|
Lovastatin
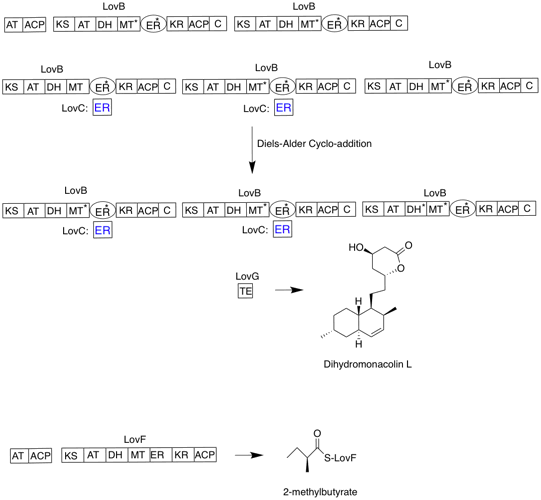
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include diarrhea, constipation, headache, muscles pains, rash, and trouble sleeping. Serious side effects may include liver problems, muscle breakdown, and kidney failure. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby and use during breastfeeding is not recommended. It works by decreasing the liver's ability to produce cholesterol by blocking the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Lovastatin was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1987. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 111th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses The primary uses of lovastatin is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statin Medication
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. As lipid-lowering medications, statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol; they are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes, and abnormal blood levels of certain liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage, and very rarely rhabdomyolysis. They act by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of chol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simvastatin
Simvastatin, sold under the brand name Zocor among others, is a statin, a type of lipid-lowering medication. It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease hyperlipidemia, elevated lipid levels. It is also used to decrease the risk of Cardiovascular disease, heart problems in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include constipation, headaches, and nausea. Serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis, muscle breakdown, liver problems, and increased blood sugar levels. A lower dose may be needed in people with chronic kidney disease, kidney problems. There is evidence of harm to the developing baby when taken during pregnancy and it should not be used by those who are breastfeeding. It is in the statin class of medications and works by decreasing the manufacture of cholesterol by the liver. Simvastatin is made from the fungus ''Aspergillus terreus''. It was patented by Merck and Co., Merck in 1980, and came into medical use in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-CoA Reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-limiting enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia. HMG-CoA reductase is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, and was long regarded as having seven transmembrane domains, with the active site located in a long carboxyl terminal domain in the cytosol. More recent evidence shows it to contain eight transmembrane domains. In humans, the gene for HMG-CoA reductase (NADPH) is located on the long arm of the fif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atorvastatin
Atorvastatin, sold under the brand name Lipitor among others, is a statin medication used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and to treat abnormal lipid levels. For the prevention of cardiovascular disease, statins are a first-line treatment in reducing cholesterol. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects may include diarrhea, heartburn, nausea, muscle pain (typically mild and dose-dependent) and, less frequently, joint pain. Muscle symptoms often occur during the first year and are commonly influenced by pre-existing health issues and the nocebo effect. Most patients can continue therapy with dose adjustment or statin switching. Rare (<0.1%) but serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis (severe muscle disorder), liver problems and diabetes. Use during may harm the |
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine, which in humans is encoded by ''CYP3A4'' gene. It organic redox reaction, oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme. While many drugs are deactivated by CYP3A4, there are also some drugs that are ''activated'' by the enzyme. Some substances, such as some drugs and furanocoumarins present in grapefruit juice, interfere with the action of CYP3A4. These substances will, therefore, either amplify or weaken the action of those drugs that are modified by CYP3A4. CYP3A4 is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of oxidizing enzymes. Several other members of this family are also involved in drug metabolism, but CYP3A4 is the most common and the most versatile one. Like all members of this family, it is a hemoprote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia is a metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high or low amounts of any or all lipids (e.g. fats, triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids) or lipoproteins in the blood. Dyslipidemia is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, which include coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral artery disease. Although dyslipidemia is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, abnormal levels do not mean that lipid lowering agents need to be started. Other factors, such as comorbid conditions and lifestyle in addition to dyslipidemia, is considered in a cardiovascular risk assessment. In developed countries, most dyslipidemias are hyperlipidemias; that is, an elevation of lipids in the blood. This is often due to diet and lifestyle. Prolonged elevation of insulin resistance can also lead to dyslipidemia. Types Risk factors Risk factors include: * Family history of dyslipidemia * Current cigarette smokin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a Chronic condition, long-term inflammatory disorder, inflammatory Autoimmune disease, autoimmune disorder which affects the skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may include weight loss, fever, lung inflammation, or light sensitivity. Complications may include calcinosis, calcium deposits in muscles or skin. Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune disorder featuring both humoral and T-cell autoimmune processes. Dermatomyositis may develop as a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with several forms of malignancy. It is known to be associated with several viruses, especially coxsackievirus, but no definitive causal link has been found. Dermatomyositis is considered a type of inflammatory myopathy. Diagnosis is typically based on some combination of symptoms, blood tests, electromyography, and muscle biopsy, muscle biopsies. Eighty percen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or, less frequently, greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine. Normal levels of bilirubin in blood are below 1.0 mg/ dl (17 μmol/ L), while levels over 2–3 mg/dl (34–51 μmol/L) typically result in jaundice. High blood bilirubin is divided into two types: unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. Causes of jaundice vary from relatively benign to potentially fatal. High unconjugated bilirubin may be due to excess red blood cell breakdown, large bruises, gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition (a situation or factor) that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain treatment. Absolute contraindications are contraindications for which there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action (that is, overriding the prohibition). For example: * Children and teenagers with viral infections should not be given aspirin because of the risk of Reye syndrome. * A person with an anaphylactic food allergy should never eat the food to which they are allergic. * A person with hemochromatosis should not be administered iron preparations. * Some medications are so teratogenic that they are absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy; examples include thalidomide and isotretinoin. Relative contraindications are contraindications for circumstances in which the patient is at hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
By Mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myopathy
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease ( Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meaning implies that the primary defect is within the muscle, as opposed to the nerves (" neuropathies" or " neurogenic" disorders) or elsewhere (e.g., the brain). This muscular defect typically results in myalgia (muscle pain), muscle weakness (reduced muscle force), or premature muscle fatigue (initially normal, but declining muscle force). Muscle cramps, stiffness, spasm, and contracture can also be associated with myopathy. Myopathy experienced over a long period (chronic) may result in the muscle becoming an abnormal size, such as muscle atrophy (abnormally small) or a pseudoathletic appearance (abnormally large). Capture myopathy can occur in wild or captive animals, such as deer and kangaroos, and leads to morbidity and mortality. It usually occurs as a result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |