|
Marcantonio Barbarigo
Marcantonio Barbarigo (6 March 1640 – 26 May 1706) was an Italian cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He was the founder of the Pontifical Institute of the Religious Teachers Filippini and also founded both the Religious Teachers Filippini of Montefiascone and the Augustinian Sisters of Divine Love. He was the great-uncle of Pope Clement XIII and was a relative of Gregorio Barbarigo. In the process towards sainthood Pope Benedict XVI approved that he lived a life of heroic virtue and bestowed upon him the title of Venerable in 2007. Biography Marcantonio Barbarigo was born on 6 March 1640 in Venice. Barbarigo studied in Padua where he earned a doctorate in both canon law and civil law. He abandoned a successful diplomatic career in order to follow his religious vocation. Bishop of Corfu Barbarigo was ordained to the priesthood in Padua and Pope Innocent XI later appointed him as the Bishop of Corfu in 1678. His relative Gregorio Barbarigo bestowed upon him episcopal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Venerable
''The Venerable'' often shortened to Venerable is a style, title, or epithet used in some Christianity, Christian churches. The title is often accorded to holy persons for their spiritual perfection and wisdom. Catholic In the Catholic Church, after a deceased Catholic has been declared a servant of God by a Bishop (Catholic Church), bishop and proposed for beatification by the pope, such a servant of God may next be declared venerable ("heroic virtue, heroic in virtue") during the investigation and process leading to possible canonization as a saint. A declaration that a person is venerable is not a pronouncement of their presence in Heaven. The pronouncement means it is considered likely that they are in heaven, but it is possible the person could still be in purgatory. Before one is considered venerable, one must be declared by a proclamation, approved by the pope, to have lived a life that was "heroic in virtue" (the theological virtues of faith, hope, and charity and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Benedict XVI
Pope BenedictXVI (born Joseph Alois Ratzinger; 16 April 1927 – 31 December 2022) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 19 April 2005 until his resignation on 28 February 2013. Benedict's election as pope occurred in the 2005 papal conclave that followed the death of Pope John Paul II. Upon his resignation, Benedict chose to be known as " pope emeritus", a title he held until his death on 31 December 2022. Ordained as a priest in 1951 in his native Bavaria, Ratzinger embarked on an academic career and established himself as a highly regarded theologian by the late 1950s. He was appointed a full professor in 1958 when aged 31. After a long career as a professor of theology at several German universities, he was appointed Archbishop of Munich and Freising and created a cardinal by Pope Paul VI in 1977, an unusual promotion for someone with little pastoral experience. In 1981, he was appointed Prefect of the Congregation for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Congregation
A religious congregation is a type of Religious institute (Catholic), religious institute in the Catholic Church. They are legally distinguished from Religious order (Catholic), religious orders – the other major type of religious institute – in that members take simple vows, whereas members of religious orders take solemn vows. History Until the 16th century, the vows taken in any of the religious orders approved by the Holy See, Apostolic See were classified as solemn.Arthur Vermeersch, "Religious Life" in The Catholic Encyclopedia, Vol. 12. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911 . Accessed 18 July 2011. This was declared by Pope Boniface VIII (1235–1303). According to this criterion, the last religious order foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucy Filippini
Lucy Filippini (; 13 January 1672 – 25 March 1732) is venerated as a Catholic saint. With the assistance of Giovanni Francesco Barbarigo, Cardinal Giovanni Francesco Barbarigo, Rose Venerini founded schools for young women, especially the poor, in Viterbo. The cardinal's relative Marcantonio Barbarigo, Cardinal Marcantonio Barbarigo invited Venerini to establish schools in his diocese of Roman Catholic Diocese of Montefiascone, Montefiascone. When Venerini had to return to Viterbo to look after the establishments there, Marcantonio entrusted the schools to Lucy Filippini. She then founded Filippini Sisters, ''the Institute of the Maestre Pie'' to staff the schools and continue her work. They are known as the "Filippini Sisters". Life Lucy Filippini was born on 13 January 1672 in Tarquinia, Corneto-Tarquinia. She was the fifth and youngest child of Filippo Filippini and Maddalena Picchi. She had not yet reached her first birthday when her mother died and was buried in the Chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
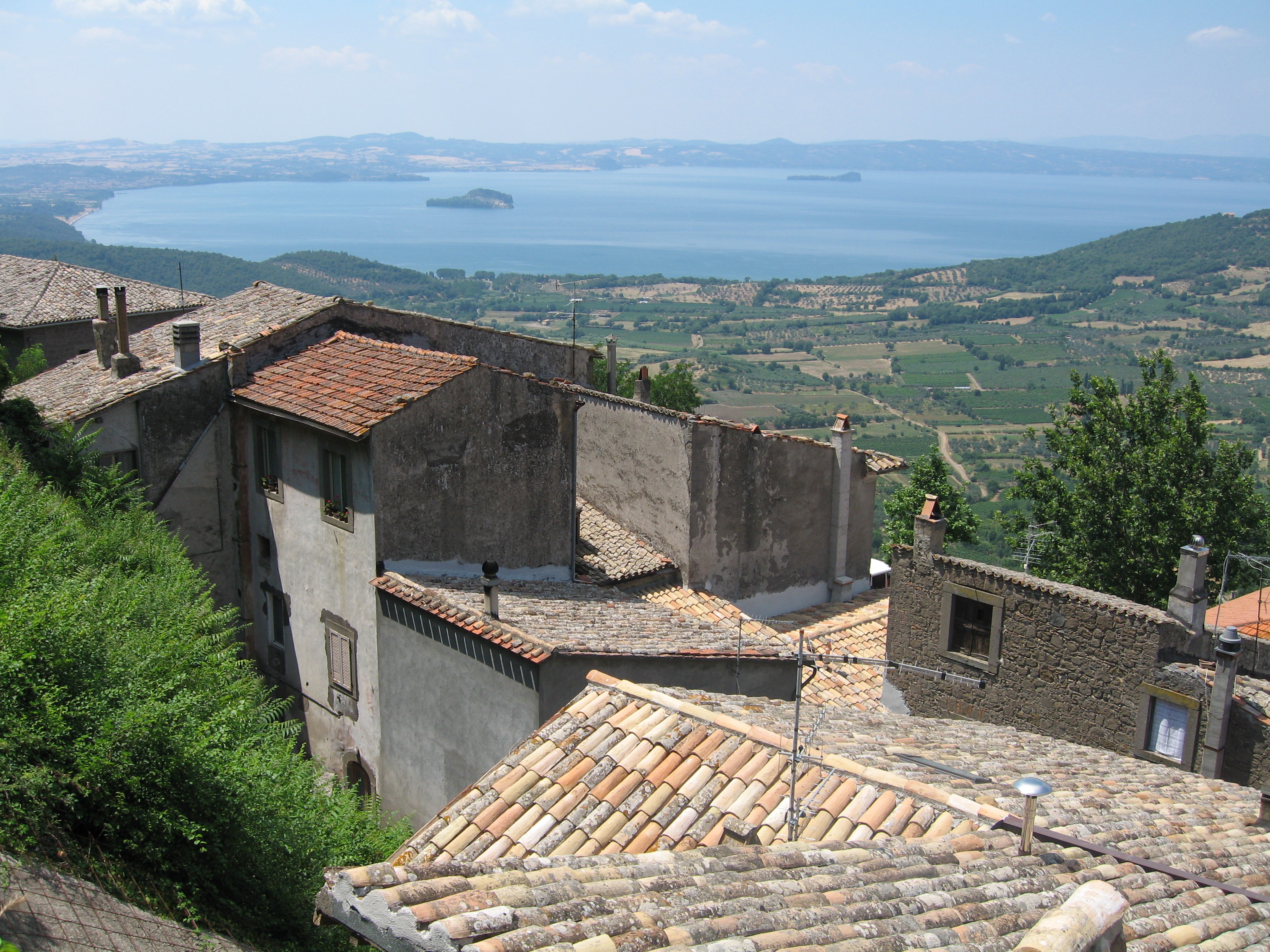
Lake Bolsena
Lake Bolsena () is a lake of volcano, volcanic origin in the northern part of the province of Viterbo called ''Alto Lazio'' ("Upper Latium") or ''Tuscia'' in central Italy. It is the largest volcanic lake in Europe. Roman historic records indicate activity of the Vulsini volcano occurred as recently as 104 BC; it has been dormant since then. The two islands in the southern part of the lake were formed by underwater eruptions following the collapse that created the depression. The lake is supplied entirely from the aquifer, rainfall and runoff, with one outlet at the southern end. A sewage treatment plant constructed in 1996 filters most of the raw sewage from the major surrounding communities, transported via pipeline to the facility on the Marta River. Fertilizers are a second source of contamination. The chemical content of the lake is monitored at several stations around it. The lake has a long historic tradition. The Romans called it ''Lacus Volsinii'', adapting the Etrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rose Venerini
Rose Venerini (9 February 1656 – 7 May 1728), also called Rosa Venerini, was an Italian Roman Catholic The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ... saint and Virgin (title), virgin who founded the first public schools for girls and young women in Italy. According to the Vatican City, Vatican document published on the occasion of Venerini's canonization in 2006, "Wherever a new school sprang up, in a short time a moral improvement could be noted in the youth". Her confraternity of teachers, after her death, was raised to a religious congregation called the Religious Teachers Venerini (or Venerini sisters), which worked with Italian immigrants in the U.S. and Switzerland established the first day care centers in the Northeastern U.S., and worked throughout the world. Her feast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallium
The pallium (derived from the Roman ''pallium'' or ''palla'', a woolen cloak; : pallia) is an ecclesiastical vestment in the Catholic Church, originally peculiar to the pope, but for many centuries bestowed by the Holy See upon metropolitan bishop, metropolitans and primate (bishop), primates as a symbol of their conferred Ecclesiastical jurisdiction, jurisdictional authorities; it remains a papal emblem. It is symbolic of the lamb which Jesus carries on his shoulders in artwork portraying him as the Good Shepherd. In its present (western) form, the pallium is a long and "three fingers broad" (narrow) white band adornment, woven from the wool of lambs raised by Trappist monks. It is donned by looping its middle around one's neck, resting upon the chasuble and two dependent lappets over one's shoulders with tail-ends (doubled) on the left with the front end crossing over the rear. When observed from the front or rear the pallium sports a stylistic letter 'y' (contrasting against a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
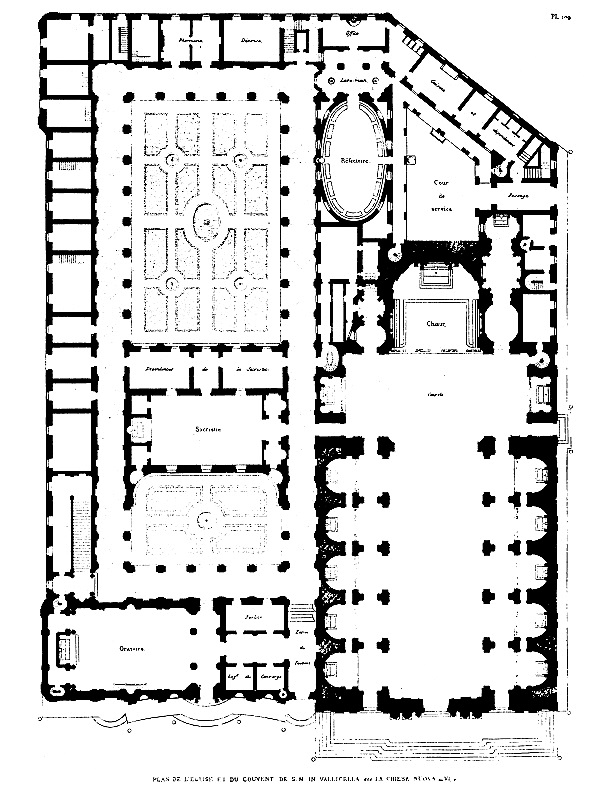
Santa Maria In Vallicella
Santa Maria in Vallicella, also called Chiesa Nuova, is a church in Rome, Italy, which today faces onto the main thoroughfare of the Corso Vittorio Emanuele and the corner of Via della Chiesa Nuova. It is the principal church of the Oratorians, a religious congregation of secular priests, founded by St Philip Neri in 1561 at a time in the 16th century when the Counter Reformation saw the emergence of a number of new religious institutes such as the Jesuits, the Theatines, and the Barnabites. These new congregations were responsible for several great preaching churches built in the Centro Storico, the others being Sant'Andrea della Valle (Theatines), San Carlo ai Catinari (Barnabites), and The Gesù and Sant'Ignazio (Jesuits). History By tradition, St. Gregory the Great built the first church on the site. By the 12th century, it was dedicated to ''Santa Maria in Vallicella'' ("Our Lady in the Little Valley"). In 1575, Pope Gregory XIII recognised Neri's group as a religiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episcopal Consecration
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role or office of the bishop is called episcopacy or the episcopate. Organisationally, several Christian denominations utilise ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority within their dioceses. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Law (legal System)
Civil law is a legal system rooted in the Roman Empire and was comprehensively codified and disseminated starting in the 19th century, most notably with France's Napoleonic Code (1804) and Germany's (1900). Unlike common law systems, which rely heavily on judicial precedent, civil law systems are characterized by their reliance on legal codes that function as the primary source of law. Today, civil law is the world's most common legal system, practiced in about 150 countries. The civil law system is often contrasted with the common law system, which originated in medieval England. Whereas the civil law takes the form of legal codes, the common law comes from uncodified case law that arises as a result of judicial decisions, recognising prior court decisions as legally binding precedent. Historically, a civil law is the group of legal ideas and systems ultimately derived from the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'', but heavily overlain by Napoleonic, Germanic, canonical, feuda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Law
Canon law (from , , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical jurisdiction, ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. Canon law includes the internal ecclesiastical law, or operational policy, governing the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and the Eastern Catholic Churches), the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox churches, and the individual national churches within the Anglican Communion. The way that such church law is legislative power, legislated, interpreted and at times court, adjudicated varies widely among these four bodies of churches. In all three traditions, a canon (canon law), canon was originally a rule adopted by a church council; these canons formed the foundation of canon law. Etymology Greek language, Greek / , Arabic language, Arabic / , Hebrew language, Hebrew / , 'straigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |