly called Tarīno (), and sometimes Tsalgari (), is a distinct variety of Pashto and is considered by some to be a different language. In some cases, Wanetsi shares similarities with the Pamir language of Munji, being a sort of bridge between the former and Pashto. It is perhaps a representation of a more archaic, or very early, form of Pashto. It is spoken by the Tareen in Balochistan, Pakistan, primarily in Harnai (هرنای) (Harnai District) and Chawter (چوتېر) area in Sanjawi, Northern Balochistan, Pakistan. The language is at risk due to lack of attention and not liking it as a language by foreigners. History Professor Prods Oktor Skjærvø states: According to Encyclopædia Iranica Waṇetsi branched off from the other Pashto dialects in the Middle Iranian stage: Research The first known linguistic research was conducted in 1929 by Georg Morgenstierne on Waṇetsi. Since then linguists like Josef Elfenbein have worked and researched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |