|
Lichades
Lichades or Lichadonisia ( el, Λιχάδες or Λιχαδονήσια) is an island complex off the north west of Euboea, in the North Euboean Gulf. The islands located opposite Lichada cape in the north-western extreme of Euboea and opposite of small town Kamena Vourla in Central Greece mainland. Administratively, they belong to Istiaia-Aidipsos municipality, in Euboea regional unit. Description The complex consists of seven islands and islets. The biggest of them is Manolia and is the only that had residents in the past. The other six are Strongyli, Mikri Strongyli, Steno, Vagia, Vorias and Limani. The biggest island, Manolia has a beautiful beach and is visited by many tourists in the summer. In the past had a small settlement but nowadays is forsaken. Strongyli is the second largest island and on top has a big lighthouse. History Lichades were formed after the huge earthquake of 426 B.C., when the land between them sank in the Euboean Sea. According to Greek mythology, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Euboean Gulf
The North Euboean Gulf ( el, Βόρειος Ευβοϊκός Κόλπος, ''Voreios Evvoïkos Kolpos'') is a gulf of the Aegean Sea. It separates the northern part of the island Euboea from the mainland of Central Greece. The narrow Euripus Strait, near Chalcis, connects the gulf to the south with the South Euboean Gulf. To the north, the gulf is connected with the Malian Gulf. The total length is approximately 60 km and its width ranges from approximately 10 to 20 km. It runs diagonally from northwest to southeast. Islands *Lichades (largest islands: Manolia, Strongyli), Atalanti Island, Ktyponisi Bays by the gulf * Agias Kyriakis Bay, south Populated places by the gulf *Drosia, south *Livanates, southwest *Kamena Vourla, northwest *Nea Artaki Nea Artaki ( el, Νέα Αρτάκη) is a town and a former municipality on the island Euboea, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is a municipal unit, part of the municipality Chalcis. The municipal unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Echinades (322 BC)
The Battle of the Echinades was one of the naval battles of the Lamian War (323–322 BC), fought between the Macedonian navy under Cleitus the White and the Athenian navy. Background The Lamian War or Hellenic War was fought by a coalition of cities including Athens and the Aetolian League against Macedon following the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC. The southern Greek city-states had never fully acquiesced to Macedonian hegemony, imposed through force of arms, but it was one of Alexander's last acts, the Exiles Decree of 324 BC that provoked open resentment, especially in Athens, where preparations for war began even before Alexander's death. The Exiles Decree stipulated the return of all exiles and the restoration of their citizenship and property, and was perceived as a direct violation of the city-states' autonomy by Alexander. To the Athenians in particular, the decree was anathema as it meant that the island of Samos, an Athenian possession since 366 BC and set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
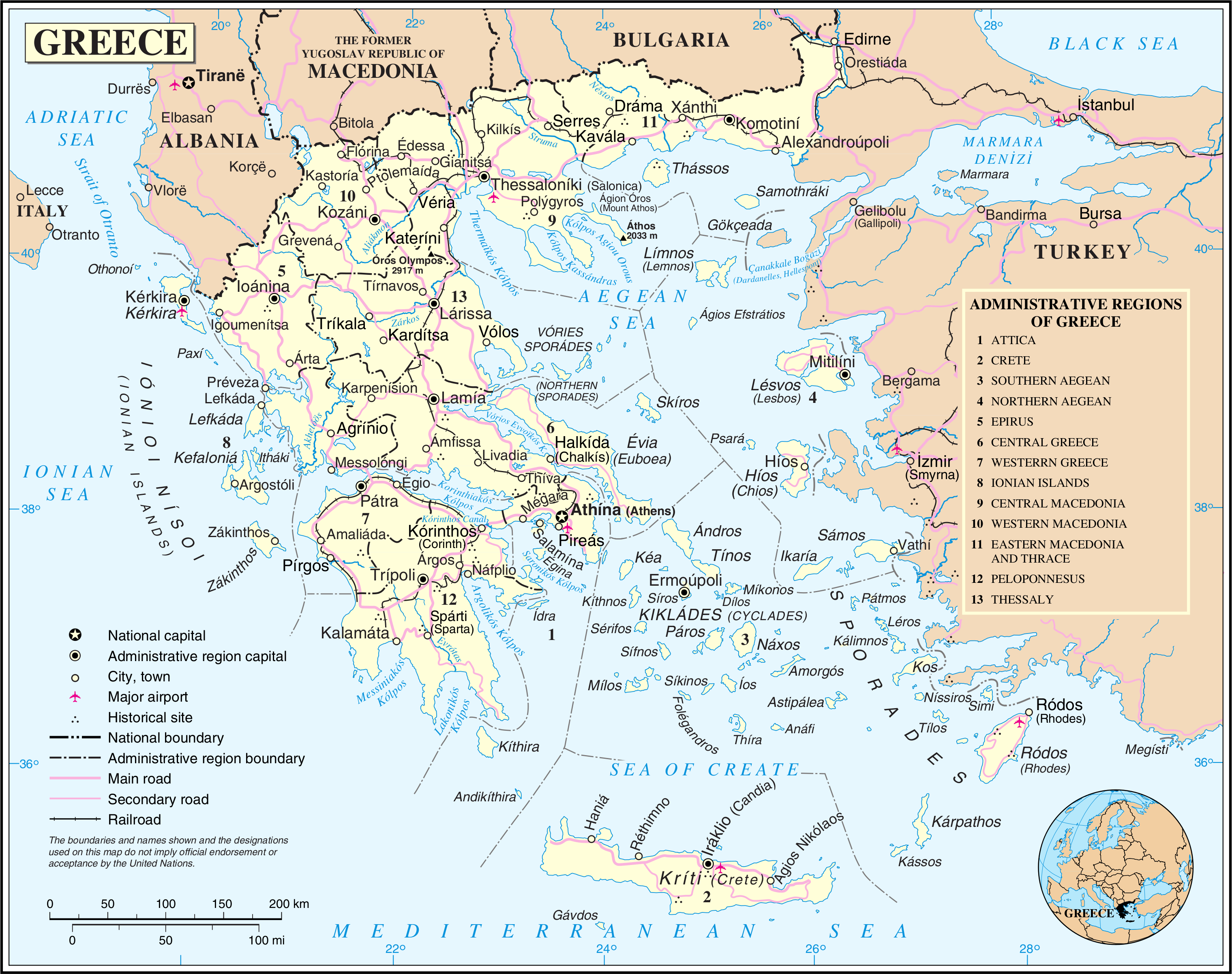
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece ( el, περιφέρειες, translit=periféries) are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was often arbitrary; not all of the pre-1986 traditional historical-geographic regions had official administrative bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan and Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its aftermath became part of the oral tradition of Homer's epic poems, the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey''. Two poems by Homer's near contemporary Hesiod, the ''Theogony'' and the '' Works and Days'', contain accounts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassocracy
A thalassocracy or thalattocracy sometimes also maritime empire, is a state with primarily maritime realms, an empire at sea, or a seaborne empire. Traditional thalassocracies seldom dominate interiors, even in their home territories. Examples of this were the Phoenician states of Tyre, Sidon and Carthage, and the Italian maritime republics of Venice and Genoa of the Mediterranean; the Chola dynasty of India and the Austronesian states of Srivijaya, the Omani Empire and Majapahit of Maritime Southeast Asia. Thalassocracies can thus be distinguished from traditional empires, where a state's territories, though possibly linked principally or solely by the sea lanes, generally extend into mainland interiors in a tellurocracy ("land-based hegemony"). The term ''thalassocracy'' can also simply refer to naval supremacy, in either military or commercial senses. The Ancient Greeks first used the word ''thalassocracy'' to describe the government of the Minoan civilization, whose po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deianira
Deianira, Deïanira, or Deianeira (; Ancient Greek: Δηϊάνειρα, ''Dēiáneira'', or , ''Dēáneira'', ), also known as Dejanira, is a Calydonian princess in Greek mythology whose name translates as "man-destroyer" or "destroyer of her husband". She was the wife of Heracles and, in late Classical accounts, his unwitting murderer, killing him with the poisoned Shirt of Nessus. She is the main character in Sophocles' play '' Women of Trachis''. Family Deianira was the daughter of Althaea and her husband Oeneus (whose name means "wine-man"), the king of Calydon (after the wine-god gave the king the vine to cultivate), and the half-sister of Meleager. Her other siblings were Toxeus, Clymenus, Periphas, Agelaus (or Ageleus), Thyreus (or Phereus or Pheres), Gorge, Eurymede and Melanippe. In some accounts, Deianira was the daughter of King Dexamenus of Olenus and thus, sister to Eurypylus, Theronice and Theraephone. Others called this daughter of Dexamenus as Mn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures. The Romans adapted the Greek hero's iconography and myths for their literature and art under the name ''Hercules''. In later Western art and literature and in popular culture, ''Hercules'' is more commonly used than ''Heracles'' as the name of the hero. Hercules is a multifaceted figure with contradictory characteristics, which enabled later artists and writers to pick and choose how to represent him. This article provides an introduction to representations of Hercules in the later tradition. Mythology Birth and early life In Roman mythology, although Hercules was seen as the champion of the weak and a great protector, his personal problems started at birth. Juno sent two witches to prevent the birth, but they were tricked by one of Alcmene's servants and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
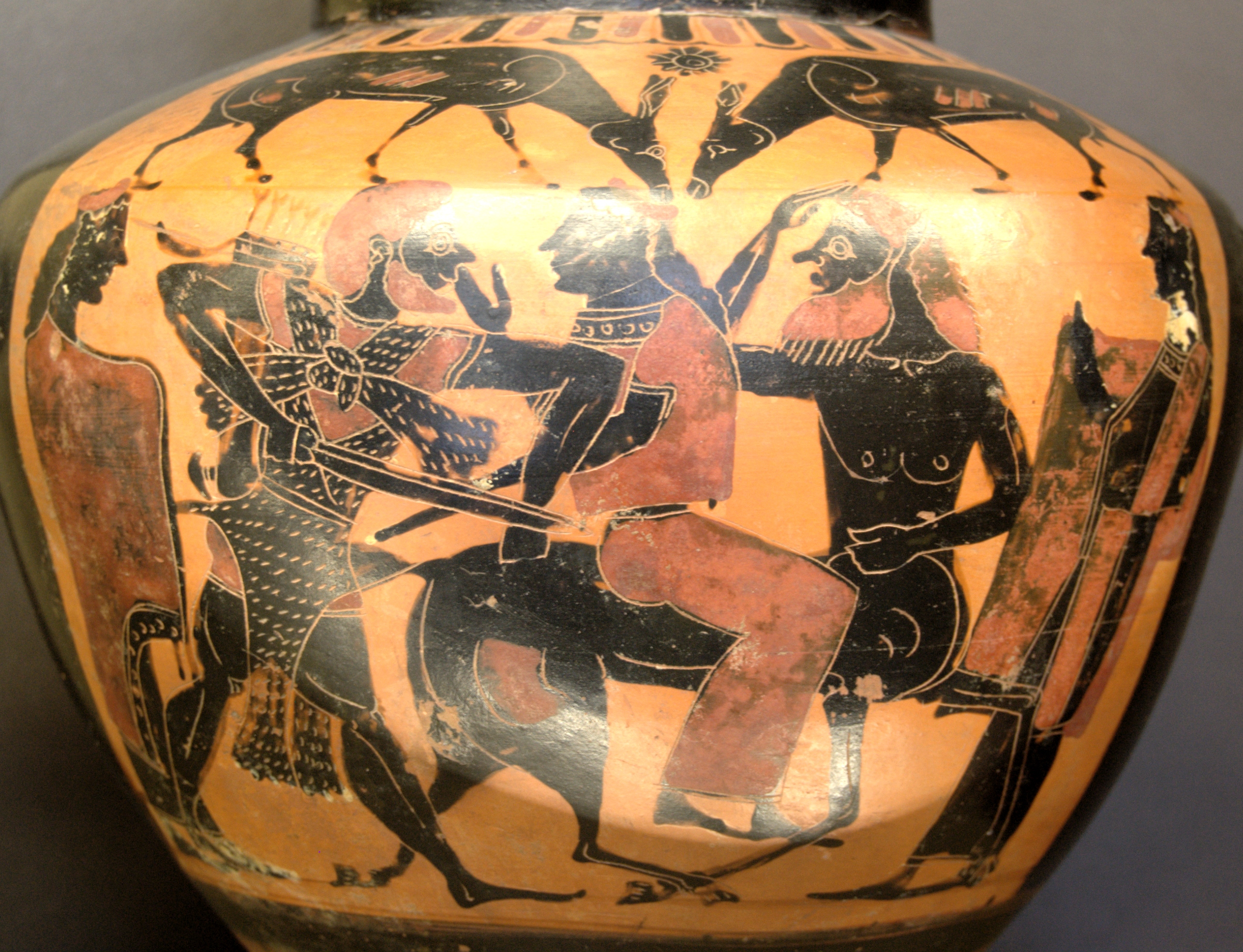
Lichas
:''Lichas can also refer to Lichas the Spartan, who discovered the bones of Orestes, or a genus of trilobite'' In Greek mythology, Lichas (; el, Λίχας) was Hercules's servant, who brought the poisoned shirt from Deianira to Hercules because of Deianira's jealousy of Iole, which killed him. Mythology Lichas brought to his master the deadly garment, and as a punishment, was thrown by him into the sea, where the Lichadian islands, between Euboea and the coast of Locris, were believed to have derived their name from him. The story is recounted in Sophocles' '' Women of Trachis'' and Ovid's ''Metamorphoses''.Ovid. ''Metamorphoses, Book 9.155 & 211'' compare with Hyginus. ''Fabulae'', 36 Ovid's account Cape Lichada is said to be where Hercules flung Lichas into the sea: So, in his frenzy, as he wandered there,he chanced upon the trembling Lichas, crouchedin the close covert of a hollow rock.Then in a savage fury he cried out,"Was it you, Lichas, brought this fatal gif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
426 BC Malian Gulf Tsunami
The 426 BC Malian Gulf tsunami devastated the coasts of the Malian and Euboean Gulfs, Greece, in the summer of 426 BC. Thucydides inquired into its causes, and concluded that the tsunami must have been caused by an earthquake.Thucydides"A History of the Peloponnesian War", 3.89.2–5/ref> He was thus historically the first known to correctly interpret the cause of a tsunami as a preceding geological event. Herodotus, in contrast, had attributed the Potidaea tsunami to the divine wrath of Poseidon. Ancient records The Malian Gulf tsunami was caused by one of a series of earthquakes in the summer of 426 BC which affected the course of the Peloponnesian War by forcing the advancing Spartans to abort their planned invasion of Attica.Thucydides“A History of the Peloponnesian War”, 3.89.1/ref> Strabo reported that throughout Greece parts of islands were submerged, rivers permanently displaced and towns devastated. Strabo"Geography", 1.3.20/ref> The tsunami itself hit the coas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Greece
Continental Greece ( el, Στερεά Ελλάδα, Stereá Elláda; formerly , ''Chérsos Ellás''), colloquially known as Roúmeli (Ρούμελη), is a traditional geographic region of Greece. In English, the area is usually called Central Greece, but the equivalent Greek term (Κεντρική Ελλάδα, ''Kentrikí Elláda'') is more rarely used. It includes the southern part of the Greek mainland (sans the Peloponnese), as well as the offshore island of Euboea. Since 1987, its territory has been divided among the administrative regions of Central Greece and Attica, and the regional unit (former prefecture) of Aetolia-Acarnania in the administrative region of Western Greece. Etymology The region has traditionally been known as ''Roúmeli'' (Ρούμελη), a name deriving from the Turkish word '' Rūm-eli'', meaning "the land of the Rūm he Romans, i.e. the Byzantine Greeks">Byzantine_Greeks.html" ;"title="he Romans, i.e. the Byzantine Greeks">he Romans, i.e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |