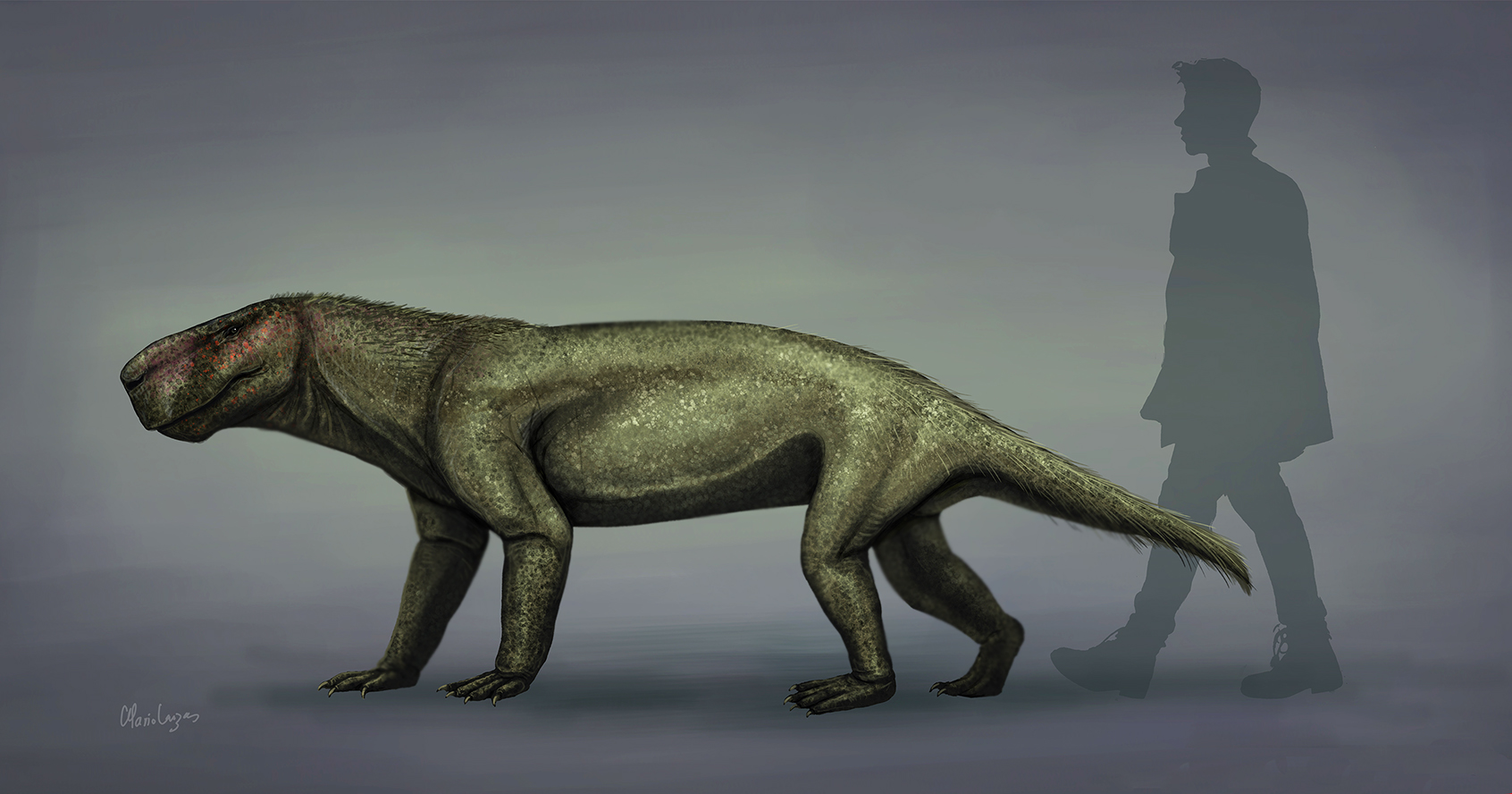|
Lycosuchid
Lycosuchidae is a Family (biology), family of therocephalians (an extinct type of therapsids, broader group which modern mammals belong to) known from fossils from what is now the Beaufort Group of South Africa and that lived during the Middle Permian, Middle to Late Permian between roughly 265 to 258 million years ago. It currently includes only two genera each with a single species, ''Lycosuchus'', represented by ''L. vanderrieti'', and ''Simorhinella'', represented by ''S. baini'', both named by paleontologist Robert Broom in 1903 and 1915, respectively (though ''Simorhinella'' was not recognised as a lycosuchid until 2014). Both species are large predators characterised by their size, reduced tooth counts with large, almost "Saber-toothed predator, sabre toothed" canine teeth, and relatively short, broad and low snouts. Lycosuchids were once thought to be defined by having two simultaneously functional pairs of canines, so-called "double canines", instead of a single pair of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therocephalia
Therocephalia is an extinct clade of therapsids (mammals and their close extinct relatives) from the Permian and Triassic periods. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their teeth, suggest that they were carnivores. Like other non-mammalian synapsids, therocephalians were once described as "mammal-like reptiles". Therocephalia is the group most closely related to the cynodonts, which gave rise to the mammals. Indeed, it had been proposed that therocephalians themselves may have given rise to the cynodonts, and therefore that therocephalians as recognised are paraphyletic in relation to cynodonts and so not a clade. Conventionally, however, Therocephalia is regarded as the sister clade of Cynodontia, together forming the clade Eutheriodontia. The close relationship of Therocephalia to Cynodontia takes evidence in a variety of skeletal features. Most notable is that the skull roof is narrowed between two enlarged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycosuchus
''Lycosuchus'' is a genus of early therocephalian (an extinct type of therapsid, the group that modern mammals belong to) that lived roughly 260–258 million years ago, straddling the boundary of the Middle and Late Permian period, from what is now the Karoo Basin of South Africa. The type and only species is ''L. vanderrieti'', named by paleontologist Robert Broom in 1903. ''Lycosuchus'' is known from a handful of well-preserved specimens mostly preserving the skull and lower jaw; the holotype specimen itself being a nearly complete and undistorted occluded skull and jaws. Other specimens have revealed more details of the palate and even its internal endocranial anatomy. ''Lycosuchus'' fossils are known from the uppermost Abrahamskraal and lowest Teekloof Formations, corresponding to the '' Tapinocephalus'' and '' Endothiodon'' faunal assemblage zones. With a skull ranging from to almost long, ''Lycosuchus'' was a large therocephalian but still relatively mid-size co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simorhinella
''Simorhinella'' is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Guadalupian, or Middle Permian, of South Africa. It is includes only a single species, ''Simorhinella baini'', named by South African paleontologist Robert Broom in 1915. Broom named ''Simorhinella'' on the basis of a single small fossil from the British Museum of Natural History collected in 1878 that includes the skull and jaws from the eye sockets forward of a young juvenile. The skull is unusual in that it has an extremely short and broad snout, unlike the longer and narrower snouts of most other early therocephalians. Because of the skull's distinctiveness, the classification of ''Simorhinella'' within Therocephalia was unclear during the 20th and early 21st centuries. In 2014, the skull of a much larger therocephalian was described and identified as an adult of ''Simorhinella'' by Fernando Abdala and colleagues based on a unique combination of shared features, including a distinctive bony crest on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsians
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to the Upper Permian, roughly between 270 and 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian is also known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Ocean; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini; and it encloses Lesotho. Covering an area of , the country has Demographics of South Africa, a population of over 64 million people. Pretoria is the administrative capital, while Cape Town, as the seat of Parliament of South Africa, Parliament, is the legislative capital, and Bloemfontein is regarded as the judicial capital. The largest, most populous city is Johannesburg, followed by Cape Town and Durban. Cradle of Humankind, Archaeological findings suggest that various hominid species existed in South Africa about 2.5 million years ago, and modern humans inhabited the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Broom
Robert Broom Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (30 November 1866 6 April 1951) was a British- South African medical doctor and palaeontologist. He qualified as a medical practitioner in 1895 and received his DSc in 1905 from the University of Glasgow. From 1903 to 1910, he was professor of zoology and geology at Stellenbosch University, Victoria College, Stellenbosch, Western Cape, Stellenbosch, South Africa, and subsequently he became keeper of vertebrate palaeontology at the South African Museum, Cape Town. Life Broom was born at 66 Back Sneddon Street in Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley, Renfrewshire (historic), Renfrewshire, Scotland, the son of John Broom, a designer of calico prints and Paisley design, Paisley shawls, and Agnes Hunter Shearer. In 1893, he married Mary Baird Baillie, his childhood sweetheart. In his medical studies at the University of Glasgow Broom specialised in obstetrics. After graduating in 1895 he travelled to Australia, supporting himself by pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saber-toothed Predator
A saber-tooth (alternatively spelled sabre-tooth) is any member of various extinct groups of predatory therapsids, predominantly carnivoran mammals, that are characterized by long, curved saber-shaped canine teeth which protruded from the mouth when closed. Among the earliest animals that can be described as "sabertooths" are the gorgonopsids, a group of non-mammalian therapsids that lived during the Middle-Late Permian, around 270-252 million years ago. Saber-toothed mammals have been found almost worldwide from the Eocene epoch to the end of the Pleistocene epoch (42 million years ago – 11,000 years ago). One of the best-known genera is the machairodont or "saber-toothed cat" ''Smilodon'', the species of which, especially ''S. fatalis'', are popularly referred to as "saber-toothed tigers", although they are not closely related to tigers (''Panthera''). Despite some similarities, not all saber-tooths are closely related to saber-toothed cats or felids in-general. Instead, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose tooth (animal), teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth. Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes (most notably sharks), many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, and most other vertebrates, with mammals being the main exception (though Polyphyodont#Evolution in mammals, not absolute). Growth New, permanent teeth grow in the jaws, usually under or just behind the old tooth, from stem cells in the dental lamina. Young animals typically have a full set of teeth when they hatch; there is no tooth change in the egg. Within days, tooth replacement begins, usually in the back of the jaw continuing forward like a wave. On average a tooth is replaced every few months. Crocodilia Crocodilia are the only non-mammalian vertebrates with tooth sockets. Alligators grow a successional tooth (a small replacement tooth) under each mature functional tooth for replacement once a y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as '' fangs''. They can appear more flattened, however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called ''incisiform''. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone. The four canines in humans are the two upper maxillary canines and the two lower mandibular canines. They are specially prominent in dogs (Canidae), hence the name. Details There are generally four canine teeth: two in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |