|
MEGF8
''Megf8'' also known as Multiple Epidermal Growth Factor-like Domains 8, is a protein coding gene that encodes a single pass membrane protein, known to participate in developmental regulation and cellular communication. It is located on chromosome 19 at the 49th open reading frame in humans (19q13.2). There are two isoform constructs known for MEGF8, which differ by a 67 amino acid indel. The isoform 2 splice version (analyzed throughout this page) is 2785 amino acids long, and predicted to be 296.6 kdal in mass. Isoform 1 is composed of 2845 amino acids and predicted to weigh 303.1 kdal. Using BLAST searches, orthologs were found primarily in mammals, but MEGF8 is also conserved in invertebrates and fishes, and rarely in birds, reptiles, and amphibians. A notably important paralog to multiple epidermal growth factor-like domains 8 is ATRNL1 (Attractin-like 1), which is also a single pass transmembrane protein, with several of the same key features and motifs as MEGF8, as indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
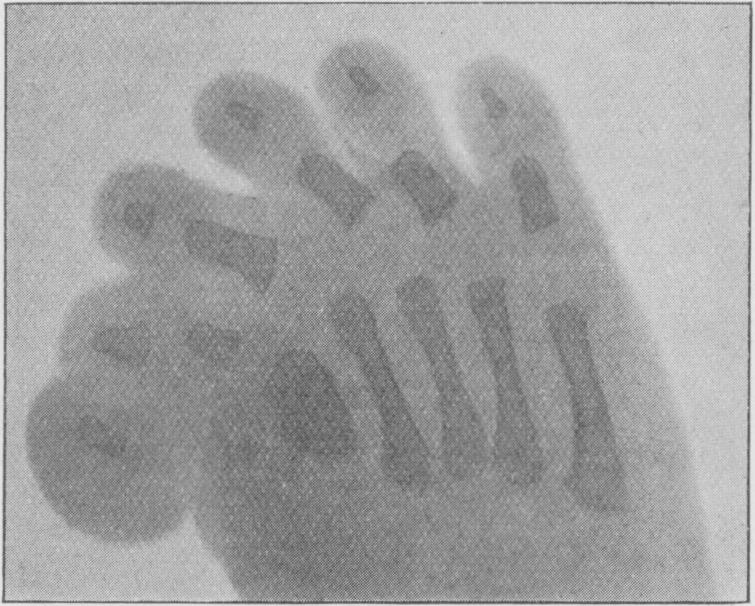
Carpenter Syndrome
Carpenter syndrome, also called acrocephalopolysyndactyly type II, is an extremely rare autosome, autosomal dominance (genetics), recessive congenital disorder characterized by craniofacial surgery, craniofacial malformations, obesity, syndactyly, and polydactyly. Acrocephalopolysyndactyly is a variation of acrocephalosyndactyly that presents with polydactyly. It was first characterized in 1909, and is named for George Alfred Carpenter. Presentation Carpenter syndrome presents several features: * Turricephaly – tower-shaped skull * Polydactyly – additional digits (fingers and toes) * Syndactyly – fused digits * Obesity * Reduced height * Undescended testes (in males) Intellectual disability is also common with the disorder, although some patients may have average intellectual capacity. Description Carpenter syndrome belongs to a rare genetic disorder known as acrocephalosyndactyly, (ACPS) (RN, 2007). There were originally five types of ACPS, but this number has been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frame
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an open reading frame (ORF) may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danio Rerio
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Danionidae of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often called a " tropical fish" although it is both tropical and subtropical). The zebrafish is an important and widely used vertebrate model organism in scientific research, particularly developmental biology, but also gene function, oncology, teratology, and drug development, in particular pre-clinical development. It is also notable for its regenerative abilities, and has been modified by researchers to produce many transgenic strains. Taxonomy The zebrafish is a derived member of the genus '' Brachydanio'', of the family Cyprinidae. It has a sister-group relationship with '' Danio aesculapii''. Zebrafish are also closely related to the genus '' Devario'', as demonstrated by a phylogenetic tree of close species. Distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelch Motif
The Kelch motif is a region of protein sequence found widely in proteins from bacteria and eukaryotes. This sequence motif is composed of about 50 amino acid residues which form a structure of a four stranded beta-sheet "blade". This sequence motif is found in between five and eight tandem copies per protein which fold together to form a larger circular solenoid structure called a beta-propeller domain. Proteins containing Kelch motifs The Kelch motif is widely found in eukaryotic and bacterial species. Notably the human genome contains around 100 proteins containing the Kelch motif. Within individual proteins the motif occurs multiple times. For example, the motif appears 6 times in ''Drosophila'' egg-chamber regulatory protein. The motif is also found in mouse protein MIPP and in a number of poxviruses. In addition, kelch repeats have been recognised in alpha- and beta-scruin, in galactose oxidase from the fungus '' Dactylium dendroides'', and in the ''Escherichia col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EGF-like Domain
The EGF-like domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain, which derives its name from the epidermal growth factor where it was first described. It comprises about 30 to 40 amino-acid residues and has been found in a large number of mostly animal proteins. Most occurrences of the EGF-like domain are found in the extracellular domain of membrane-bound proteins or in proteins known to be secreted. An exception to this is the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase. The EGF-like domain includes 6 cysteine residues which in the epidermal growth factor have been shown to form 3 disulfide bonds. The structures of 4-disulfide EGF-domains have been solved from the laminin and integrin proteins. The main structure of EGF-like domains is a two-stranded β-sheet followed by a loop to a short C-terminal, two-stranded β-sheet. These two β-sheets are usually denoted as the major (N-terminal) and minor (C-terminal) sheets. EGF-like domains frequently occur in numerous tandem copies in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CUB Domain
CUB domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain. The CUB domain (for complement C1r/C1s, Uegf, Bmp1) is a structural motif of approximately 110 residues found almost exclusively in extracellular and plasma membrane-associated proteins, many of which are developmentally regulated. These proteins are involved in a diverse range of functions, including complement activation, developmental patterning, tissue repair, axon guidance and angiogenesis, cell signalling, fertilisation, haemostasis, inflammation, neurotransmission, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and tumour suppression. Many CUB-containing proteins are peptidases belonging to MEROPS peptidase families M12A (astacin) and S1A (chymotrypsin). Examples Proteins containing a CUB domain include: * Mammalian complement subcomponents C1s/C1r, which form the calcium-dependent complex C1, the first component of the classical pathway of the complement system. * '' Cricetidae sp.'' (Hamster) serine protease Casp, which deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PHYRE2
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as ''fire'') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1,500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques (see protein threading), it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Description The Phyre and Phyre2 servers predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein sequence using the principles and techniques of homology modeling. Because the structure of a protein is more conserved in evolution than its amino acid sequence, a protein sequence of interest (the target) can be modeled with reasonable accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sequence Alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis and can highlight homologous features between sequences. Alignments highlight mutation events such as point mutations (single amino acid or nucleotide changes), insertion mutations and deletion mutations, and alignments are used to assess sequence conservation and infer the presence and activity of protein domains, tertiary structures, secondary structures, and individual amino acids or nucleotides. Multiple sequence alignments require more sophisticated methodologies than pairwise alignments, as they are more computationally complex. Most multiple sequence alignment programs use heuristic methods rather than global optimization because identifying the optimal alignment between more than a few sequences of moderate length is prohibiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide Bonds
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups. In inorganic chemistry, the anion appears in a few rare minerals, but the functional group has tremendous importance in biochemistry. Disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. Compounds of the form are usually called '' persulfides'' instead. Organic disulfides Structure Disulfides have a C–S–S–C dihedral angle approaching 90°. The S–S bond length is 2.03 Å in diphenyl disulfide, similar to that in elemental sulfur. Disulfides are usually symmetric but they can also be unsymmetric. Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organosulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematostella Vectensis
The starlet sea anemone (''Nematostella vectensis'') is a species of small sea anemone in the family Edwardsiidae native to the east coast of the United States, with introduced populations along the coast of southeast England and the west coast of the United States (class ''Anthozoa'', phylum ''Cnidaria'', a sister group of Bilateria). Populations have also been located in Nova Scotia, Canada. This sea anemone is found in the shallow brackish water of coastal lagoons and salt marshes where its slender column is usually buried in the mud and its tentacles exposed. Its genome has been sequenced and it is cultivated in the laboratory as a model organism, but the IUCN has listed it as being a "Vulnerable species" in the wild. Description The starlet sea anemone has a bulbous basal end and a contracting column that ranges in length from less than . There is a fairly distinct division between the scapus, the main part of the column, and the capitulum, the part just below the crown of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus
''Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' is a species of sea urchin in the family Strongylocentrotidae commonly known as the purple sea urchin. It lives along the eastern edge of the Pacific Ocean extending from Ensenada, Mexico, to British Columbia, Canada. This sea urchin species is deep purple in color, and lives in lower inter-tidal and nearshore sub-tidal communities. Its eggs are orange when secreted in water. January, February, and March function as the typical active reproductive months for the species. Sexual maturity is reached around two years. It normally grows to a diameter of about 10 cm (4 inches), consisting of an exoskeleton called a test. They may live as long as 70 years. ''Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' is used as a model organism and its genome was the first echinoderm genome to be sequenced. Role in biomedical research The initial discovery of three distinct eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases was made using ''S. purpuratus'' as a model org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Pulex
''Daphnia pulex'' is the most common species of water flea. It has a cosmopolitan distribution: the species is found throughout the Americas, Europe, and Australia. It is a model species, and was the first crustacean to have its genome sequenced. Description ''D. pulex'' is an arthropod whose body segments are difficult to distinguish. It can only be recognised by its appendages (only ever one pair per segment), and by studying its internal anatomy. The head is distinct and is made up of six segments, which are fused together even as an embryo. It bears the arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts, and two pairs of antenna (biology), antennae, the second pair of which is enlarged into powerful organs used for swimming. No clear division is seen between the thorax and abdomen, which collectively bear five pairs of appendages. The shell surrounding the animal extends posteriorly into a Spine (zoology), spine. Like most other ''Daphnia'' species, ''D. pulex'' reproduces by cyclical parthenog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |