|
Luash
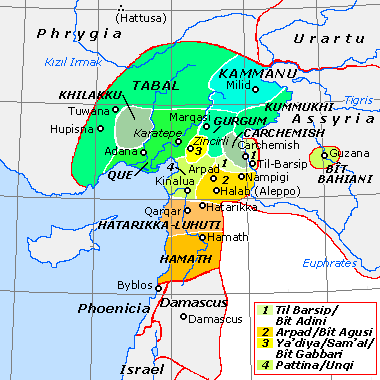
Luhuti, Lukhuti or Lu'ash, was a Syro-Hittite region during the early 1st millennium BC, located in northern Syria, in an area that used to be called Nuhašše. Political situation and capital Luhuti was a region of uncertain political status, known primarily from Assyrian inscriptions, and the stele of king Zakkur of Hamath. Luhuti is never attested as a kingdom of its own or as having a single central authority, although it did constitute an independent interconnected region. The Assyrian inscriptions that describe Luhuti as a country with many cities and troops. Luhuti had many cities. Shuksi was the maritime center, But the most important center and capital was the city of Hazrik (modern Tell Afis, Known as Hatarikka to the Assyrians), located south of Aleppo. History Luhuti was first attested in 870 BC. The inscriptions of Ashurnasirpal II record his conquest of its neighbour Pattin, then his use of Pattin's subordinate city of Aribua as his military base for operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele Of Zakkur
The Stele of Zakkur (or ''Zakir'') is a royal stele of King Zakkur of Hamath and Luhuti (or Lu'aš) in the province Nuhašše of Syria, who ruled around 785 BC. Description The inscription was on the lower part of the original stele. The upper part is now missing; it probably had the statue of king Zakkur sitting on a chair. Only some small parts of the upper part are still preserved such as the feet. Discovery The Stele was discovered in 1903 at Tell Afis (mentioned in the Stele as ''Hazrach''), 45 km southeast of Aleppo, in the territory of the ancient kingdom of Hamath. It was published in 1907. The long inscription is known as Kanaanäische und Aramäische Inschriften, KAI 202; it reads, in part: :''I am Zakkur, king of Hamath and Luash . . . Bar-Hadad, son of Hazael, king of Aram, united against me seventeen kings . . .all these kings laid siege to Hazrach . . . Baalshamayn said to me, "Do not be afraid! . . .I will save you from all [these kings who] have besieged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Agusi
Bit Agusi or Bit Agushi (also written Bet Agus) was an ancient Aramaean Syro-Hittite state, established by Gusi of Yakhan at the beginning of the 9th century BC. It had included the cities of Arpad, Nampigi (Nampigu) and later on Aleppo Arpad was the capital of the state-kingdom. Bit Agusi stretched from the A'zaz area in the north to Hamath in the south. Chronology According to Dan'el Kahn, there were seven stages of Bit Agusi history in Northern Syria in the ninth and eighth centuries BC. * Stage 1 (858–ca. 842 BC). Early on, Bit Agusi was apparently free of political alliances with neighbors. Arame, the second king of Bit Agusi, submitted to Assyria freely in 858 BCE, along with many other rulers of the region, including the southern Anatolia. * Stage 2 (841–823 BC). A period of Bit Agusi subjugation to Assyria. * Stage 3. Around 823 BC, or maybe a little later, Bit Agusi leads a local alliance opposing Assyrian hegemony, and achieves independence. * Stage 4. Also, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Afis
Tell Afis is an archaeological site in the Idlib Governorate of northern Syria, lying about fifty kilometers southeast of Aleppo and 11 kilometers north of the ancient site of Ebla.Venturi, F., "La Siria nell’Età delle Trasformazioni: Nuovi Contributi dallo Scavo di Tell Afis", Cooperativa Libraria Universitaria Editirice Bologna, 2007 The site is thought to be that of ancient Hazrek (under Neo-Assyrians - Hatarikka) capital of the Kingdom of Hamath and Luhuti. The Stele of Zakkur (KAI 202), dated c, 785 BC, which contains a dedication in Aramaic to the gods Iluwer and Baalshamin, was discovered at the top of the acropolis in 1903 by the French Consul Henri Pognon. It is now in the Louvre Museum. History Occupation of the site extends from the Late Chalcolithic, Ubaid period, Early Bronze I period, Middle Bronze II, until the Iron Age. Late Chalcolithic In the Late Chalcolithic (4000-3200 BC) it was surrounded by a megalithic stone wall at the base of the acropolis with a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattin
Pattin (also known as Pattina, Patina, Unqu and Unqi), was an ancient Luwian Syro-Hittite states, Syro-Hittite state at the beginning of the 1st millennium BC. It was known to the Assyrians as Unqi and Aramaeans as Unqu. It was located at the north-western coast of ancient Syria, associated with the modern-day Hatay. The capital of the state was Kinalua (Kunalua, Kalneh, or Kinaluwa), which has been tentatively associated with Tell Tayinat in modern-day Turkey. The state was formed in the 9th century BC towards the end of the Dark Age period, and shared a north-western border with the Syro-Hittite state of Quwê. Khazazu (modern-day Azaz) was one of Pattin's dependencies which was invaded by Neo-Assyrian Empire, Assyria around 870 BC. The frontier fortress of ''Aribua'' (associated with the modern-day region of Idlib Governorate, Idlib) within the land of Hatarikka-Luhuti, Lukhuti to the immediate south of Pattin was also ravaged. List of kings *Taita I (11th century).. *Taita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor R
Trevor ( Trefor in the Welsh language) is a common given name or surname of Welsh origin. It is an habitational name, deriving from the Welsh ''tre(f)'', meaning "homestead", or "settlement" and ''fawr'', meaning "large, big". The Cornish language equivalent is Trevorrow and is most associated with Ludgvan. Trevor is also a reduced Anglicized form of the Gaelic ''Ó Treabhair'' (descendant of Treabhar), which may derive from the original Welsh name. As a surname People * Claire Trevor (1910–2000), American actress *Hugh Trevor (1903–1933), American actor * John Trevor (other), various people *William Trevor (1928–2016), Irish writer * William Spottiswoode Trevor (1831–1907), recipient of the Victoria Cross Fictional characters *Steve Trevor, in the DC Comics, 1970s television series and 2017 film ''Wonder Woman'' As a given name People *Trevor Ariza (born 1985), American basketball player *Trevor Bailey, English cricketer * Trevor Bauer, American baseball pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shalmaneser IV
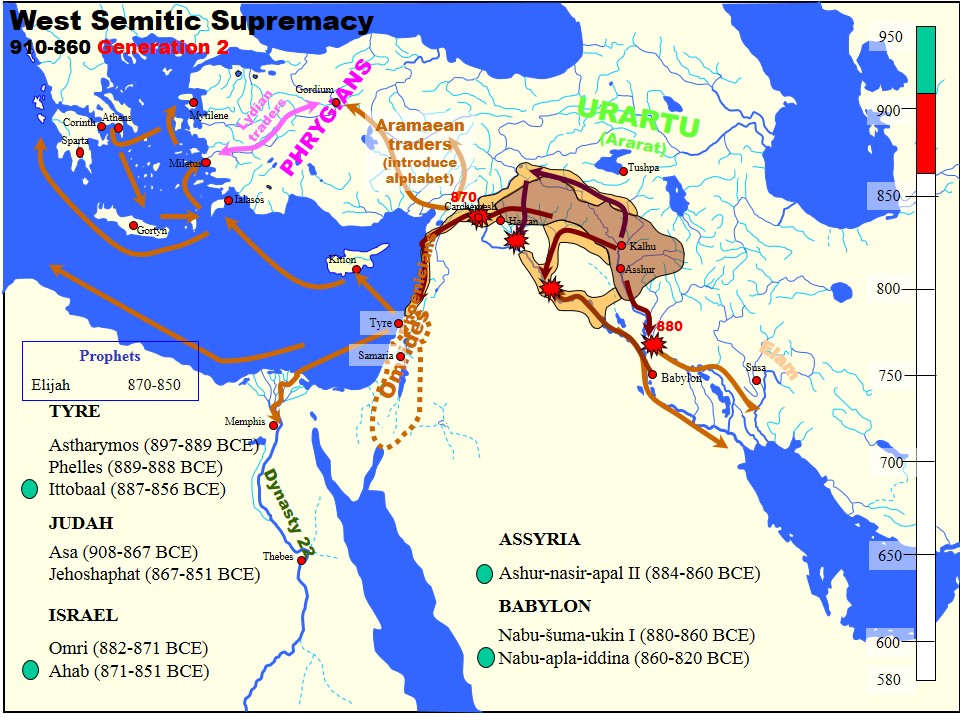
Shalmaneser IV ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "Salmānu is foremost") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 783 BC to his death in 773 BC. Shalmaneser was the son and successor of his predecessor, Adad-nirari III, and ruled during a period of Assyrian decline from which few sources survive. As such his reign, other than broad political developments, is poorly known. Shalmaneser's time was marked both by an increase in the power held by Assyrian officials relative to that of the king and Assyria's enemies growing increasingly powerful. Most of Shalmaneser's military efforts were spent warring against the Kingdom of Urartu in the north, which during this time was reaching the peak of its power. Biography Shalmaneser IV was the son and successor of Adad-nirari III (811–783 BC), inheriting the throne upon his father's death in 783 BC. The accession of Shalmaneser IV marks the beginning of an obscure period in Assyrian history, from which little information survives. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aram-Damascus
Aram-Damascus ( ) was an Arameans, Aramean polity that existed from the late-12th century BCE until 732 BCE, and was centred around the city of Damascus in the Southern Levant. Alongside various tribal lands, it was bounded in its later years by the polities of Assyria to the north, Ammon to the south, and Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel to the west. The compound name "Aram-Damascus" is only found in the Hebrew Bible, where it sometimes also is referred to as simply "Aram" or "Damascus". It is also referred to as "Aram" in some Aramaic inscriptions. In Assyrian sources, "Aram" was never used to designate it. It was often referred to as "Damascus" or "imērīšu" (meaning "his donkey"), and sometimes "Bīt-Ḫaza’ili" (meaning "house of Hazael"), in Assyrian sources. History The Tanakh gives accounts of Aram-Damascus' history, mainly in its interaction with History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah. There are biblical texts referencing battles that took place b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben-Hadad III
Bar-Hadad III ( Aram.) (ܒܪ ܚܕܕ) or Ben-Hadad III ( Heb.) (בֶּן-הֲדַד) was king of Aram Damascus, the son and successor of Hazael. His succession is mentioned in 2 Kings (, ). He is thought to have ruled from 796 BC to 792 BC, although there are many conflicting opinions among Biblical archaeologists as to the length of his reign. The archaeological Stele of Zakkur The Stele of Zakkur (or ''Zakir'') is a royal stele of King Zakkur of Hamath and Luhuti (or Lu'aš) in the province Nuhašše of Syria, who ruled around 785 BC. Description The inscription was on the lower part of the original stele. The upper ... mentions "''Bar Hadad, son of Hazael''". Luis Robert Siddall''The Reign of Adad-nīrārī III: An Historical and Ideological Analysis of An Assyrian King and His Times''.BRILL, 2013 p.37 See also * List of biblical figures identified in extra-biblical sources * List of Syrian monarchs * Timeline of Syrian history * Zakkur References External lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II (transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning " Ashur is guardian of the heir") was the third king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 883 to 859 BC. Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II. His son and successor was Shalmaneser III and his queen was Mullissu-mukannišat-Ninua. Reign During his reign he embarked on a vast program of expansion, first conquering the peoples to the north in Asia Minor as far as Nairi and exacting tribute from Phrygia, then invading Aram (modern Syria) conquering the Aramaeans and Neo-Hittites between the Khabur and the Euphrates Rivers. The palaces, temples and other buildings raised by him bear witness to a considerable development of wealth and art. Cruelty Ashurnasirpal II was notorious for his brutality, using enslaved captives to build a new Assyrian capital at Kalhu (Nimrud) in Mesopotamia where he built many impressive monuments. He was also a shrewd administrator, who realized that he could gain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |