|
Martin Benno Schmidt
Martin Benno Schmidt (23 August 1863 – 27 November 1949) was a German pathologist born in Leipzig. He spent several years as an assistant at the University of Strasbourg, where he worked under Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen (1833-1910). In 1906 he became a professor of pathology at the medical academy in Düsseldorf, and afterwards worked as a pathologist in Zurich and Marburg. In 1913 he succeeded Richard Kretz (1865-1920) as professor of pathology at the University of Würzburg, a position he maintained until his retirement in 1934. Schmidt specialized in pathological investigations of bone disorders such as rickets, osteogenesis imperfecta, and osteomalacia. He is remembered for his description of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome, type II, a disease characterized by autoimmune activity against more than one endocrine gland. This condition is sometimes referred to as "Schmidt's syndrome". He also performed important studies involving iron metabolism. Publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathologist
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, post-infectious IBS, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), Alopecia Areata and multiple sclerosis (MS). Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids. Autoimmunity means presence of antibodies or T cells that react with self-protein and is present in all individuals, even in normal health state. It causes autoimmune diseases if self-reactivity can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1949 Deaths
Events January * January 1 – A United Nations-sponsored ceasefire brings an end to the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947. The war results in a stalemate and the division of Kashmir, which still continues as of 2022. * January 2 – Luis Muñoz Marín becomes the first democratically elected Governor of Puerto Rico. * January 11 – The first "networked" television broadcasts take place, as KDKA-TV in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania goes on the air, connecting east coast and mid-west programming in the United States. * January 16 – Şemsettin Günaltay forms the new government of Turkey. It is the 18th government, last single party government of the Republican People's Party. * January 17 – The first VW Type 1 to arrive in the United States, a 1948 model, is brought to New York by Dutch businessman Ben Pon. Unable to interest dealers or importers in the Volkswagen, Pon sells the sample car to pay his travel expenses. Only two 1949 models are sold in Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1863 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Abraham Lincoln signs the Emancipation Proclamation during the third year of the American Civil War, making the abolition of slavery in the Confederate states an official war goal. It proclaims the freedom of 3.1 million of the nation's four million slaves and immediately frees 50,000 of them, with the rest freed as Union armies advance. * January 2 – Lucius Tar Painting Master Company (''Teerfarbenfabrik Meirter Lucius''), predecessor of Hoechst, as a worldwide chemical manufacturing brand, founded in a suburb of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. * January 4 – The New Apostolic Church, a Christian and chiliastic church, is established in Hamburg, Germany. * January 7 – In the Swiss canton of Ticino, the village of Bedretto is partly destroyed and 29 killed, by an avalanche. * January 8 ** The Yorkshire County Cricket Club is founded at the Adelphi Hotel, in Sheffield, England. ** American Civil War &nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Pathologists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents ( pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. The diseases are caused by specific types of bacterial infection. Epidemic typhus is due to '' Rickettsia prowazekii'' spread by body lice, scrub typhus is due to ''Orientia tsutsugamushi'' spread by chiggers, and murine typhus is due to '' Rickettsia typhi'' spread by fleas. Vaccines have been developed, but none are commercially available. Prevention is achieved by reducing exposure to the organisms that spread the disease. Treatment is with the antibiotic doxycycline. Epidemic typhus generally occurs in outbreaks when poor sanitary conditions and crowding are present. While once common, it is now rare. Scrub typhus occurs in Southeast Asia, Japan, and northern Australia. Murine typhus occurs in tropical and subtropical areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications may include pus around the kidney, sepsis, or kidney failure. It is typically due to a bacterial infection, most commonly ''Escherichia coli''. Risk factors include sexual intercourse, prior urinary tract infections, diabetes, structural problems of the urinary tract, and spermicide use. The mechanism of infection is usually spread up the urinary tract. Less often infection occurs through the bloodstream. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and supported by urinalysis. If there is no improvement with treatment, medical imaging may be recommended. Pyelonephritis may be preventable by urination after sex and drinking sufficient fluids. Once present it is generally treated with antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin or ceftriaxone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Aschoff
Karl Albert Ludwig Aschoff (10 January 1866 – 24 June 1942) was a German physician and pathologist. He is considered to be one of the most influential pathologists of the early 20th century and is regarded as the most important German pathologist after Rudolf Virchow. Early life and education Aschoff was born in Berlin, Prussia on 10 January 1866. He studied medicine at the University of Bonn, University of Strasbourg, and the University of Würzburg. Career After his habilitation in 1894, Ludwig Aschoff was appointed professor for pathology at the University of Göttingen in 1901. Aschoff transferred to the University of Marburg in 1903 to head the department for pathological anatomy. In 1906, he accepted a position as ordinarius at the University of Freiburg, where he remained until his death. Aschoff was interested in the pathology and pathophysiology of the heart. He discovered nodules in the myocardium present during rheumatic fever, the so-called Aschoff bodies. Aschof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
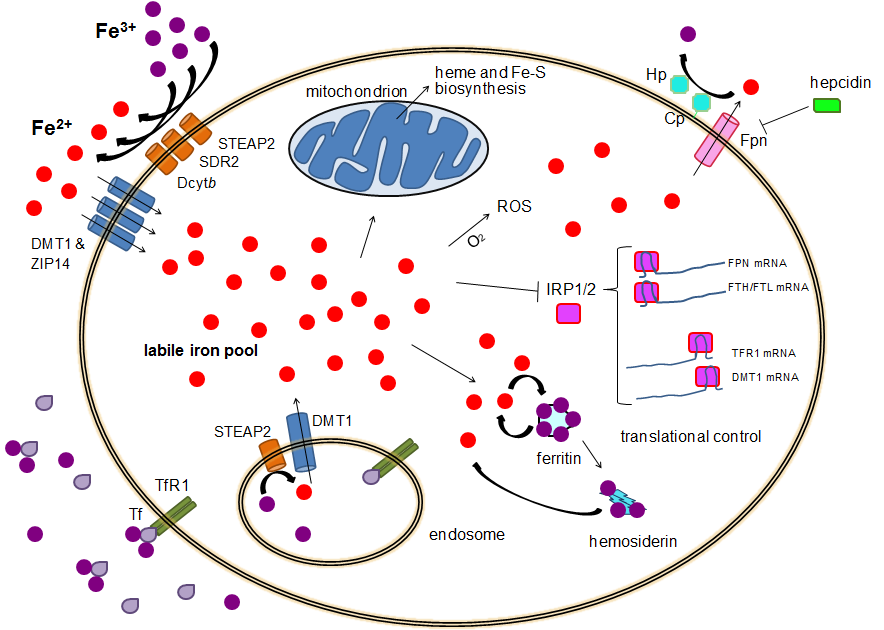
Iron Metabolism
Human iron metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that maintain human homeostasis of iron at the systemic and cellular level. Iron is both necessary to the body and potentially toxic. Controlling iron levels in the body is a critically important part of many aspects of human health and disease. Hematologists have been especially interested in systemic iron metabolism because iron is essential for red blood cells, where most of the human body's iron is contained. Understanding iron metabolism is also important for understanding diseases of iron overload, such as hereditary hemochromatosis, and iron deficiency, such as iron-deficiency anemia. Importance of iron regulation Iron is an essential bioelement for most forms of life, from bacteria to mammals. Its importance lies in its ability to mediate electron transfer. In the ferrous state (Fe2+), iron acts as an electron donor, while in the ferric state (Fe3+) it acts as an acceptor. Thus, iron plays a vital role in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine Gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are neuroendocrine organs. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland hangs from the base of the brain by the pituitary stalk, and is enclosed by bone. It consists of a hormone-producing glandular portion of the anterior pituitary and a neural portion of the posterior pituitary, which is an extension of the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus regulates the hormonal output of the anterior pituitary and creates two hormones that it exports to the posterior pituitary for storage and later release. Four of the six anterior pituitary hormones are tropic hormones that regulate the function of other endocrine organs. Most anterior pituitary hormones exhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes (APSs), also called polyglandular autoimmune syndromes (PGASs) or polyendocrine autoimmune syndromes (PASs), are a heterogeneous group of rare diseases characterized by autoimmune activity against more than one endocrine organ, although non-endocrine organs can be affected. There are three types of APS, and there are a number of other diseases which involve endocrine autoimmunity. Types * Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1, an autosomal recessive syndrome due to mutation of the ''AIRE'' gene resulting in hypoparathyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, hypogonadism, vitiligo, candidiasis and others. * Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 2, an autosomal dominant syndrome due to multifactorial gene involvement resulting in adrenal insufficiency plus hypothyroidism and/or type 1 diabetes. * Immunodysregulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X-linked syndrome (IPEX syndrome) is X-linked recessive due to mutation of the '' FOXP3'' gene on the X chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)