|
List Of NGC Objects
The following is a list of NGC objects, that is objects listed in the New General Catalogue (NGC). It is one of the largest comprehensive astronomical catalogues for deep sky objects such as star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies. *List of NGC objects (1–1000) *List of NGC objects (1001–2000) * List of NGC objects (2001–3000) *List of NGC objects (3001–4000) *List of NGC objects (4001–5000) * List of NGC objects (5001–6000) *List of NGC objects (6001–7000) *List of NGC objects (7001–7840) Superlative entries NGC objects of superlative significance include: * NGC 2573 - Polarissima Australis, the closest NGC object to the south celestial pole * NGC 3172 - Polarissima Borealis, the closest NGC object to the north celestial pole Stars Some objects originally thought to be deep sky objects and listed in the NGC have been subsequently shown to be ordinary stars, so their inclusion in the catalog is now considered erroneous. This list of stars is based on the 'NGC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalog, astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxy, galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William Herschel, William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the Celestial sphere, celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
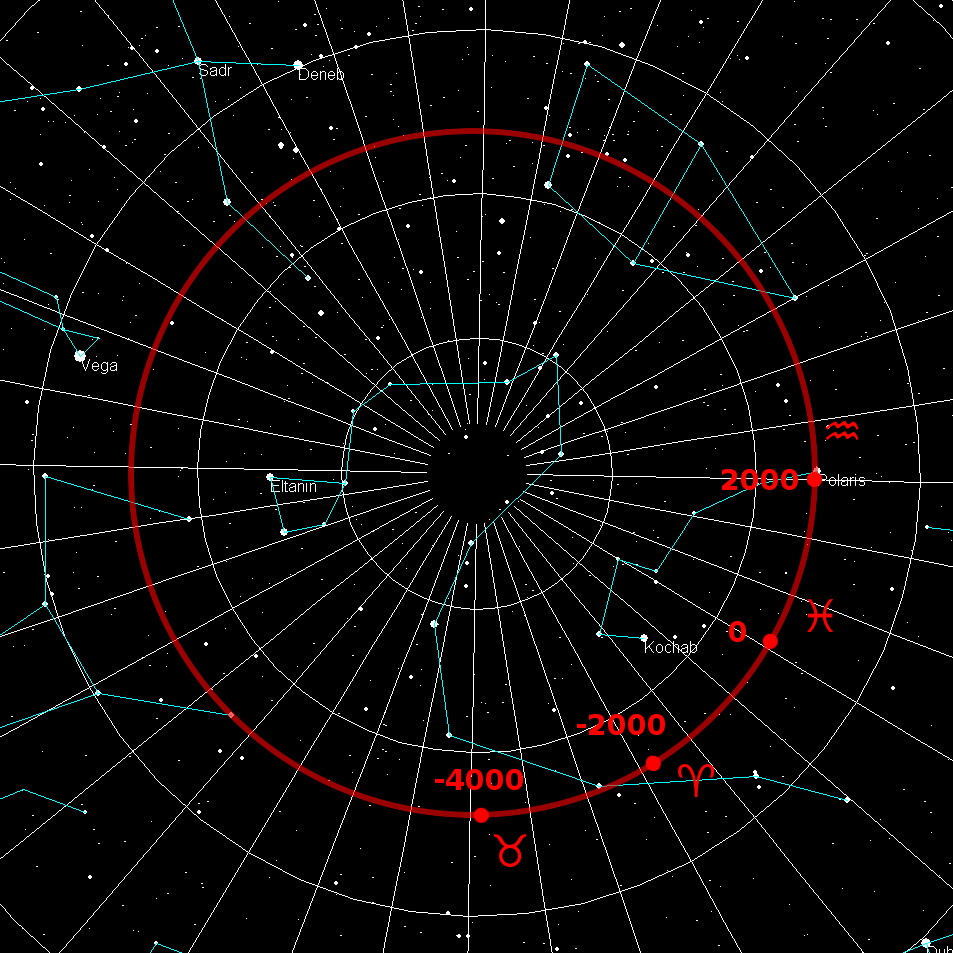
North Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich D'Arrest
Heinrich Louis d'Arrest (13 August 1822 – 14 June 1875; ) was a German astronomer, born in Berlin. His name is sometimes given as Heinrich Ludwig d'Arrest. Biography While still a student at the University of Berlin, d'Arrest was party to Johann Gottfried Galle's search for Neptune. On 23 September 1846, he suggested that a recently drawn chart of the sky, in the region of Urbain Le Verrier's predicted location, could be compared with the current sky to seek the displacement characteristic of a planet, as opposed to a stationary star. Neptune was discovered that very night. D'Arrest's later work at the Leipzig Observatory led him, in 1851, to the discovery of the comet named for him (formally designated 6P/d'Arrest). He also studied asteroids, discovering 76 Freia, nebulae, and galaxies, discovering NGC 1 in 1861 and NGC 26 and NGC 358 in 1865. In 1864 D'Arrest made an unsuccessful search for Martian satellites, and posited an upper limit of 70 minutes of arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 162
NGC 162 is a star in the Andromeda constellation. It was discovered by Heinrich d'Arrest in 1862. A few galaxies (PGC 2148 and PGC 212552) have been mis-identified as NGC 162. See also * Double star * List of NGC objects The following is a list of NGC objects, that is objects listed in the New General Catalogue (NGC). It is one of the largest comprehensive astronomical catalogues for deep sky objects such as star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies. *List of NGC obje ... References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 162 Andromeda (constellation) Astronomical objects discovered in 1862 0162 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 158
NGC 158 is a double star in the Cetus constellation. It was discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1882. See also * Double star * List of NGC objects The following is a list of NGC objects, that is objects listed in the New General Catalogue (NGC). It is one of the largest comprehensive astronomical catalogues for deep sky objects such as star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies. *List of NGC obje ... References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 158 Cetus Astronomical objects discovered in 1882 0158 Double stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 156
NGC 156 is a double star located in the Cetus constellation. It was discovered on 1882 by Ernst Wilhelm Leberecht Tempel. See also * New General Catalogue * List of NGC objects The following is a list of NGC objects, that is objects listed in the New General Catalogue (NGC). It is one of the largest comprehensive astronomical catalogues for deep sky objects such as star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies. *List of NGC obje ... References Further reading * * External links NGC 156 * * NGC katalog Interaktivni NGC Online KatalogAstronomska baza podataka SIMBAD NGC/IC projektNGC na ''The Night Sky Atlas'' sajtu {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 156 Cetus 0156 Double stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 82
NGC 82 is a magnitude 14.8 star located in the Andromeda constellation. It was first recorded by French astronomer Guillaume Bigourdan on October 23, 1884. References External links * 0082 8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ... Andromeda (constellation) 18841023 Discoveries by Guillaume Bigourdan {{Star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 46
NGC 46, occasionally referred to as PGC 5067596, is an F8 star located approximately 962 ± 281 light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was first discovered on October 22, 1852 by Irish astronomer Edward Joshua Cooper, who incorrectly identified it as a nebula. See also * List of NGC objects (1–1000) * Pisces (constellation) Pisces is a constellation of the zodiac. Its vast bulk – and main asterism viewed in most European cultures per Greco-Roman antiquity as a distant pair of fishes connected by one cord each that join at an apex – are in the Norther ... References External links * * SEDS 0046 18521022 Pisces (constellation) F-type subgiants Discoveries by Edward Joshua Cooper {{subgiant-star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 44
NGC commonly refers to: * New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, a catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy NGC may also refer to: Companies * NGC Corporation, name of US electric company Dynegy, Inc. from 1995 to 1998 * National Gas Company of Trinidad and Tobago, state-owned natural gas company in Trinidad and Tobago * National Grid plc, a former name of National Grid Electricity Transmission plc, the operator of the British electricity transmission system * Northrop Grumman Corporation, aerospace and defense conglomerate formed from the merger of Northrop Corporation and Grumman Corporation in 1994 * Numismatic Guaranty Corporation, coin certification company in the United States Other uses * National Gallery of Canada, art gallery founded in 1880 in Ottawa, Canada * National Geographic, documentary and reality television channel established in the United States in 2001 formerly called National Geographic Channel * Native Girls Code, US non-profit organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |