|
LMS Hughes Crab
The London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Hughes Crab or Horwich Mogul is a class of mixed-traffic 2-6-0 steam locomotive built between 1926 and 1932. They are noted for their appearance with large steeply-angled cylinders to accommodate a restricted loading gauge. Overview Designed by George Hughes, Chief Mechanical Engineer of the LMS, and built at the ex-L&YR works at Horwich and the ex- LNWR works at Crewe. The inspiration came from a Caledonian Railway design at the grouping, however the cylinders were too large for the LMS's English section's loading gauge, resulting in Hughes having to adapt the concept. They were put into service by his successor, Henry Fowler. The design incorporated a number of advanced features for the time such as long travel valves, compensated brake gear, a new design of tender and a new boiler, the latter based on the one fitted to Hughes's four-cylinder Baltic tank locomotives built at Horwich. Fowler tried to have the design alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Hughes (engineer)
George Hughes (9 October 1865 – 27 October 1945) was an English locomotive engineer, and chief mechanical engineer (CME) of the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) and the London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS). Biography George Hughes was born on 9 October 1865 and served a premium apprenticeship at the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Crewe Works between 1882 and 1886. At the L&YR he started in the test room, and Bulleid notes the L&YR's John Aspinall was most pleased with his work there. He progressed through various positions at the L&YR culminating in achieving in becoming chief mechanical engineer in March 1904. He introduced the L&YR locomotive classification system around 1919. When the L&YR amalgamated into the LNWR in January 1922 he became the CME of the combined group and was appointed the CME of the LMS on its formation at the 1923 grouping. He retired in July 1925 after only two and a half years at the LMS. He was succeeded by Henry Fowle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was a major Scottish railway company. It was formed in the early 19th century with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh and Aberdeen, with a dense network of branch lines in the area surrounding Glasgow. It was absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway in 1923. Many of its principal routes are still used, and the original main line between Carlisle and Glasgow is in use as part of the West Coast Main Line railway (with a modified entry into Glasgow itself). Introduction In the mid-1830s, railways in England evolved from local concerns to longer routes that connected cities, and then became networks. In Scotland it was clear that this was the way forward, and there was a desire to connect the Central Belt to the incipient English network. There was controversy over the route that such a line might take, but the Caledonian Railway was formed on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railfan
A railfan, rail buff or train buff (American English), railway enthusiast, railway buff or trainspotter ( Australian/British English), or ferroequinologist is a person who is recreationally interested in trains and rail transport systems. Railfans often combine their interest with other hobbies, especially photography and videography, radio scanning, railway modelling, studying railroad history and participating in railway station and rolling stock preservation efforts. There are many magazines and websites dedicated to railfanning and railway enthusiasts, including '' Trains'', '' Railfan & Railroad'', ''The Railway Magazine'', ''Locomotive Magazine'', and ''Railway Gazette International''. Other names In the United Kingdom, rail enthusiasts are often called trainspotters or anoraks. The term ''gricer'' has been used in the UK since at least 1969 and is said to have been current in 1938 amongst members of the Manchester Locomotive Society, according to the ''Oxford Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Settle Rail Crash
The Settle rail crash was a railway accident that occurred at Langcliffe near Settle, England, on the night of 21 January 1960 in which two trains collided, killing five people and injuring eight more. The accident BR Standard Class 7 No 70052 ''Firth of Tay'' was leading the 21:05 8-carriage express train from Glasgow St Enoch to London St Pancras. On the descent from Ais Gill Aisgill is the southernmost of the hamlets that form the parish of Mallerstang in the English county of Cumbria. It is on the B6259 road, at the head of Mallerstang dale, just before the boundary between Cumbria and North Yorkshire. The highest ... summit, the driver heard a repeated knocking which he thought came from the connecting rods where they were connected to the locomotive's drive wheels. He reduced speed and later stopped the train in a gale-force wind while it was snowing at Garsdale, but was unable to find the cause of the noise. He continued south at what he thought was less than ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a historic county in southeast England. Its area is almost entirely within the wider urbanised area of London and mostly within the ceremonial county of Greater London, with small sections in neighbouring ceremonial counties. Three rivers provide most of the county's boundaries; the Thames in the south, the Lea to the east and the Colne to the west. A line of hills forms the northern boundary with Hertfordshire. Middlesex county's name derives from its origin as the Middle Saxon Province of the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Essex, with the county of Middlesex subsequently formed from part of that territory in either the ninth or tenth century, and remaining an administrative unit until 1965. The county is the second smallest, after Rutland, of the historic counties of England. The City of London became a county corporate in the 12th century; this gave it self-governance, and it was also able to exert political control over the rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS 1933 Renumbering Scheme
A number of different numbering and classification schemes were used for the locomotives owned by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) and its constituent companies; this page explains the principal systems that were used. The following abbreviations for the constituent companies are used on this page: * ''Principal Constituents'' Caledonian Railway (CR), Furness Railway (FR), Glasgow and South Western Railway (GSWR), Highland Railway (HR), Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (LYR), London and North Western Railway (LNWR), Maryport and Carlisle Railway (MCR), Midland Railway (MR), North London Railway (NLR) and North Staffordshire Railway (NSR) * ''Minor Companies'' Cleator and Workington Junction Railway (C&WJR), Glasgow and Paisley Joint Railway (G&PJR), Knott End Railway (KER), Stratford-upon-Avon and Midland Junction Railway (S&MJR), and Wirral Railway (WR) * ''Later Additions'' Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway (S&DJR) - absorbed October 1936 For informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS Stanier Mogul
The London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Stanier Class 5 2-6-0 or Stanier Mogul is a class of 2-6-0 mixed traffic steam locomotive. Forty were built between October 1933 and March 1934. Overview Although all built at Crewe Works, they were designed at Horwich Works and were developed from the Horwich Mogul, the LMS Hughes Crab, LMS Hughes ''Crab'' 2-6-0. They had the addition of several features brought over from the Great Western Railway by newly arrived Chief Mechanical Engineer William Stanier, most notably the taper boiler. (Stanier would have been familiar with the GWR 4300 Class). In an effort to please Stanier, Horwich had designed in a GWR style top-feed cover and locomotive 13245 appeared with the feature fitted. Stanier was not at all pleased, ordering it promptly removed and replaced with the normal LMS cover. Due to a higher boiler pressure than the ''Crabs'' the cylinders were 3" smaller in diameter and so the cylinders were able to be mounted horizontally: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Stanier
Sir William Arthur Stanier, (27 May 1876 – 27 September 1965) was a British railway engineer, and was chief mechanical engineer of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway. Biography Sir William Stanier was born in Swindon, where his father worked for the Great Western Railway (GWR) as William Dean's Chief Clerk, and educated at Swindon High School and also, for a single year, at Wycliffe College. In 1891 he followed his father into a career with the GWR, initially as an office boy and then for five years as an apprentice in the workshops. Between 1897 and 1900 he worked in the Drawing Office as a draughtsman, before becoming Inspector of Materials in 1900. In 1904, George Jackson Churchward appointed him as Assistant to the Divisional Locomotive Superintendent in London. In 1912 he returned to Swindon to become the Assistant Works Manager and in 1920 was promoted to the post of Works Manager. In late 1931, he was "headhunted" by Sir Josiah Stamp, chairman of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Mechanical Engineer
Chief mechanical engineer and locomotive superintendent are titles applied by British, Australian, and New Zealand railway companies to the person ultimately responsible to the board of the company for the building and maintaining of the locomotives and rolling stock. In Britain, the post of ''locomotive superintendent'' was introduced in the late 1830s, and ''chief mechanical engineer'' in 1886. Emerging professional roles In the early Victorian era, projected canal or railway schemes were prepared by groups of promoters who hired specialists such as civil engineers, surveyors, architects or contractors to survey a route; and this resulted in the issue of a prospectus setting out their proposals. Provided that adequate capital could be raised from potential investors, agreements obtained from the landowners along the proposed route and, in Britain, an Act of Parliament obtained (different terminology is used in other countries), then construction might begin either by a new compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugby Locomotive Testing Station
The Rugby Locomotive Testing Station was a British railway testing plant in Rugby, Warwickshire. Originally envisioned by Sir Nigel Gresley as a joint LMS-LNER operation, construction was started in the late 1930s but then deferred by the war. It was eventually opened in 1948 after both its owners had become constituents of British Railways. The location was one with access to both LMS and LNER main lines (West Coast Main Line and Great Central Main Line respectively. The GWR meanwhile had their own testing plant at Swindon Works. There was a rolling road to test engines. The testing station was relatively short lived; the final test was made in 1965, and the plant was officially closed in 1970, however the building continued to be used until the early-1980s as an outpost of the British Rail Research Division, until it was demolished in 1984. The site is now an industrial estate. The records of the Rugby LTS are part of the National Railway Collection held by the National Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
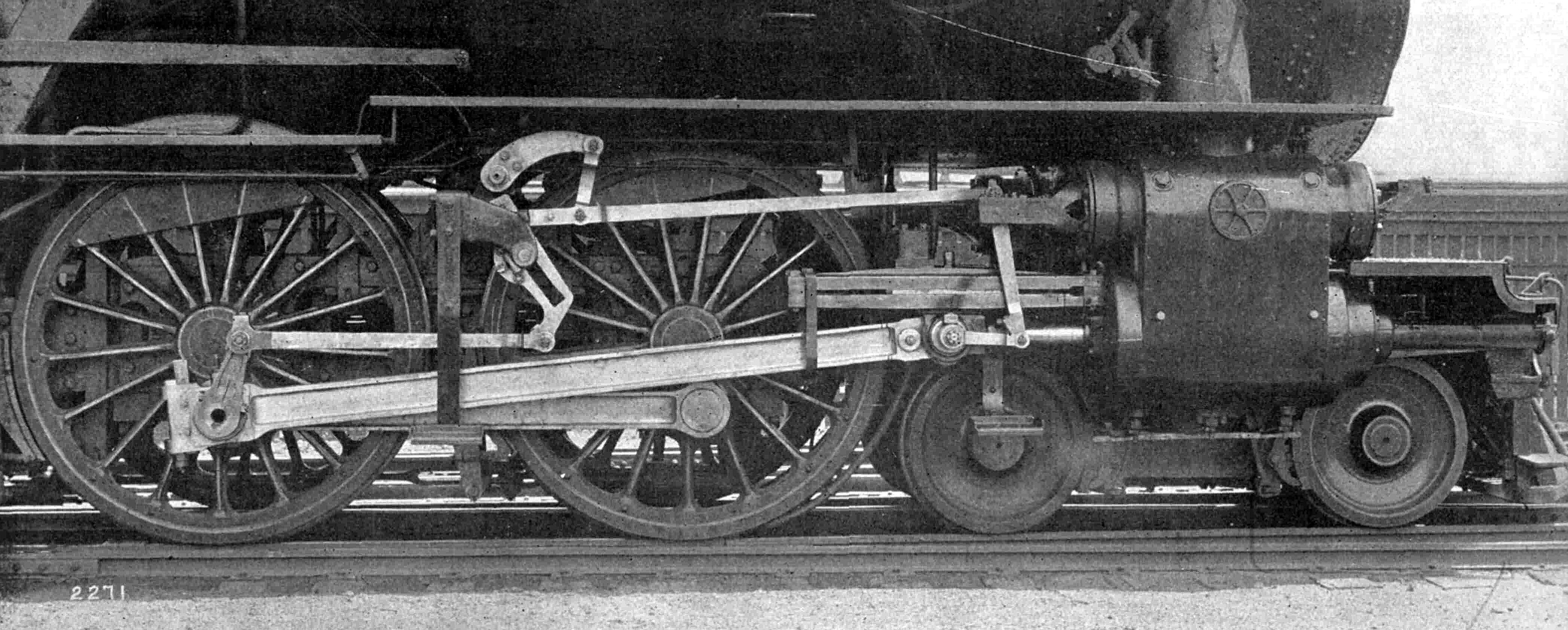
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Lentz
Hugo Lentz (1859–1944) was an Austrian mechanical engineer, born in South Africa. He was the inventor of many award-winning improvements to the steam engine. The correct spelling of his name is Lenz but it has been Anglicised to Lentz in English-speaking countries. Life and career Lentz was born on 21 July 1859 in South Africa. When he was six years old, his father died and the family returned to relatives in Germany. He became an engineer in the Prussian Navy. In 1888, Lentz founded his own machine factory in Vienna. At an exposition in honour of Alessandro Volta in Como in 1899, his first steam engine won the first prize. At the Exposition Universelle (1900) in Paris, it won the ''Grand Prix'' while Lentz himself was awarded the gold medal. From 1907, ''Davey, Paxman & Co'', [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)