|
Manchester Baby
The Manchester Baby, also called the Small-Scale Experimental Machine (SSEM), was the first electronic stored-program computer. It was built at the University of Manchester by Frederic Calland Williams, Frederic C. Williams, Tom Kilburn, and Geoff Tootill, and ran its first program on 21 June 1948. The Baby was not intended to be a practical computing engine, but was instead designed as a testbed for the Williams tube, the first truly random-access memory. Described as "small and primitive" 50 years after its creation, it was the first working machine to contain all the elements essential to a modern electronic digital computer. As soon as the Baby had demonstrated the feasibility of its design, a project was initiated at the university to develop it into a full-scale operational machine, the . The Mark 1 in turn quickly became the prototype for the Ferranti Mark 1, the world's first commercially available general-purpose computer. The Baby had a 32-bit Word (computer architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Computers
The Manchester computers were an innovative series of Von Neumann architecture, stored-program Computer, electronic computers developed during the 30-year period between 1947 and 1977 by a small team at the Victoria University of Manchester, University of Manchester, under the leadership of Tom Kilburn. They included the world's first stored-program computer, the world's first transistorised computer, and what was the world's fastest computer at the time of its inauguration in 1962. The project began with two aims: to prove the practicality of the Williams tube, an early form of computer storage, computer memory based on standard cathode-ray tubes (CRTs); and to construct a machine that could be used to investigate how computers might be able to assist in the solution of mathematical problems. The first of the series, the Manchester Baby, ran its first program on 21 June 1948. As the world's first stored-program computer, the Baby, and the Manchester Mark 1 developed from it, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Inverse
In mathematics, the additive inverse of an element , denoted , is the element that when added to , yields the additive identity, 0 (zero). In the most familiar cases, this is the number 0, but it can also refer to a more generalized zero element. In elementary mathematics, the additive inverse is often referred to as the opposite number, or its negative. The unary operation of arithmetic negation is closely related to '' subtraction'' and is important in solving algebraic equations. Not all sets where addition is defined have an additive inverse, such as the natural numbers. Common examples When working with integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers, the additive inverse of any number can be found by multiplying it by −1. The concept can also be extended to algebraic expressions, which is often used when balancing equations. Relation to subtraction The additive inverse is closely related to subtraction, which can be viewed as an add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (, abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 35 locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. The DLR acts as the German space agency and is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries. As of 2020, the German Aerospace Center had a national budget of €1.348 billion. Overview DLR has approximately 10.000 employees at 30 locations in Germany. Institutes and facilities are spread over 13 sites, as well as offices in Brussels, Paris and Washington, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing source code, code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the Domain (software engineering), application domain, details of programming languages and generic code library (computing), libraries, specialized algorithms, and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic. Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include Requirements analysis, analyzing requirements, Software testing, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
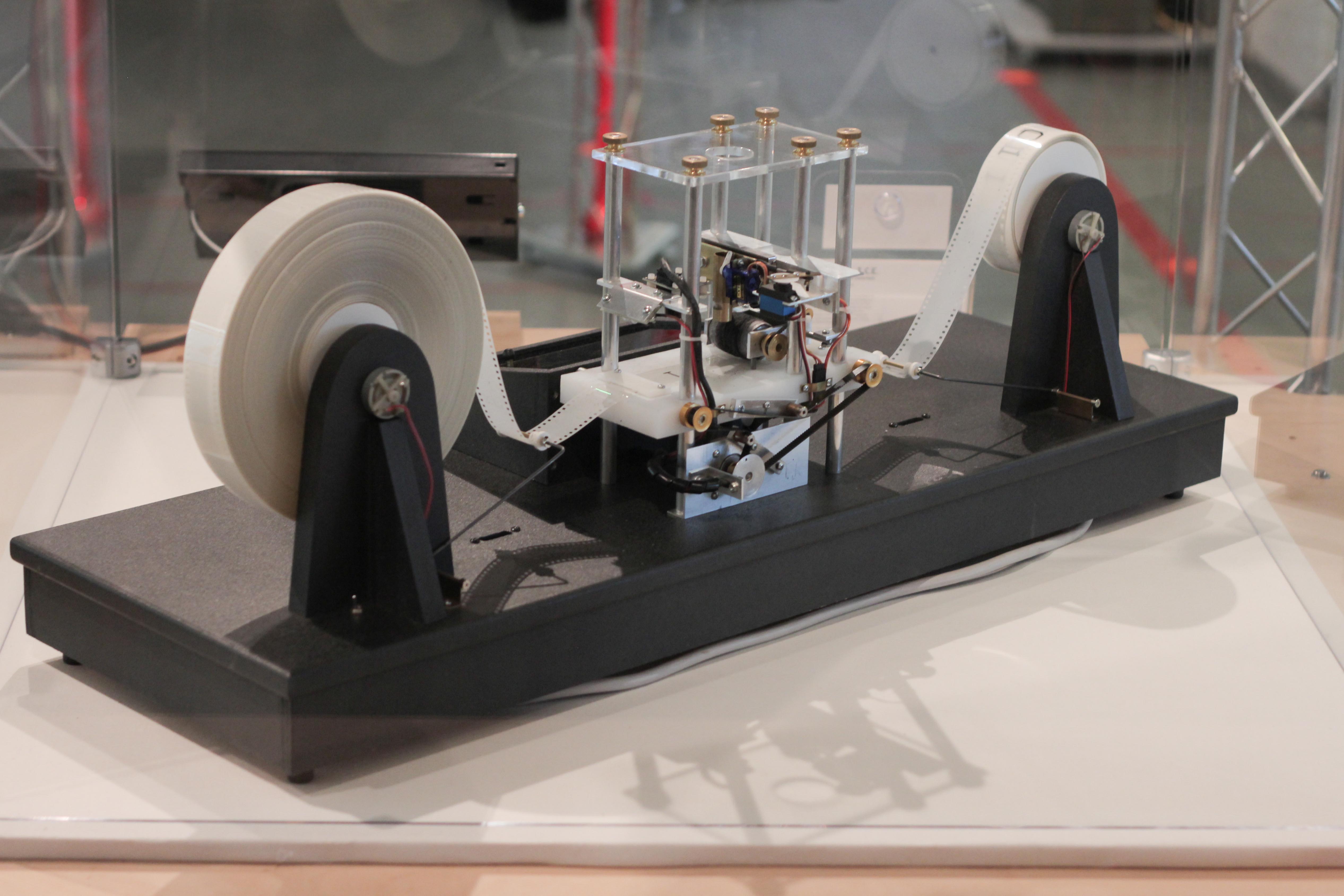
Z3 (computer)
The Z3 was a German electromechanical computer designed by Konrad Zuse in 1938, and completed in 1941. It was the world's first working Computer programming, programmable, fully automatic digital computer. The Z3 was built with 2,600 relays, implementing a 22-bit Word (data type), word length that operated at a clock frequency of about 5–10 Hertz, Hz. Program code was stored on punched celluloid, film. Initial values were entered manually. The Z3 was completed in Berlin in 1941. It was not considered vital, so it was never put into everyday operation. Based on the work of the German aerodynamics engineer Hans Georg Küssner (known for the Küssner effect), a "Program to Compute a Complex Matrix" was written and used to solve wing flutter problems. Zuse asked the German government for funding to replace the relays with fully electronic switches, but funding was denied during World War II since such development was deemed "not war-important". The original Z3 was destroyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konrad Zuse
Konrad Ernst Otto Zuse (; ; 22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, List of pioneers in computer science, pioneering computer scientist, inventor and businessman. His greatest achievement was the world's first programmable computer; the functional program-controlled Turing completeness, Turing-complete Z3 (computer), Z3 became operational in May 1941. Thanks to this machine and its predecessors, Zuse is regarded by some as the inventor and father of the modern computer. Zuse was noted for the S2 computing machine, considered the first process control computer. In 1941, he founded one of the earliest computer businesses, producing the Z4 (computer), Z4, which became the world's first commercial computer. From 1943 to 1945 he designed Plankalkül, the first high-level programming language. In 1969, Zuse suggested the concept of a digital physics, computation-based universe in his book (''Calculating Space''). Much of his early work was financed by his f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algorithm. The machine operates on an infinite memory tape divided into discrete mathematics, discrete cells, each of which can hold a single symbol drawn from a finite set of symbols called the Alphabet (formal languages), alphabet of the machine. It has a "head" that, at any point in the machine's operation, is positioned over one of these cells, and a "state" selected from a finite set of states. At each step of its operation, the head reads the symbol in its cell. Then, based on the symbol and the machine's own present state, the machine writes a symbol into the same cell, and moves the head one step to the left or the right, or halts the computation. The choice of which replacement symbol to write, which direction to move the head, and whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science. Born in London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated from University of Cambridge, King's College, Cambridge, and in 1938, earned a doctorate degree from Princeton University. During World War II, Turing worked for the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking centre that produced Ultra (cryptography), Ultra intelligence. He led Hut 8, the section responsible for German naval cryptanalysis. Turing devised techniques for speeding the breaking of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli Number
In mathematics, the Bernoulli numbers are a sequence of rational numbers which occur frequently in analysis. The Bernoulli numbers appear in (and can be defined by) the Taylor series expansions of the tangent and hyperbolic tangent functions, in Faulhaber's formula for the sum of ''m''-th powers of the first ''n'' positive integers, in the Euler–Maclaurin formula, and in expressions for certain values of the Riemann zeta function. The values of the first 20 Bernoulli numbers are given in the adjacent table. Two conventions are used in the literature, denoted here by B^_n and B^_n; they differ only for , where B^_1=-1/2 and B^_1=+1/2. For every odd , . For every even , is negative if is divisible by 4 and positive otherwise. The Bernoulli numbers are special values of the Bernoulli polynomials B_n(x), with B^_n=B_n(0) and B^+_n=B_n(1). The Bernoulli numbers were discovered around the same time by the Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, after whom they are named, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ada Lovelace
Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (''née'' Byron; 10 December 1815 – 27 November 1852), also known as Ada Lovelace, was an English mathematician and writer chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognise that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation. Lovelace was the only legitimate child of poet Lord Byron and reformer Anne Isabella Milbanke. All her half-siblings, Lord Byron#Children, Lord Byron's other children, were born out of wedlock to other women. Lord Byron separated from his wife a month after Ada was born and left England forever. He died in Greece when she was eight. Lady Byron was anxious about her daughter's upbringing and promoted Lovelace's interest in mathematics and logic in an effort to prevent her from developing her father's perceived insanity. Despite this, Lovelace remained interested in her father, naming her two sons Byron King-Noel, V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. Babbage is considered by some to be "List of pioneers in computer science, father of the computer". He is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the difference engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in his analytical engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. As part of his computer work, he also designed the first Printer (computing), computer printers. He had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his 1832 book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. He was an important figure in the social scene in London, and is credited with importing the "scientific soirée" from France with hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |