|
Mancunian Way
The Mancunian Way is a two mile long grade separated elevated motorway in Manchester, England. It is officially made up of the A57(M) and A635(M) motorways, although the latter does not appear on road signs for practical reasons. It is also part of two other roads: the A57 to the west, which runs east–west through Greater Manchester linking the M602 and M67 motorways, and a short section of non-motorway A635 to the east. Part of this non-motorway section collapsed on 14 August 2015 due to a sinkhole. Route The road forms a major part of the Manchester-Salford Inner Ring Road and runs south of the city centre. Running eastbound, it starts as a two-lane dual carriageway and passes underneath the A56. Following this, the road widens to three lanes. At the next junction which leads to the A5103, the road reduces to two lanes and becomes an elevated highway. This section runs atop link roads and two roundabouts before reaching the next junction with the A34. At this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester City Council
Manchester City Council is the local authority for Manchester, a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. Manchester is the sixth largest city in England by population. Its city council is composed of 96 councillors, three for each of the 32 electoral wards of Manchester. The council is controlled by the Labour Party and led by Bev Craig. The official opposition is the Green Party with three councillors. Joanne Roney is the chief executive. Many of the council's staff are based at Manchester Town Hall. History Manchester was incorporated in 1838 under the Municipal Corporations Act 1835 as the Corporation of Manchester or Manchester Corporation. It achieved city status in 1853, only the second such grant since the Reformation. The area included in the city has been increased many times, in 1885 (Bradford, Harpurhey and Rusholme), 1890 (Blackley, Crumpsall, part of Droylsden, Kirkmanshulme, Moston, Newton Heath, Openshaw, and West Gorton), 1903 (Heaton) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Inner Ring Road
Manchester and Salford Inner Relief Route is a ring road in Greater Manchester, England. It is the product of the amalgamation of several major roads around Manchester and Salford city centres to form a circular route. It was completed in 2004 with the opening of a final section to Trinity Way. A major component of the ring road is the Mancunian Way motorway to the south of Manchester city centre. When it was built, it was planned to be the first of many such inner-city elevated roads. The road is a pivotal part of the ring road for east–west traffic across the southern part of the city centre. The principal section of Trinity Way opened in 1987 easing congestion on Deansgate and opening a route north-west of the city centre. Improvements were made to Great Ancoats Street, north-east of the city centre, making it mostly dual carriageway. Great Ancoats Street (to the north and east), Trinity Way (to the north and west) and the Mancunian Way (to the south) almost formed a cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène Freyssinet
Eugène Freyssinet () (13 July 1879 – 8 June 1962) was a French structural and civil engineer. He was the major pioneer of prestressed concrete. Biography Freyssinet was born in at Objat, Corrèze, France. He worked in the '' École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées'' in Paris, France where he designed several bridges until the First World War intervened. His tutors included Charles Rabut. He served in the French Army from 1904 to 1907 and again from 1914 to 1918 as a road engineer. His most significant early bridge was the three span Pont le Veurdre near Vichy, built in 1911. At the time, the 72.5 metre (238 ft) spans were the longest so far constructed in France although Grafton Bridge a 97.6 metre reinforced concrete bridge had been opened in April 1910 and the Rocky River Bridge in Cleveland Ohio, an 85.34 metre unreinforced bridge had been opened in October 1910. Freyssinet's proposal was for three reinforced concrete truss spans, and was significantly less expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestressed Concrete
Prestressed concrete is a form of concrete used in construction. It is substantially "prestressed" (Compression (physics), compressed) during production, in a manner that strengthens it against tensile forces which will exist when in service. Post-tensioned concreted is "structural concrete in which internal stresses have been introduced to reduce potential tensile stresses in the concrete resulting from loads." This compression is produced by the Tension (physics), tensioning of high-strength "tendons" located within or adjacent to the concrete and is done to improve the performance of the concrete in service. Tendons may consist of single wires, multi-wire Wire rope, strands or threaded bars that are most commonly made from high-tensile steels, carbon fiber or aramid fiber. The essence of prestressed concrete is that once the initial compression has been applied, the resulting material has the characteristics of high-strength concrete when subject to any subsequent compression fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precast Concrete
Precast concrete is a construction product produced by casting concrete in a reusable mold or "form" which is then cured in a controlled environment, transported to the construction site and maneuvered into place; examples include precast beams, and wall panels for tilt up construction. In contrast, cast-in-place concrete is poured into site-specific forms and cured on site. Recently lightweight expanded polystyrene foam is being used as the cores of precast wall panels, saving weight and increasing thermal insulation. Precast stone is distinguished from precast concrete by the finer aggregate used in the mixture, so the result approaches the natural product. Overview Precast concrete is employed in both interior and exterior applications, from highway, bridge, and hi-rise projects to tilt-up building construction. By producing precast concrete in a controlled environment (typically referred to as a precast plant), the precast concrete is afforded the opportunity to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A6 Road (Great Britain)
The A6 is one of the main north–south roads in England. It runs from Luton in Bedfordshire to Carlisle in Cumbria, although it formerly started at a junction with the A1 at Barnet. It is the fourth longest numbered road in Britain; only the A1, A38 and A30 are longer. Running north-west from Luton, the road passes through Bedford, bypasses Rushden, Kettering and Market Harborough, continues through Leicester, Loughborough, Derby and Matlock before passing through the Peak District to Bakewell, Buxton, Stockport, Manchester, Salford, Pendleton, Irlams o' th' Height, Pendlebury, Swinton, Wardley, Linnyshaw, Walkden, Little Hulton, Westhoughton, Chorley, Preston, Lancaster, Kendal and Penrith before reaching Carlisle. South of Derby, the road is paralleled by the M1 motorway; between Manchester and Preston, the M6 and M61 motorways approximate its course; and from Preston to its northern terminus in Carlisle, it is paralleled by the M6 only. Between Der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
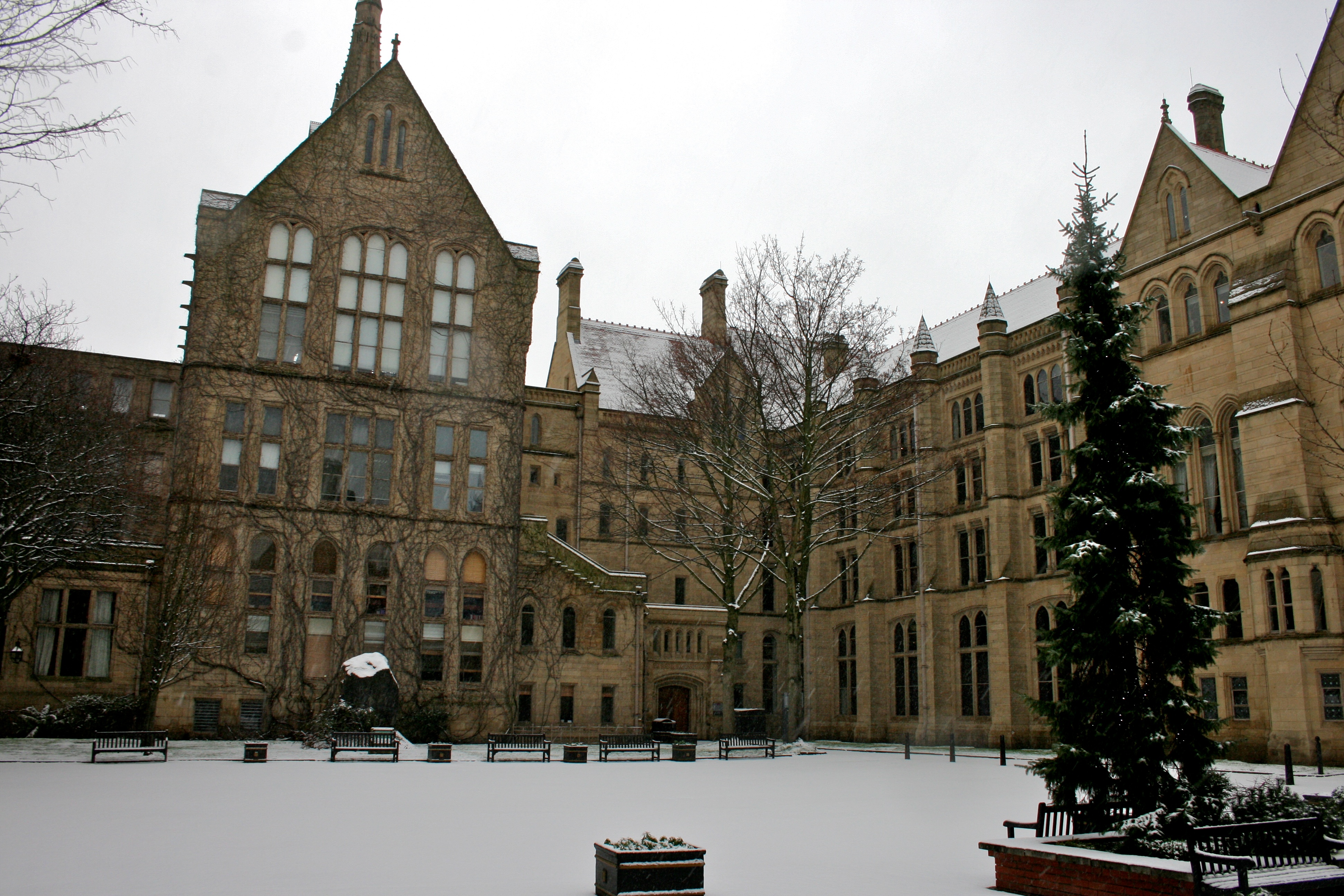
Manchester Metropolitan University
Manchester Metropolitan University is located in the centre of Manchester, England. The university has over 40,000 students and over 4,000 members of staff. It is home to four faculties (Arts and Humanities, Business and Law, Health and Education and Science and Engineering) and is one of the largest universities in the UK for biggest student population in 2020/21. History Manchester Metropolitan University was developed from mergers of various colleges with various specialisms, including technology, art and design. Its founding can be traced back to the Manchester Mechanics Institute, and the Manchester School of Design latterly known as the Manchester School of Art. The painter L. S. Lowry attended in the years after the First World War, where he was taught by the noted impressionist Adolphe Valette. Schools of Commerce (founded 1889), Education (f. 1878), and Domestic Science (f. 1880) were added alongside colleges at Didsbury, Crewe, Alsager and the former Domestic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The university owns and operates major cultural assets such as the Manchester Museum, The Whitworth art gallery, the John Rylands Library, the Tabley House, Tabley House Collection and the Jodrell Bank Observatory—a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The University of Manchester is considered a red brick university, a product of the civic university movement of the late 19th century. The current University of Manchester was formed in 2004 following the merger of the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (UMIST) and the Victoria University of Manchester. This followed a century of the two institutions working closely with one another. The University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology was founded in 1824 as the Manchester Mechanics' Institute, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UMIST
, mottoeng = By Knowledge and Work , established = 1824 , closed = 2004 (merged into newly formed University of Manchester in 2004) , affiliation = , endowment = , officer_in_charge = , chairman = , chancellor = , president = , vice-president = , superintendent = , provost = , vice_chancellor = , rector = , principal = , dean = , director = , head_label = , head = , faculty = , administrative_staff = 1,500 (2003) , students = , undergrad = 4,800 (2002) , postgrad = 1,700 (2002) , doctoral = , other = , city = Manchester , state = , province = , country = United Kingdom , coor = , campus = , former_names = Manchester Mechanics' Institute; Manchester Municipal School of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A34 Road (Great Britain)
The A34 is a major road in England. It runs from the A33 and M3 at Winchester in Hampshire, to the A6 and A6042 in Salford, close to Manchester City Centre. It forms a large part of the major trunk route from Southampton, via Oxford, to Birmingham, The Potteries and Manchester. For most of its length (together with the A5011 and parts of the A50, and A49), it forms part of the former Winchester–Preston Trunk Road. Improvements to the section of road forming the Newbury Bypass around Newbury were the scene of significant direct action environmental protests in the 1990s. It is 151 miles (243 km) long. Route The road is in two sections. The northern section runs south through Manchester and Cheadle, and bypasses Handforth, Wilmslow and Alderley Edge, before passing through Congleton, Newcastle-under-Lyme, and the southern suburbs of Stoke-on-Trent. It then continues south via Stone, Stafford, Cannock and Walsall, passes through the middle of Birmingham (where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
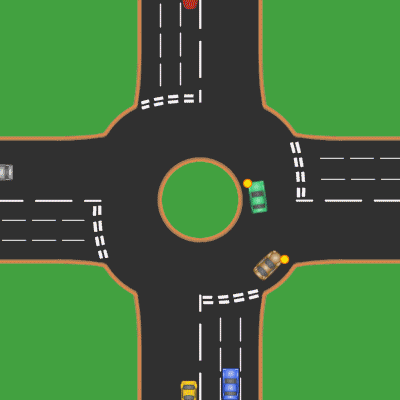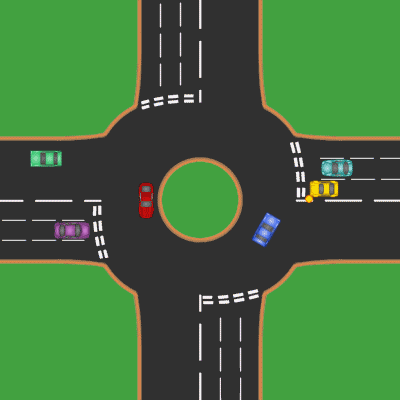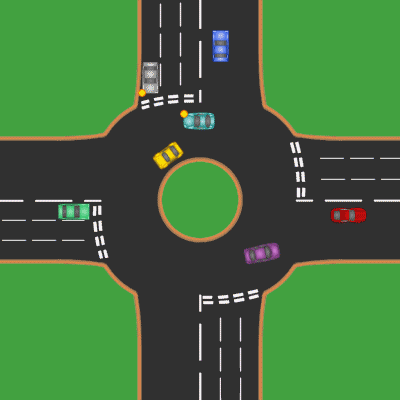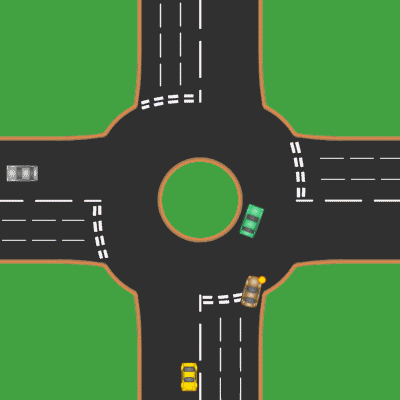
Roundabouts
A roundabout is a type of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junction.''The New Shorter Oxford English Dictionary,'' Volume 2, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1993), page 2632 Engineers use the term modern roundabout to refer to junctions installed after 1960 that incorporate various design rules to increase safety. Both modern and non-modern roundabouts, however, may bear street names or be identified colloquially by local names such as rotary or traffic circle. Compared to stop signs, traffic signals, and earlier forms of roundabouts, modern roundabouts reduce the likelihood and severity of collisions greatly by reducing traffic speeds and minimizing T-bone and head-on collisions. Variations on the basic concept include integration with tram or train lines, two-way flow, higher speeds and many others. For pedestrians, traffic exiting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)