|
Lodeynopolsky Uyezd
Lodeynopolsky Uyezd () was one of the seven subdivisions of the Olonets Governorate of the Russian Empire. Its capital was Lodeynoye Pole. Lodeynopolsky Uyezd was located in the southern part of the governorate (in the northeastern part of the present-day Leningrad Oblast and the northwestern part of Vologda Oblast). In terms of present-day administrative borders, the territory of Lodeynopolsky Uyezd is divided between the Lodeynopolsky and Podporozhsky districts of Leningrad Oblast and Vytegorsky District of Vologda Oblast. Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Lodeynopolsky Uyezd had a population of 46,255. Of these, 79.8% spoke Russian Russian(s) may refer to: *Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *A citizen of Russia *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *''The Russians'', a b ..., 19.2% Veps, 0.5% Finnish, 0.2% Karelian and 0.1% Polish as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olonets Governorate
Olonets Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, extending from Lake Ladoga almost to the White Sea, bounded west by Finland, north and east by Arkhangelsk and Vologda, and south by Novgorod and Saint Petersburg. The area was 57,422 km2, of which 6,794 km2 were covered by lakes. Geology Its north-western portion belonged orographically and geologically to the Finland region; it is thickly dotted with hills reaching 1,000 ft. in altitude, and diversified by numberless smaller ridges and hollows running from northwest to south-east. The rest of the governorate was a flat plateau sloping towards the marshy lowlands of the south. The geological structure was very varied. Granites, syenites, and diorites, covered with Laurentian metamorphic slates, occurred extensively in the north-west. Near Lake Onega they were overlain with Devonian sandstones and limestones, yielding marble and sandstone for building; to the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is the native language of the Russians. It was the ''de facto'' and ''de jure'' De facto#National languages, official language of the former Soviet Union.1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 Russian has remained an official language of the Russia, Russian Federation, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Russian language in Israel, Israel. Russian has over 253 million total speakers worldwide. It is the List of languages by number of speakers in Europe, most spoken native language in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Subdivisions Of Leningrad Oblast
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodeynopolsky Uyezd
Lodeynopolsky Uyezd () was one of the seven subdivisions of the Olonets Governorate of the Russian Empire. Its capital was Lodeynoye Pole. Lodeynopolsky Uyezd was located in the southern part of the governorate (in the northeastern part of the present-day Leningrad Oblast and the northwestern part of Vologda Oblast). In terms of present-day administrative borders, the territory of Lodeynopolsky Uyezd is divided between the Lodeynopolsky and Podporozhsky districts of Leningrad Oblast and Vytegorsky District of Vologda Oblast. Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Lodeynopolsky Uyezd had a population of 46,255. Of these, 79.8% spoke Russian Russian(s) may refer to: *Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *A citizen of Russia *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *''The Russians'', a b ..., 19.2% Veps, 0.5% Finnish, 0.2% Karelian and 0.1% Polish as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2024, there were over 39.7 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth-most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional Dialects of Polish, dialects. It maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (, , , , , , , , ) to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet. The traditional set compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
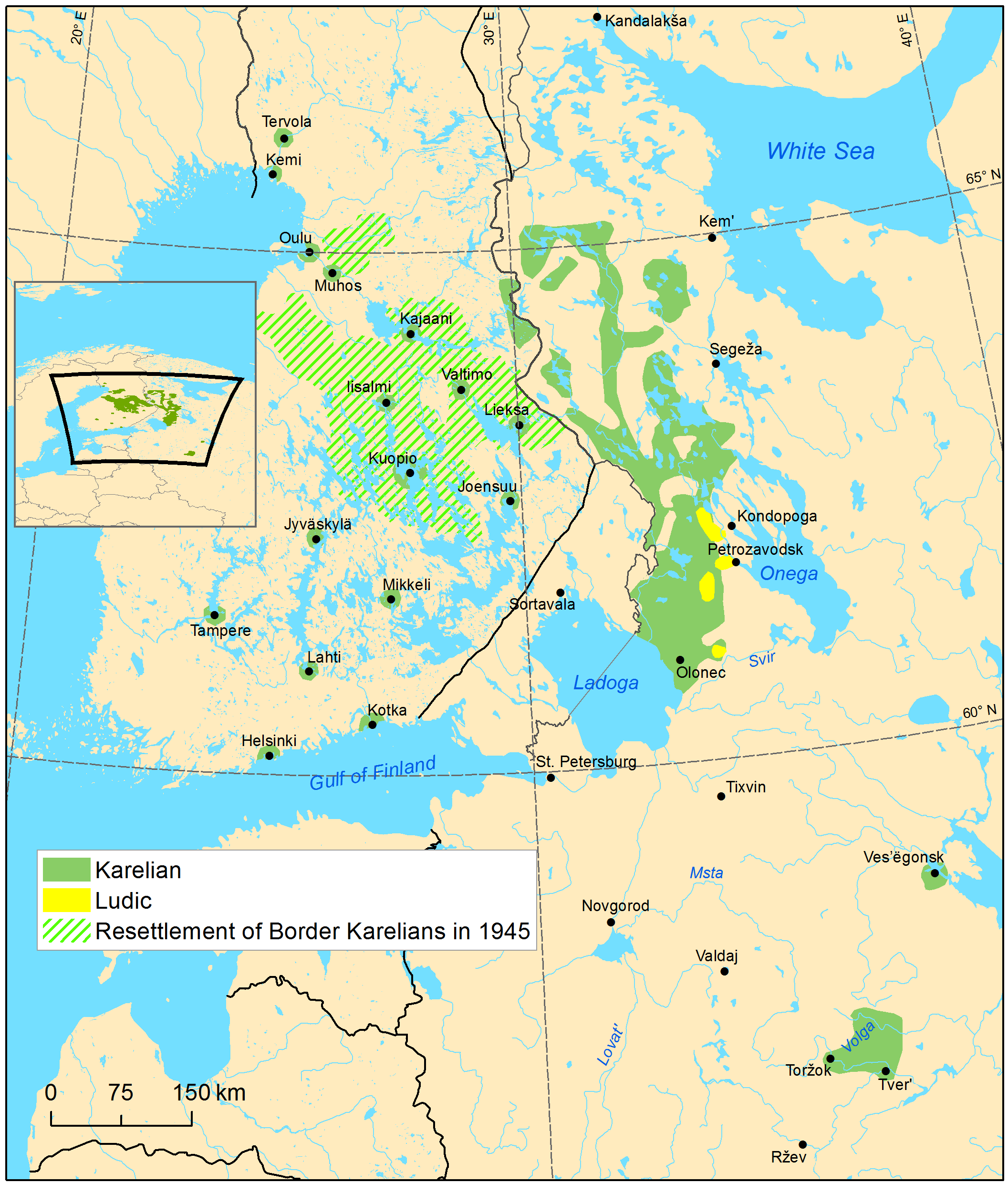
Karelian Language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the South Karelian dialects, Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland, and around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian. The Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian dialect, Northern Kareli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Finnic languages, Finnic language of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland, alongside Swedish language, Swedish. In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. Kven language, Kven, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norway, Norwegian counties of Troms and Finnmark by a minority of Finnish descent. Finnish is morphological typology, typologically agglutinative language, agglutinative and uses almost exclusively Suffix, suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, Numeral (linguistics), numerals and verbs are inflection, inflected depending on their role in the Sentence (linguistics), sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veps Language
Veps, also known as Vepsian (, or ), is an endangered Finnic languages, Finnic language from the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, that is spoken by Vepsians. The language is written in the Latin script, and is closely related to Finnish language, Finnish and Karelian language, Karelian. According to Soviet Union, Soviet statistics, 12,500 people were self-designated ethnic Veps at the end of 1989. There were 5,900 self-designated ethnic Veps in 2010, and around 3,600 native speakers. According to the location of the people, the language is divided into three main dialects: Northern Veps (at Lake Onega to the south of Petrozavodsk, to the north of the river Svir River, Svir, including the former Veps National Volost), Central Veps (in the east of the Leningrad Oblast and northwest of the Vologda Oblast), and Southern Veps (in the Leningrad Oblast). The Northern dialect seems the most distinct of the three; however, it is still mutually intelligible for speakers of the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vytegorsky District
Vytegorsky District () is an administrativeLaw #371-OZ and municipalLaw #1113-OZ district (raion), one of the administrative divisions of Vologda Oblast, twenty-six in Vologda Oblast, Russia. It is located in the northwest of the oblast and borders with Pudozhsky District of the Republic of Karelia in the north, Kargopolsky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast in the east, Kirillovsky District, Kirillovsky, Vashkinsky District, Vashkinsky, and Belozersky District, Vologda Oblast, Belozersky Districts in the southeast, Vologodsky District in the southeast, Babayevsky District in the southwest, and with Podporozhsky District of Leningrad Oblast in the west. The area of the district is , making it the largest district in Vologda Oblast. Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, town of Vytegra.Resolution #178 Population: 31,757 (Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census); The population of Vytegra accounts for 38.6% of the district's total population. Geography The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podporozhsky District
Podporozhsky District () is an administrativeOblast Law #32-oz and municipalLaw #51-oz district (raion), one of the seventeen in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It is located in the northeast of the oblast and borders with Prionezhsky District of the Republic of Karelia in the north, Vytegorsky District of Vologda Oblast in the east, Babayevsky District of Vologda Oblast in the southeast, Tikhvinsky District in the south, Lodeynopolsky District in the southwest, and Olonetsky and Pryazhinsky Districts of the Republic of Karelia in the northwest. In the northeast, the district is bounded by Lake Onega. The area of the district is , which makes it the largest district in Leningrad Oblast. Its administrative center is the town of Podporozhye. Population (excluding the administrative center): 14,845 ( 2002 Census); Geography Almost the whole area of the district belongs to the drainage basin of the Svir River. The Svir, which connects Lake Onega and Lake Ladoga, has its source in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |