|
Longbowmen
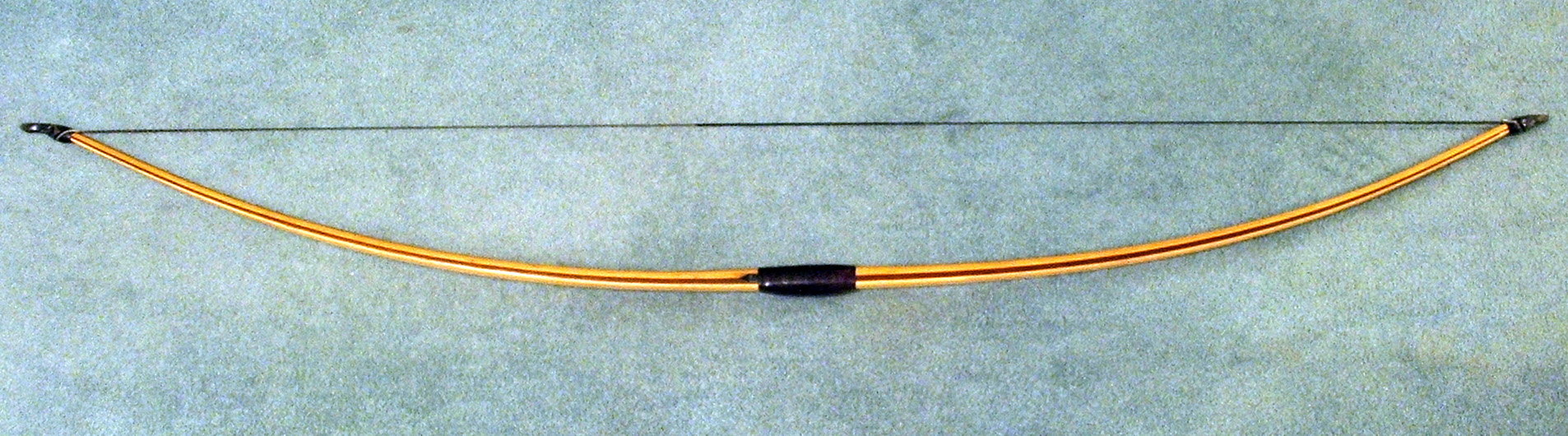
A longbow is a type of tall bow that makes a fairly long draw possible. Longbows for hunting and warfare have been made from many different woods in many cultures; in Europe they date from the Paleolithic era and, since the Bronze Age, were made mainly from yew, or from wych elm if yew was unavailable. The historical longbow was a self bow made of a single piece of wood, but modern longbows may also be made from modern materials or by gluing different timbers together. History Europe Prehistory A longbow was found in 1991 in the Ötztal Alps with a natural mummy known as Ötzi. His bow was made from yew and was long; the body has been dated to around 3300 BC. A slightly shorter bow comes from the Scottish parish of Tweedsmuir in a peat bog known as Rotten Bottom. The bow, made from yew, has been given a calibrated radiocarbon date of 4040 BC to 3640 BC. Another bow made from yew, found within some peat in Somerset, England has been dated to 2700–2600 BC. Forty longbows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Longbow
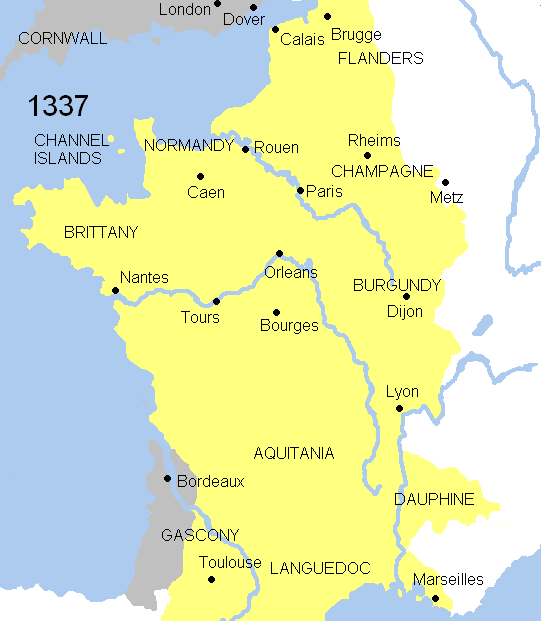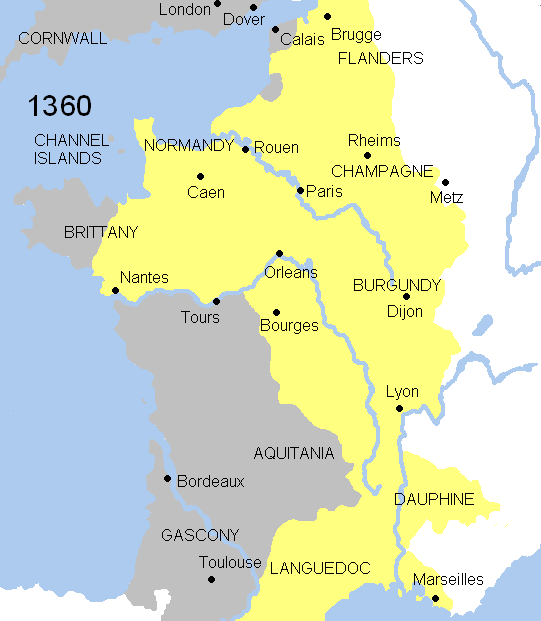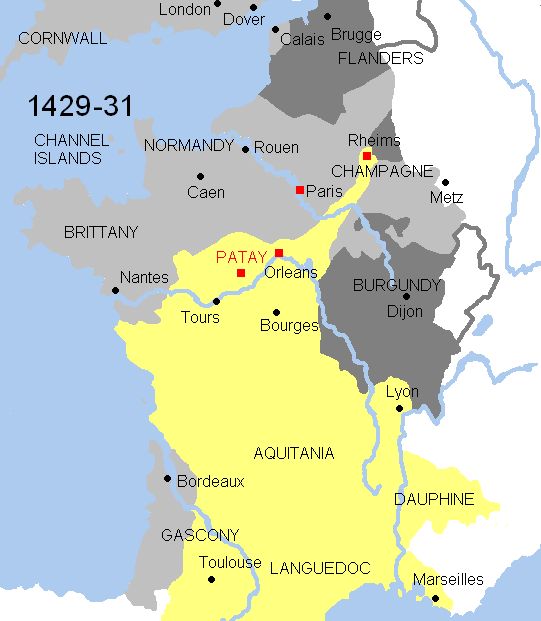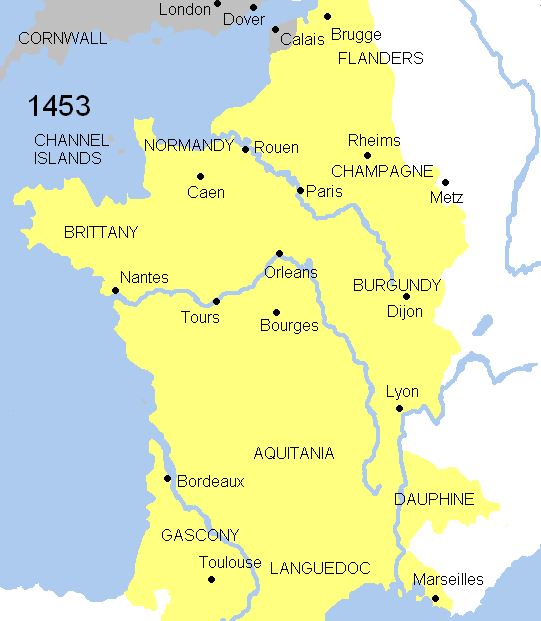
The English longbow was a powerful medieval type of bow, about long. While it is debated whether it originated in England or in Wales from the Welsh bow, by the 14th century the longbow was being used by both the English and the Welsh as a weapon of war and for hunting. English longbows were effective against the French during the Hundred Years' War, particularly in the battles of Sluys (1340), Crécy (1346), Poitiers (1356), and Agincourt (1415). They were less successful later on, as longbowmen had their lines broken at the Battle of Verneuil (1424), although the English won a decisive victory there; they were completely routed at the Battle of Patay (1429) when they were charged by the French mounted men-at-arms before they had prepared the terrain and finished defensive arrangements. The Battle of Pontvallain (1370) had also previously shown longbowmen were not particularly effective when not given the time to set up defensive positions. No English longbows survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Poitiers
The Battle of Poitiers was fought on 19September 1356 between a Kingdom of France, French army commanded by King John II of France, King JohnII and an Kingdom of England, Anglo-Gascony, Gascon force under Edward the Black Prince, Edward, the Black Prince, during the Hundred Years' War. It took place in western France, south of Poitiers, when approximately 14,000 to 16,000 French attacked a strong defensive position held by 6,000 Anglo-Gascons. Nineteen years after the start of the war, the Black Prince, eldest son and heir of the English King, set out on a major campaign in south-west France. His army marched from Bergerac, Dordogne, Bergerac to the River Loire, which they were unable to cross. John gathered a large and unusually mobile army and pursued Edward's forces. The Anglo-Gascons had by this point established a strong defensive position near Poitiers, and after unsuccessful negotiations between the two sides, were attacked by the French. The first assault included tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Agincourt
The Battle of Agincourt ( ; ) was an English victory in the Hundred Years' War. It took place on 25 October 1415 (Saint Crispin's Day) near Azincourt, in northern France. The unexpected victory of the vastly outnumbered English troops against the numerically superior French army boosted English morale and prestige, crippled France, and started a new period of English dominance in the war that would last for 14 years until England was defeated by France in 1429 during the Siege of Orléans. After several decades of relative peace, the English had Hundred Years' War (1415–53), resumed the war in 1415 amid the failure of negotiations with the French. In the ensuing campaign, many soldiers died from disease, and the English numbers dwindled; they tried to withdraw to Pale of Calais, English-held Calais but found their path blocked by a considerably larger French army. Despite the numerical disadvantage, the battle ended in an overwhelming victory for the English. King Henry V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 in northern France between a French army commanded by King PhilipVI and an English army led by King Edward III. The French attacked the English while they were traversing northern France during the Hundred Years' War, resulting in an English victory and heavy loss of life among the French. The English army had landed in the Cotentin Peninsula on 12 July. It had burnt a path of destruction through some of the richest lands in France to within of Paris, sacking many towns on the way. The English then marched north, hoping to link up with an allied Flemish army which had invaded from Flanders. Hearing that the Flemish had turned back, and having temporarily outdistanced the pursuing French, Edward had his army prepare a defensive position on a hillside near Crécy-en-Ponthieu. Late on 26 August the French army, which greatly outnumbered the English, attacked. During a brief archery duel a large force of French mercenary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy of Aquitaine and was triggered by English claims to the French throne, a claim to the French throne made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic, and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodisation of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces. The Hundred Years' War was a significant conflict in the Middle Ages. During the war, five generations of kings from two rival Dynasty, dynasties fought for the throne of France, then the wealthiest and most populous kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longbowmen
A longbow is a type of tall bow that makes a fairly long draw possible. Longbows for hunting and warfare have been made from many different woods in many cultures; in Europe they date from the Paleolithic era and, since the Bronze Age, were made mainly from yew, or from wych elm if yew was unavailable. The historical longbow was a self bow made of a single piece of wood, but modern longbows may also be made from modern materials or by gluing different timbers together. History Europe Prehistory A longbow was found in 1991 in the Ötztal Alps with a natural mummy known as Ötzi. His bow was made from yew and was long; the body has been dated to around 3300 BC. A slightly shorter bow comes from the Scottish parish of Tweedsmuir in a peat bog known as Rotten Bottom. The bow, made from yew, has been given a calibrated radiocarbon date of 4040 BC to 3640 BC. Another bow made from yew, found within some peat in Somerset, England has been dated to 2700–2600 BC. Forty longbows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longbow
A longbow is a type of tall bow that makes a fairly long draw possible. Longbows for hunting and warfare have been made from many different woods in many cultures; in Europe they date from the Paleolithic era and, since the Bronze Age, were made mainly from yew, or from wych elm if yew was unavailable. The historical longbow was a self bow made of a single piece of wood, but modern longbows may also be made from modern materials or by gluing different timbers together. History Europe Prehistory A longbow was found in 1991 in the Ötztal Alps with a natural mummy known as Ötzi. His bow was made from yew and was long; the body has been dated to around 3300 BC. A slightly shorter bow comes from the Scottish parish of Tweedsmuir in a peat bog known as Rotten Bottom. The bow, made from yew, has been given a calibrated radiocarbon date of 4040 BC to 3640 BC. Another bow made from yew, found within some peat in Somerset, England has been dated to 2700–2600 BC. Forty longbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Bow
A self bow or simple bow is a bow made from a single piece of wood. Extra material such as horn nocks on the ends, or built-up handles, would normally be accepted as part of a self bow. Some modern authorities would also accept a bow spliced together in the handle from two pieces of wood. Comparison with composite bows An effective self bow can be made from widely available local material in most inhabited parts of the world, with limited tools whose functions include chopping, shaving, and scraping. A day of work may be needed, starting with a seasoned stave; a composite bow requires a week's work, and could possibly take up to several years, starting with a much greater range of materials and skills.. Self bows must be approximately the height of the archer if they are to allow a long draw, and they are less efficient in the specialized art of flight archery. Well-designed composite bows of high draw-weight give higher arrow velocity, and the bow itself is shorter. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward III Of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after the disastrous and unorthodox reign of his father, Edward II. Edward III transformed the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe. His fifty-year reign is List of monarchs in Britain by length of reign#Ten longest-reigning British monarchs, one of the longest in English history, and saw vital developments in legislation and government, in particular the evolution of the English Parliament, as well as the ravages of the Black Death. He outlived his eldest son, Edward the Black Prince, and was succeeded by his grandson, Richard II. Edward was crowned at age fourteen after his father was deposed by his mother, Isabella of France, and her lover, Roger Mortimer, 1st Earl of March, Roger Mortimer. At the age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia (English)
The English Militia was the principal military reserve force of the Kingdom of England. Militia units were repeatedly raised in England from the History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period onwards for internal security duties and to defend against external invasions. One of the first militia units in England were the ''fyrd'', which were raised from Estates of the realm, freemen to defend the estate of their local Shire's lord or accompany the housecarls on offensive expeditions. During the Middle Ages, English militia units continued to be raised for service in various conflicts such as the Wars of Scottish Independence, the Hundred Years' War and the Wars of the Roses. Militia troops continued to see service in Tudor period, Tudor and Stuart periods, most prominently in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Following the Acts of Union 1707, the English Militia was transformed into the Militia (Great Britain), British Militia. Origins The origins of military obligation in Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Flodden
The Battle of Flodden, Flodden Field, or occasionally Branxton or Brainston Moor was fought on 9 September 1513 during the War of the League of Cambrai between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland and resulted in an English victory. The battle was fought near Branxton, Northumberland, Branxton, in the county of Northumberland, in northern England, between an invading Scots army under King James IV of Scotland, James IV and an English army commanded by the Thomas Howard, 2nd Duke of Norfolk, Earl of Surrey. In terms of troop numbers, it was the largest battle ever fought between the two kingdoms.''The Seventy Greatest Battles of All Time''. Published by Thames & Hudson Ltd. 2005. Edited by Jeremy Black. pp. 95–97. . After besieging and capturing several English border castles, James encamped his invading army on a commanding hilltop position at Flodden, awaited the English force that had been sent against him and declined a challenge to fight in an open field. Surr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |