|
Laccoliths
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apart the host rock strata. The pressure of the magma is high enough that the overlying strata are forced upward, giving the laccolith its dome-like form. Over time, erosion can expose the solidified laccolith, which is typically more resistant to weathering than the host rock. The exposed laccolith then forms a hill or mountain. The Henry Mountains of Utah, US, are an example of a mountain range composed of exposed laccoliths. It was here that geologist Grove Karl Gilbert carried out pioneering field work on this type of intrusion. Laccolith mountains have since been identified in many other parts of the world. Description A laccolith is a type of igneous intrusion, formed when magma forces its way upwards through the Earth's crust b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laccolith Shape
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apart the host rock strata. The pressure of the magma is high enough that the overlying strata are forced upward, giving the laccolith its dome-like form. Over time, erosion can expose the solidified laccolith, which is typically more resistant to weathering than the host rock. The exposed laccolith then forms a hill or mountain. The Henry Mountains of Utah, US, are an example of a mountain range composed of exposed laccoliths. It was here that geologist Grove Karl Gilbert carried out pioneering field work on this type of intrusion. Laccolith mountains have since been identified in many other parts of the world. Description A laccolith is a type of igneous intrusion, formed when magma forces its way upwards through the Earth's crust b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laccolith
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apart the host rock strata. The pressure of the magma is high enough that the overlying strata are forced upward, giving the laccolith its dome-like form. Over time, erosion can expose the solidified laccolith, which is typically more resistant to weathering than the host rock. The exposed laccolith then forms a hill or mountain. The Henry Mountains of Utah, US, are an example of a mountain range composed of exposed laccoliths. It was here that geologist Grove Karl Gilbert carried out pioneering field work on this type of intrusion. Laccolith mountains have since been identified in many other parts of the world. Description A laccolith is a type of igneous intrusion, formed when magma forces its way upwards through the Earth's crust but co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained ( phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrusion Types
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained ( phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrusions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained ( phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Mountains
The Henry Mountains is a mountain range located in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Utah that runs in a generally north-south direction, extending over a distance of about . They were named by Almon Thompson in honor of Joseph Henry, the first secretary of the Smithsonian Institution. The nearest town of any size is Hanksville, Utah, which is north of the mountains. The Henry Mountains were the last mountain range to be added to the map of the 48 contiguous U.S. states (1872), and before their official naming by Thompson were sometimes referred to as the "Unknown Mountains." In Navajo, the range is still referred to as ''Dził Bizhiʼ Ádiní'' ("mountain whose name is missing"). The great majority of the land within the Henry Mountains is owned by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management. A herd of 350 American Bison roams freely in the Henrys. Geography and geology The range is clustered into two main groups, with Highway 276 dividing the two portions. The northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
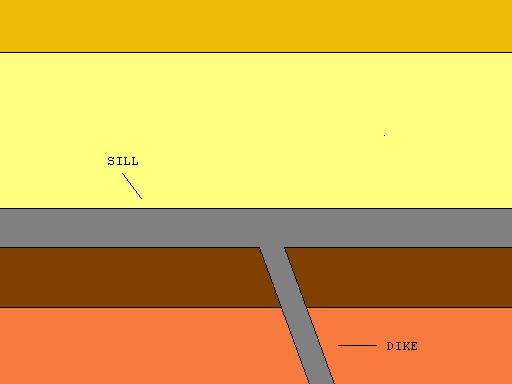
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A ''sill'' is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that a sill does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex . and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existing beddin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithostatic Pressure
Pressure is force magnitude applied over an area. Overburden pressure is a geology term that denotes the pressure caused by the weight of the overlying layers of material at a specific depth under the earth's surface. Overburden pressure is also called lithostatic pressure, or vertical stress. In a stratigraphic layer that is in hydrostatic equilibrium; the overburden pressure at a depth z, assuming the magnitude of the gravity acceleration is approximately constant, is given by: P(z) = P_0 + g \int_^ \rho(z) \, dz Where: * z is the depth in meters. * P(z) is the overburden pressure at depth z. * P_0 is the pressure at the surface. * \rho(z) is the density of the material above the depth z. * g is the gravity acceleration in m/s^2 . In deep-earth geophysics/geodynamics, gravitational acceleration varies significantly over depth and g should not be assumed to be constant, and should be inside the integral. Some sections of stratigraphic layers can be sealed or isolated. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the fourth-largest state by area, the eighth-least populous state, and the third-least densely populated state. Its state capital is Helena. The western half of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges found throughout the state. Montana has no official nickname but several unofficial ones, most notably "Big Sky Country", "The Treasure State", "Land of the Shining Mountains", and "The Last Best Place". The economy is primarily based on agriculture, including ranching and cereal grain farming. Other significant economic resources include oil, gas, coal, mining, and lumber. The health ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shonkin Sag
The Shonkin Sag is a prehistoric fluvioglacial landform located along the northern edge of the Highwood Mountains in the state of Montana in the United States. The Sag is a river channel formed by the Missouri River and glacial meltwater pouring from Glacial Lake Great Falls. It is one of the most famous prehistoric meltwater channels in the world. Location and size Shonkin Sag is located in central Montana. It begins south of Highwood, Montana, (about east of the city of Great Falls) and runs in an easterly direction for about until it reaches the Judith River."Societies and Academies: Geological Society of Washington." ''Science.'' May 7, 1895, p. 559-560. It varies from to in width and is about deep. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheet Intrusion
A sheet intrusion, or tabular intrusion, is a planar sheet of roughly the same thickness, that forms inside a pre-existing rock.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak When it cuts into another unlayered mass, or across layers, it is called a " dike". When it is formed between layers in a layered rock mass, it is called a "sill". An igneous sheet intrusion is formed where a mass of molten magma takes advantage of a pre-existing linear feature in a host rock, such as a long rupture or fault, and forces its way into these spaces. Thus the magma, intruded between existing rocks, solidifies into large thin sheets of igneous rock. They are among the most extensive igneous features on Earth, in the form of dikes, laccolith A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apar ...s, cone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |