|
Lobster Eye Optics
Lobster-eye optics is an X-ray optics design that mimic the structure of the lobster's eyes and has an ultra wide field of view. It was proposed in 1979, and first used in the Chinese technology demonstrator spacecraft Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy, launched in 2022. Currently several space telescopes that use lobster-eye optics are under development or consideration. Description Lobster-eye optics mimic the structure of the lobster's eyes, that are made up of long, narrow cells that each reflect a tiny amount of light from a given direction. This allows the light from a wide viewing area to be focused into a single image. The optics is made of microchannel plates (or micropores) — thin, curved slabs of material dotted with tiny tubes across the surface. X-ray light can enter these tubes from multiple angles and is focused through grazing-incidence reflection that gives a wide field of view necessary for finding and imaging transient events that cannot be predicted in adva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic Diagram Of Lobster Eye Lens
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center
The Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center (TSLC) also known as ''Base 25'' (), is a People's Republic of China space vehicle, space and defense launch facility (spaceport). It is situated in Kelan County, Xinzhou, Shanxi, Xinzhou, Shanxi Province and is the second of four launch sites having been founded in March 1966 and coming into full operation in 1968. Taiyuan sits at an altitude of 1500 meters and its dry climate makes it an ideal launch site. The site is primarily used to launch meteorological satellites, Earth resource satellites and scientific satellites on Long March (rocket family), Long March launch vehicles into Sun-synchronous orbits. TSLC is also a major launch site for intercontinental ballistic missiles and overland submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) tests. The site has a sophisticated Technical Center and Mission Command and Control Center. It is served by two feeder railways that connect with the Ningwu–Kelan railway. Launch pads * Launch Site 7: Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Light (astronomy)
In astronomy, first light is the first use of a telescope (or, in general, a new instrument) to take an astronomical image after it has been constructed. This is often not the first viewing using the telescope; optical tests will probably have been performed to adjust the components. Characteristics The first light image is normally of little scientific interest and is of poor quality, since the various telescope elements are yet to be adjusted for optimum efficiency. Despite this, a first light is always a moment of great excitement, both for the people who design and build the telescope and for the astronomical community, who may have anticipated the moment for many years while the telescope was under construction. A well-known and spectacular astronomical object is usually chosen as a subject. Historical examples The famous Hale Telescope of Palomar Observatory saw first light on 26 January 1949, targeting NGC 2261 under the direction of American astronomer Edwin Powel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein Probe
The Einstein Probe (EP) is an X-ray space telescope mission by Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in partnership with ESA and the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE) dedicated to time-domain high-energy astrophysics. The primary goals are "to discover high-energy transients and monitor variable objects". It will carry two instruments: the Wide-field X-ray Telescope (WXT) and the Follow-up X-ray Telescope (FXT). FXT has optics adopted from eROSITA, "the mirror module consists of 54 nested Wolter mirrors with a focal length of 1600 mm and an effective area of greater than 300 cm2 at 1.5 keV." WXT has a new optics design, called " lobster-eye", that has wider field of view. "Lobster-eye" optics was first tested by the Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy (LEIA) mission, launched in 2022. The probe weights 1450 kg and is 3-by-3.4 metres. EP was launched on 9 January 2024, at 07:03 UTC by a Long March 2C rocket from the Xichang Satellite Launch Centre in China, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extragalactic
Extragalactic astronomy is the branch of astronomy concerned with objects outside the Milky Way galaxy. In other words, it is the study of all astronomical objects which are not covered by galactic astronomy. The closest objects in extragalactic astronomy include the galaxies of the Local Group, which are close enough to allow very detailed analyses of their contents (e.g. supernova remnants, stellar associations). As instrumentation has improved, distant objects can now be examined in more detail and so extragalactic astronomy includes objects at nearly the edge of the observable universe. Research into distant galaxies (outside of our local group) is valuable for studying aspects of the universe such as galaxy evolution and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) which give insight into physical phenomena (e.g. super massive black hole accretion and the presence of dark matter). It is through extragalactic astronomy that astronomers and physicists are able to study the effects of General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
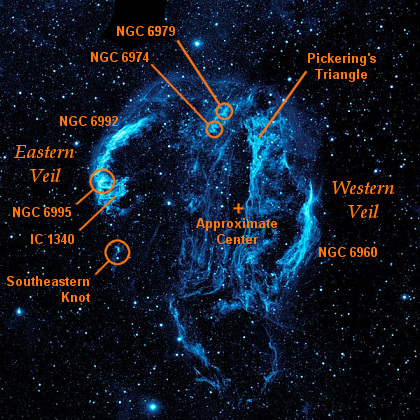
Cygnus Loop
The Cygnus Loop (radio source W78, or Sharpless 103) is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebula or Cirrus Nebula, emit in the visible electromagnetic range. Radio, infrared, and X-ray images reveal the complete loop. Visual components: the Veil Nebula The visual portion of the Cygnus Loop is known as the Veil Nebula, also called the Cirrus Nebula or the Filamentary Nebula. Several components have separate names and identifiers, including the "Western Veil" or "Witch's Broom", the "Eastern Veil", and Pickering's Triangle. NGC 6960 NGC 6960, the ''Western Veil'', is the western part of the remnant, also known as the "Witch's Broom", located at J2000 RA Dec . As the westernmost NGC object in the nebula (first in right ascension), its number is sometimes used as an NGC identifier for the nebula as a whole. NGC 6992, NGC 6995, and IC 1340 T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cas A
Cassiopeia A (Cas A) () is a supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately away within the Milky Way; given the width of the Orion Arm, it lies in the next-nearest arm outwards, the Perseus Arm, about 30 degrees from the Galactic anticenter. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova now appears approximately across from Earth's perspective. It has been seen in wavelengths of visible light with amateur telescopes down to 234 mm (9.25 in) with filters. It is estimated that light from the supernova itself first reached Earth near the 1690s, although there are no definitively corresponding records from then. Cas A is circumpolar at and above mid-Northern latitudes which had extensive records and basic telescopes. Its likely omission in records is probably due to interstellar dust absorbing optical wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sco X-1
Scorpius X-1 is an X-ray source located roughly 9000 light years away in the constellation Scorpius. Scorpius X-1 was the first extrasolar X-ray source discovered, and, aside from the Sun, it is the strongest apparent source of X-rays in the sky. The X-ray flux varies day-to-day, and is associated with an optically visible star, V818 Scorpii, that has an apparent magnitude which fluctuates between 12-13. Discovery and early study The possible existence of cosmic soft X-rays was first proposed by Bruno Rossi, MIT Professor and Board Chairman of American Science and Engineering in Cambridge, Massachusetts to Martin Annis, President of AS&E. Following his urging, the company obtained a contract from the United States Air Force to explore the lunar surface prior to the launch of astronauts to the Moon, and incidentally to perhaps see galactic sources of X-rays. Subsequently, Scorpius X-1 was discovered in 1962 by a team, under Riccardo Giacconi, who launched an Aerobee 150 sounding r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellanic Clouds
The Magellanic Clouds (''Magellanic system'' or ''Nubeculae Magellani'') are two irregular dwarf galaxies in the southern celestial hemisphere. Orbiting the Milky Way galaxy, these satellite galaxies are members of the Local Group. Because both show signs of a bar structure, they are often reclassified as Magellanic spiral galaxies. The two galaxies are: * Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), approximately 163,000 light-years away * Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), approximately 206,000 light years away Magellanic clouds are visible to the unaided eye in the Southern Hemisphere but they cannot be observed from the most northern latitudes. History The Magellanic Clouds have been known since ancient times to indigenous peoples across South America and Africa, and from the first millennium in Western Asia. The first preserved mention of the Large Magellanic Cloud is believed to be in petroglyphs and rock drawings found in Chile. They may be the objects mentioned by the polymath Ibn Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula. There are around 10 million stars within one parsec of the Galactic Center, dominated by red giants, with a significant population of massive supergiants and Wolf–Rayet stars from star formation in the region around 1 million years ago. The core stars are a small part within the much wider galactic bulge. Discovery Because of interstellar dust along the line of sight, the Galactic Center cannot b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Degree
__NOTOC__ A square degree (deg2) is a non- SI unit measure of solid angle. Other denotations include ''sq. deg.'' and (°)2. Just as degrees are used to measure parts of a circle, square degrees are used to measure parts of a sphere. Analogous to one degree being equal to radians, a square degree is equal to ()2 steradians (sr), or about sr or about . The whole sphere has a solid angle of which is approximately : : 4 \pi \left(\frac\right)^2 \, ^2 = \frac\,\, ^2 = \frac \,\, ^2 \approx 41\,252.96 \,\, ^2 Examples * The full moon covers only about of the sky when viewed from the surface of the Earth. The Moon is only a half degree across (i.e. a circular diameter of roughly ), so the moon's disk covers a circular area of: ()2, or 0.2 square degrees. The moon varies from 0.188 to depending on its distance to the Earth. * Viewed from Earth, the Sun is roughly half a degree across (the same as the full moon) and covers only as well. * It would take times the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Of View
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation. Humans and animals In the context of human and primate vision, the term "field of view" is typically only used in the sense of a restriction to what is visible by external apparatus, like when wearing spectacles or virtual reality goggles. Note that eye movements are allowed in the definition but do not change the field of view when understood this way. If the analogy of the eye's retina working as a sensor is drawn upon, the corresponding concept in human (and much of animal vision) is the visual field. It is defined as "the number of degrees of visual angle during stable fixation of the eyes".Strasburger, Hans; Pöppel, Ernst (2002). Visual Field. In G. Adelman & B.H. Smith (Eds): ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''; 3rd edition, on CD-ROM. El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |