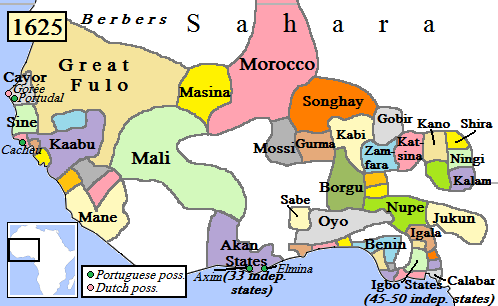
|
Lulami
Lulami (also Loulami) was the capital of the Dendi of the Songhai Empire. It was established by Askia Nuh, son of Askia Dawud and it is from here the Songhai resistance against Morocco continued. In 1639, during the reign of Askia Ismail, the Moroccan Pasha Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of ... Mesaoud sacked the town of Lulami. The location of this town is unknown but believed to be south of the town of Say in Niger. References {{Authority control Songhai Empire French West Africa Communities on the Niger River Capitals of former nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendi (province)
The Dendi (or Dandi, Dendiganda) was a former province of the Songhai Empire. It survived the fall of the Empire as a kingdom until 1901, when it was conquered by France and incorporated into French West Africa. Its centers today are the cities of Gaya in Niger, Kamba in Nigeria and Malanville in Benin. Dendi Kingdom Under the Songhai empire, Dendi had been the easternmost province, governed by the prestigious ''Dendi-fari'' ("governor of the eastern front"). Some members of the Askia dynasty and their followers fled here after being defeated by the invading Saadi dynasty of Morocco at the Battle of Tondibi and at another battle seven months later. There, they resisted Moroccan Invaders and maintained the tradition of the Songhai with the same Askia rulers and their newly established capital at Lulami. The first ruler, Askia Ishaq II was deposed by his brother Muhammad Gao, who was in turn murdered on the order of the Moroccan pasha. The Moroccans then appointed Sulayman as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songhai People
The Songhai people ( autonym: Ayneha) are an ethnolinguistic group in West Africa who speak the various Songhai languages. Their history and ''lingua franca'' is linked to the Songhai Empire which dominated the western Sahel in the 15th and 16th century. Predominantly adherents of Islam, the Songhai are primarily located in Niger and Mali. Historically, the term "Songhai" did not denote an ethnic or linguistic identity but referred to the ruling caste of the Songhay Empire known as the Songhaiborai. However, the correct term used to refer to this group of people collectively by the natives is "Ayneha". Although some speakers in Mali have also adopted the name ''Songhay'' as an ethnic designation, other Songhay-speaking groups identify themselves by other ethnic terms such as Zarma (or Djerma, the largest subgroup) or Isawaghen. The dialect of Koyraboro Senni spoken in Gao is unintelligible to speakers of the Zarma dialect of Niger, according to at least one report. The Song ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askia Nuh
Askia Nuh was a ruler of the Dendi Kingdom, the rump state of the Songhai Empire. He was a son of Askia Dawud and established his capital at Lulami, from where Songhai resistance to the Saadi Moroccans continued. Conflict with the Saadi dynasty Askia Nuh resisted the invasion of the Moroccan Pasha, Mahmud ibn Zarqun, by costly warfare lasting two years. In 1594 Mahmud was forced to cease the conflict and retreated, but was killed in the same year by the Dogon people, probably allies of Askia Nuh. The new pasha called Mansur continued the war against Dendi Kingdom and Nuh adopted guerilla warfare once again. This state of affairs lasted until 1599, when Nuh's followers became tired of the war and deposed him in favor of his brother Harun Harun (, ), also transliterated as Haroon or Haroun or Hamroun, is a common male given name of Arabic origin, related to the Hebrew name of the Prophet Aaron. Both are most likely of Egyptian origin, from '' ꜥḥꜣ rw'', meaning "warrior l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renaissance). Around 1350, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and Plague (disease), plagues, including the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it had been before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. Kingdom of France, France and Kingdom of England, England experienced serious peasant uprisings, such as the Jacquerie and the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict, the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was temporarily shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively, those events ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendi People
The Dendi are an ethnic group located in Benin, Niger, Nigeria and northern Togo mainly in the plains of the Niger River. They are part of the Songhai people, and were an integral part of the Songhai Empire as the Dendi province or Dendiganda. Derived from the Songhay language, the term "Dendi" translates to "down the river." The community consists of 195,633 people. Among them, only 4,505 live in Nigeria. In Niger they live in around the city of Gaya. Their mother tongue is Dendi. History The Dendi and the Songhai descended from the ancient kingdom of Za, whose presence has been recorded since the eighth century between the towns of Kukiya and Gao in modern Mali. In 1010, the Arabs came to the territory. They converted the people to Islam, which was then mixed with their indigenous religion (based on the belief of the holy rivers, soil and hunting). The Songhay Empire collapsed at the end of the sixteenth century, when Morocco conquered the territory. Culture The ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its largest ethnic group and ruling elite, the Songhai people. Sonni Ali established Gao as the empire's capital, although a Songhai state had existed in and around Gao since the 11th century. Other important cities in the kingdom were Timbuktu and Djenné, where urban-centred trade flourished; they were conquered in 1468 and 1475, respectively. Initially, the Songhai Empire was ruled by the Sonni dynasty (–1493), but it was later replaced by the Askia dynasty (1493–1591). During the second half of the 13th century, Gao and the surrounding region had grown into an important trading center and attracted the interest of the expanding Mali Empire. Mali conquered Gao near the end of the 13th century. Gao remained under Malian command until the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askia Dawud
Askia Daoud (also Askia Dāwūd, Askiya Dawud) was the ruler of the Songhai Empire from 1549 to 1582. His rule saw the empire rise to a peak of peace and prosperity following a series of succession disputes and short reigns."Songhai empire." ''Britannica Academic'', Encyclopædia Britannica, 5 Aug. 2019. academic-eb-com.queens.ezproxy.cuny.edu/levels/collegiate/article/Songhai-empire/68696. Accessed 30 Nov. 2019. Background and rise to power Dawud was one of many sons of Askia Muhammad Ture, the first ruler of the Askia dynasty. Under his rule, the Songhai economy thrived and developed a profoundly Islamized society, with the government promoting trade, education, and literacy. Dawud and his brothers received a good Islamic education. Beginning with his father's deposition in 1528, the Songhai empire was shaken by a series of succession disputes until his brother Askia Ishaq I was peacefully elected Askia in 1539.Root, Mario. "Songhay Empire." ''Encyclopedia of Black Studies'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasha
Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of Egypt and it was also used in Morocco in the 20th century, where it denoted a regional official or governor of a district. Etymology The English word ''pasha'' comes from Turkish language, Turkish ('; also ()). The Oxford English Dictionary attributes the origin of the English borrowing to the mid-17th century. The etymology of the Turkish word itself has been a matter of debate. Contrary to titles like emir (''amīr'') and bey (sir), which were established in usage much earlier, the title ''pasha'' came into Ottoman Empire, Ottoman usage right after the reign of Osman I (d. 1324), though it had been used before the Ottomans by some Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian Turkish rulers of the same era. Old Turkish had no fixed distinction betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Say, Niger
Say (Saayi) is a town in southwest Niger, situated on the Niger River. It is the capital of the Say Department in the Tillabéri Region. Say was a small Songhai proper, Songhai town prior to the arrival of the Fulani marabout Alfa Mohamed Diobo in the nineteenth century who converted the town to a center for Islamic learning and established the Emirate of Say. The municipality has 58,290 inhabitants, and its economy is dominated by agriculture, herding and small trade. Today, the inhabitants of Say are mostly Peulh, Songhai people (subgroup), Songhai and Zarma people, Zarma. Overview The town houses the Islamic University of Niger (''Université Islamique de Say''), an institute of international scope, whose founding was decided following a meeting of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, Organisation of the Islamic Conference in 1974, but that opened only in 1986. In 1996, it had 400 students, who paid fees much lower than those of the University of Niamey. In Say there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French West Africa
French West Africa (, ) was a federation of eight French colonial empires#Second French colonial empire, French colonial territories in West Africa: Colonial Mauritania, Mauritania, French Senegal, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), French Ivory Coast, Ivory Coast, French Upper Volta, Upper Volta (now Burkina Faso), French Dahomey, Dahomey (now Benin) and Colony of Niger, Niger. The federation existed from 1895 until 1958. Its capital was Saint-Louis, Senegal, Saint-Louis in Senegal until 1902, and then Dakar until the federation's collapse in 1960. With an area of 4,689,000 km2, French West Africa was eight times the size of Metropolitan France. French Equatorial Africa had an additional area of 2,500,000 km2. History Until after World War II, almost none of the Africans living in the colonies of France were citizens of France. Rather, they were "French subjects," lacking rights before the law, property ownership rights, rights to travel, dissen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communities On The Niger River
A community is a social unit (a group of people) with a shared socially-significant characteristic, such as place, set of norms, culture, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, town, or neighborhood) or in virtual space through communication platforms. Durable good relations that extend beyond immediate genealogical ties also define a sense of community, important to people's identity, practice, and roles in social institutions such as family, home, work, government, TV network, society, or humanity at large. Although communities are usually small relative to personal social ties, "community" may also refer to large-group affiliations such as national communities, international communities, and virtual communities. In terms of sociological categories, a community can seem like a sub-set of a social collectivity. In developmental views, a community can emerge out of a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |