|
Location Hypotheses Of Atlantis
There exist a variety of speculative proposals that real-world events could have inspired Plato's fictional story of Atlantis, told in the ''Timaeus (dialogue), Timaeus'' and ''Critias (dialogue), Critias''. While Plato's story was not part of the Greek myth, Greek mythic tradition and his dialogues use it solely as an allegory about hubris, speculation about real natural disasters that could have served as inspiration have been published in popular accounts and in a few academic contexts. Additionally, many works of pseudohistory and pseudoarchaeology treat the story as fact, offering reinterpretations that tie to national mysticism or legends of ancient astronauts, ancient aliens. While Plato's story explicitly locates Atlantis in the Atlantic Ocean beyond the Pillars of Hercules, other proposed locations for Atlantis include Helike, Thera, Troy, and the North Pole. North-West of Egypt: From Greece to Spain Most proposals for the location of Atlantis center on the Mediterran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantis Map 1882 Crop
Atlantis () is a fictional island mentioned in Plato's works '' Timaeus'' and ''Critias'' as part of an allegory on the hubris of nations. In the story, Atlantis is described as a naval empire that ruled all Western parts of the known world, making it the literary counter-image of the Achaemenid Empire. After an ill-fated attempt to conquer "Ancient Athens," Atlantis falls out of favor with the deities and submerges into the Atlantic Ocean. Since Plato describes Athens as resembling his ideal state in the ''Republic'', the Atlantis story is meant to bear witness to the superiority of his concept of a state. Despite its minor importance in Plato's work, the Atlantis story has had a considerable impact on literature. The allegorical aspect of Atlantis was taken up in utopian works of several Renaissance writers, such as Francis Bacon's ''New Atlantis'' and Thomas More's ''Utopia''. On the other hand, nineteenth-century amateur scholars misinterpreted Plato's narrative as histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudbeck Atlantis
The Rudbeck family, also spelled Rudebeck or von Rudebeck is a Swedish noble family, originating from Northern Schleswig. They were ennobled in 1719 by Queen Ulrika Eleanora and in 1776 awarded with the title of Baron in Sweden.https://www.adelsvapen.com/genealogi/Rudbeck_nr_282 The family is related to the Nobel family. Notable members *Johannes Rudbeck (1581–1646), Bishop at Västerås, Sweden, from 1619 until his death *Olaus Rudbeck (1630–1702), Swedish scientist and writer, professor of medicine at Uppsala University, son of Bishop Johannes Rudbeck at Västerås *Olof Rudbeck the Younger Olof Rudbeck the Younger or Olaus Rudbeckius d.y. (15 March 1660 – 23 March 1740) was a Swedish explorer, scientist, botanist, ornithologist and rector of Uppsala University. Biography Olof Rudbeck was born in Uppsala, Sweden, the son of O ... (1660–1740), Swedish explorer and scientist, son of Olaus Rudbeck Sr., ennobled 1719 by Queen Ulrika Eleanora. References {{surna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus Dwarf Elephant
''Palaeoloxodon cypriotes'' is an extinct species of dwarf elephant that inhabited the island of Cyprus during the Late Pleistocene. A probable descendant of the large straight-tusked elephant of mainland Europe and West Asia, the species is among the smallest known dwarf elephants, with fully grown individuals having an estimated shoulder height of only . It represented one of only two large animal species on the island alongside the Cypriot pygmy hippopotamus. The species became extinct around 12,000 years ago, around the time humans first colonised Cyprus, and potential (but disputed) evidence of human hunting has been found. History of research and excavations The first recorded finds were by Dorothea Bate in 1902Bate, D. M. A.: "Preliminary Note on the Discovery of a Pygmy Elephant in the Pleistocene of Cyprus" in '' Proceedings of the Royal Society of London'' Vol. 71 (1902–1903), pp. 498–500 from the cave deposit of Páno Díkomo-''Imbohary'' in the southern part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of islands in the Mediterranean, third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily and Sardinia. It is located southeast of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, northwest of Israel and Palestine, and north of Egypt. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. Cyprus hosts the British Overseas Territories, British military bases Akrotiri and Dhekelia, whilst the northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Northern Cyprus, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which is separated from the Republic of Cyprus by the United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus, United Nations Buffer Zone. Cyprus was first settled by hunter-gatherers around 13,000 years ago, with farming communities em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.. The Mycenaeans were mainland Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own. The most prominent site was Mycenae, after which the culture of this era is named. Other centers of power that emerged included Pylos, Tiryns, and Midea in the Peloponnese, Orchomenos, Thebes, and Athens in Central Greece, and Iolcos in Thessaly. Mycenaean settlements also appeared in Epirus, Macedonia, on islands in the Aegean Sea, on the south-west coast of Asia Minor, and on Cyprus, while Mycenaean-influenced settlements appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
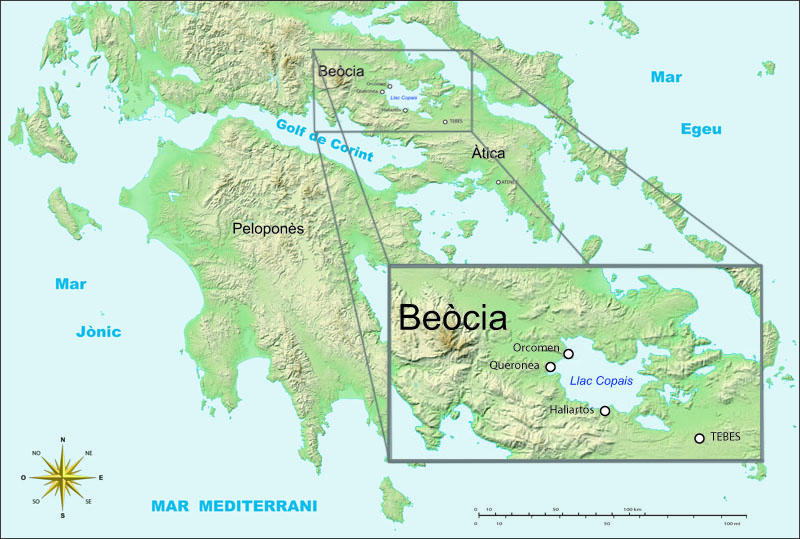
Lake Copais
Lake Copais, also spelled Kopais or Kopaida (; ), was a lake in the centre of Boeotia, Greece, west of Thebes. It was first drained in the Bronze Age, and drained again in the late 19th century. It is now flat dry land and is still known as Kopaida. A one-time island in the lake was modified in ancient times into a megalithic citadel, now called Gla. Lake Copais is also featured in Ubisoft's Assassin's Creed Odyssey (2018). Drainage When the lake existed, the towns of Haliartus, Orchomenus, and Chaeronea were on its shores. Rivers feeding the lake included the Cephissus, Termessus and Triton. The lake was (and is) surrounded by fertile land, but the lake increasingly encroached on the surrounding land because of inadequate drainage. First, though abortive, plans to drain the lake were made in 1834-1838. In 1865 a French company, Montferrier and Bonnair, signed a contract with the Greek government to drain the lake. But in 1873 after having drained the lake partially, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology (magazine)
''Archaeology'' is a bimonthly magazine for the general public, published by the Archaeological Institute of America The Archaeological Institute of America (AIA) is North America, North America's oldest learned society and largest organization devoted to the world of archaeology. AIA professionals have carried out archaeological fieldwork around the world and .... The institute also publishes the professional '' American Journal of Archaeology.'' Its first issue was published in the spring of 1948. The editor-in-chief was Peter Young until 2011 when he was replaced by Claudia Valentino. Jarrett A. Lobell assumed the editorship from Valentino in November 2018. References External links * Science and technology magazines published in the United States Archaeology magazines Magazines established in 1948 Bimonthly magazines published in the United States Magazines published in New York City {{archaeology-mag-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete is located about south of the Peloponnese, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete covers 260 km from west to east but is narrow from north to south, spanning three longitudes but only half a latitude. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete (), which is the southernmost of the 13 Modern regions of Greece, top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akrotiri (prehistoric City)
Akrotiri (Greek language, Greek: Ακρωτήρι, pronounced ) is the site of a Cycladic Culture, Cycladic Bronze Age settlement on the volcanic Greece, Greek island of Santorini (Thera). The name comes from the nearby village of Akrotiri, Santorini, Akrotiri. The settlement was destroyed in the Minoan eruption, Theran eruption sometime in the 16th century BCE and buried in volcanic ash, which preserved the remains of fine frescoes and many objects and artworks. Akrotiri has been excavated since 1967 after earlier excavations on Santorini. History The earliest evidence for human habitation of Akrotiri can be traced back as early as the fifth millennium BCE when it was a small fishing and farming village. By the end of the third millennium, this community developed and expanded significantly. One factor for Akrotiri's growth may be the trade relations it established with other Aegean civilization, cultures in the Aegean, as evidenced in fragments of foreign pottery at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Eruption
The Minoan eruption was a catastrophic volcanic eruption that devastated the Aegean island of Thera (also called Santorini) circa 1600 BCE. It destroyed the Minoan settlement at Akrotiri, as well as communities and agricultural areas on nearby islands and the coast of Crete with subsequent earthquakes and paleotsunamis. With a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 7, it resulted in the ejection of approximately of dense-rock equivalent (DRE), the eruption was one of the largest volcanic events in human history. Since tephra from the Minoan eruption serves as a marker horizon in nearly all archaeological sites in the Eastern Mediterranean, its precise date is of high importance and has been fiercely debated among archaeologists and volcanologists for decades, without coming to a definite conclusion. Although there are no clear ancient records of the eruption, its plume and volcanic lightning may have been described in the Egyptian Tempest Stele. The Chinese ''Bamboo Annal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santorini ASTER
Santorini (, ), officially Thira (, ) or Thera, is a Greek island in the southern Aegean Sea, about southeast from the mainland. It is the largest island of a small, circular archipelago formed by the Santorini caldera. It is the southernmost member of the Cyclades group of islands, with an area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 15,480. The municipality of Santorini includes the inhabited islands of Santorini and Therasia, and the uninhabited islands of Nea Kameni, Palaia Kameni, Aspronisi, Anydros, and Christiana. The total land area is . Santorini is part of the Thira regional unit. It is the most active volcanic centre in the South Aegean Volcanic Arc. The volcanic arc is approximately long and wide. The region first became volcanically active around 3–4 million years ago, though volcanism on Thera began around 2 million years ago with the extrusion of dacitic lavas from vents around Akrotiri. One of the largest volcanic eruptions in recorded histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |