|
Line (unit)
The line (abbreviated L or l or ‴ or lin.) was a small English unit of length, variously reckoned as , , , or of an inch. It was not included among the units authorized as the British Imperial system in 1824. Size The line was not recognized by any statute of the English Parliament but was usually understood as of a barleycorn, (which itself was recognized by statute as of an inch) making it of an inch, and of a foot. The line was eventually decimalized as of an inch, without recourse to barleycorns. The US button trade uses the same or a similar term but defined as one-fortieth of the US-customary inch (making a button-maker's line equal to ). In use Botanists formerly used the units (usually as inch) to measure the size of plant parts. Linnaeus's ''Philosophia botanica'' (1751) includes the Linea in its summary of units of measurements, defining it as []; Stearns gives its length as . Even after metrication, British botanists continued to employ tools with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Units
English units were the units of measurement used in England up to 1826 (when they were replaced by Imperial units), which evolved as a combination of the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon and Ancient Roman units of measurement, Roman systems of units. Various standards have applied to English units at different times, in different places, and for different applications. Use of the term "English units" can be ambiguous, as, in addition to the meaning used in this article, it is sometimes used to refer to the units of the descendant Imperial system as well to those of the descendant system of United States customary units. The two main sets of English units were the Winchester measure, Winchester Units, used from 1495 to 1587, as affirmed by Henry VII of England, King Henry VII, and the Exchequer Standards, in use from 1588 to 1825, as defined by Queen Elizabeth I. In England (and the British Empire), English units were replaced by Imperial units in 1824 (effective as of 1 January 1826) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
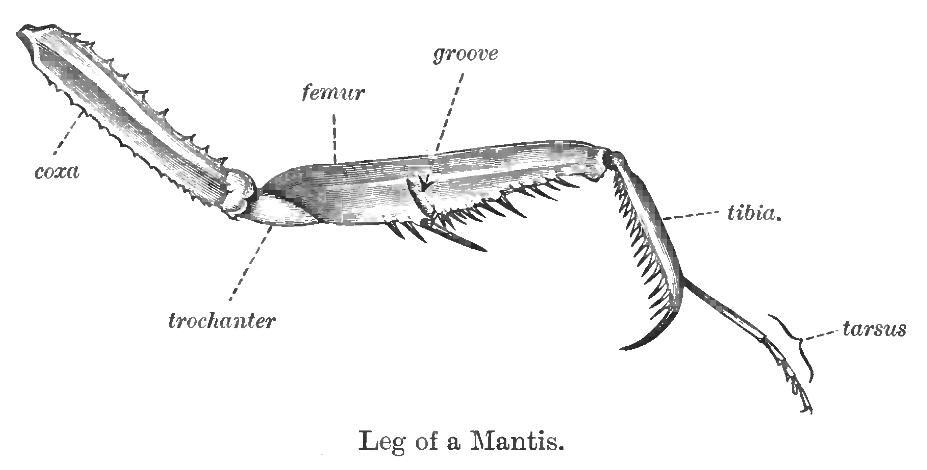
Mantidae
Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species ''Mantis religiosa''; most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many references still use the term "mantid" to refer to any mantis. Technically, however, "mantid" refers only to members of the family Mantidae, and not the numerous remaining families of mantises. Some of the most recent classifications have promoted a number of the mantid subfamilies to the rank of family, e.g. Iridopterygidae, Sibyllidae, Tarachodidae, Thespidae, and Toxoderidae, while other classifications have reduced the number of subfamilies without elevating them to higher rank. Subfamilies and genera Following the major revision of the Mantodea in 2019, the ''Mantodea Species File'' includes ten subfamilies: Choeradodinae The Americas, Asia * ''Asiadodis'' Roy, 2004 * ''Choeradodis'' Serville, 1831 Deromantinae Africa * '' Deromantis'' Giglio-T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Units Of Measurement
The units of measurement of German-speaking countries consist of a variety of units, with varying local standard definitions. While many were made redundant with the introduction of the metric system, some of these units are still used in everyday speech and even in stores and on street markets as shorthand for similar amounts in the metric system. For example, some customers ask for one pound (''ein Pfund'') of something when they want 500 grams. The metric system became compulsory on 1 January 1872, in Germany and on 1 January 1876, in Austria. Some obsolete German units have names similar to units that were traditionally used in other countries, and that are still used in a limited number of cases in the United Kingdom (imperial units) and in the United States (United States customary units). German system Before the introduction of the metric system in Germany, almost every town had its own definitions of the units shown below. Often towns posted local definitions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Customary Units
Portuguese units were used in Portugal, Brazil, and other parts of the Portuguese Empire until the adoption of the metric system in the 19th century and have continued in use in certain contexts since. The various systems of weights and measures used in Portugal until the 19th century combine remote Roman influences with medieval influences from northern Europe and Islam. These influences are obvious in the names of the units. The measurement units themselves were, in many cases, inherited from a distant past. From the Romans, Portugal inherited names like (), (), , (), (), (), (). From medieval northern Europe, Portugal inherited names like (, ), (, ), (, ), (, ), (Fr. ), etc. From the Moors, Portugal receive unit names like (Arabic language, Arabic: ), (Arabic language, Arabic: ), (Arabic language, Arabic: ), (Arabic language, Arabic: ), (Arabic language, Arabic: ), (Arabic language, Arabic: ), (Arabic language, Arabic: ), etc. The Roman and northern European in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
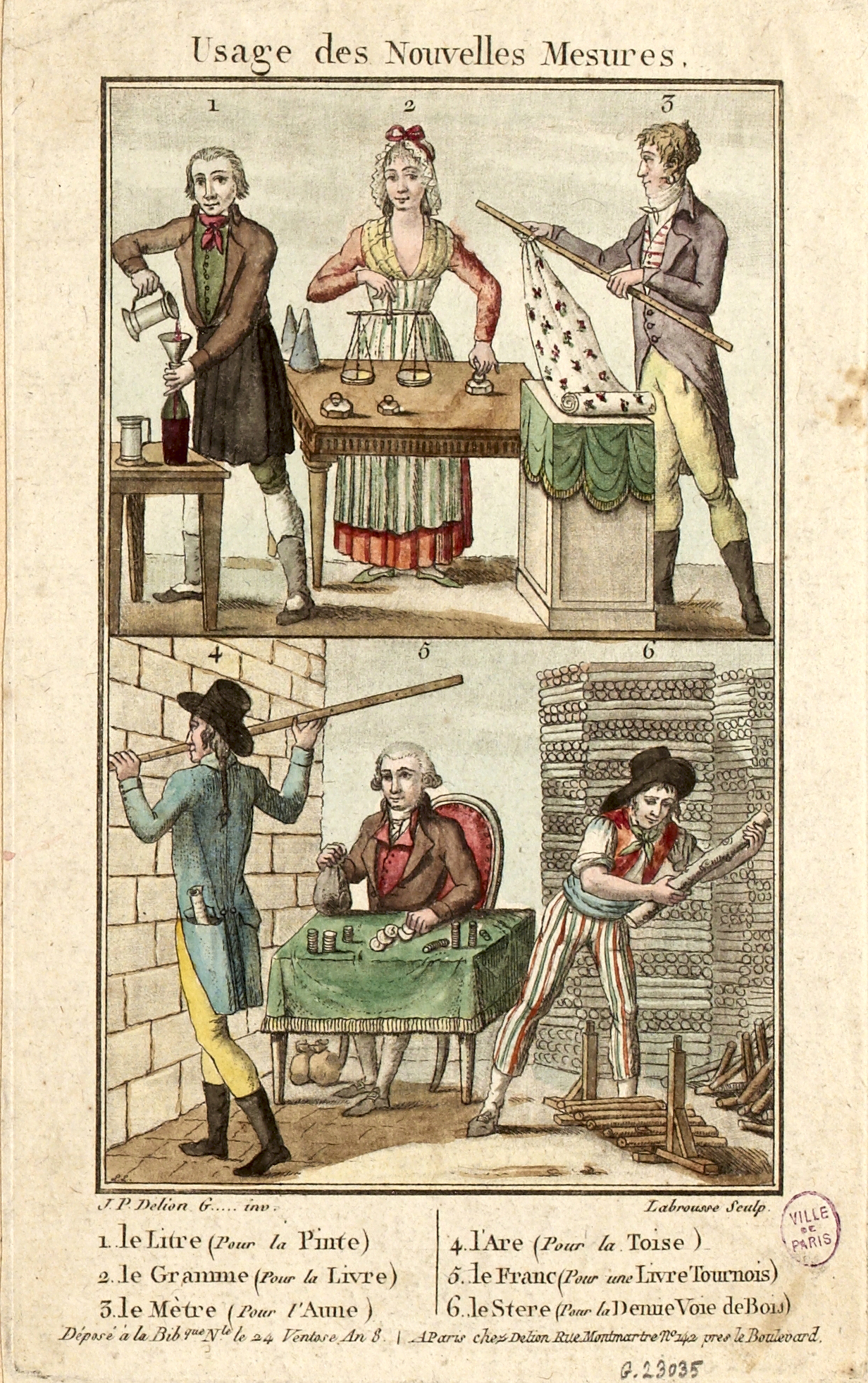
French Units Of Measurement
200px, Table of the measuring units used in the 17th century at region of southeastern France France has a unique history of Unit of measurement, units of measurement due to its radical decision to invent and adopt the metric system after the French Revolution. In the Ancien régime and until 1795, France used a system of measures that had many of the characteristics of the modern Imperial System of units but with no unified system. There was widespread abuse of the king's standards, to the extent that the ''lieue'' could vary from 3.268 km in Beauce to 5.849 km in Provence. During the revolutionary era and motivated in part by the inhomogeneity of the old system, France switched to the first version of the metric system. This system was not well received by the public, and between 1812 and 1837, the country used the '' mesures usuelles'' – traditional names were restored, but the corresponding quantities were based on metric units: for example, the ''livre'' (poun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V of Russia, Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Swedish Empire, Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Imperial Russian Navy, Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a Treaty of Nystad, significant portion of the eastern Baltic Sea, Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a Tsardom of Russia, tsardom to an Russian Empire, empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsolete Russian Units Of Measurement
Historical Russian units of measurement were standardized and used in the Russian Empire and after the Russian Revolution, but were abandoned after 21 July 1925, when the Soviet Union adopted the metric system. The Tatar system is very similar to the Russian one, but some names are different. The Polish system is also very close to the Russian. The system existed since Kievan Rus', but under Peter the Great, the Russian units were redefined relative to the English system.Шостьин Н. А. Очерки истории русской метрологии XI – начала XX века. М.: 1975. Until Peter the Great the system also used Cyrillic numerals, and only in the 18th century did Peter the Great replace it with the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. Length The basic unit was the Russian ell, called the ''arshin'', which came into use in the 16th century. It was standardized by Peter the Great in the 18th century to measure exactly twenty-eight English inches (). Thu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M2 Browning Machine Gun
The M2 machine gun or Browning .50-caliber machine gun (informally, "Ma Deuce") is a heavy machine gun that was designed near the end of World War I by John Browning. While similar to Browning's M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge, the M2 uses Browning's larger and more powerful .50 BMG (12.7 mm) cartridge. The design has had many designations; the official U.S. military designation for the infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It has been used against infantry, light armored vehicles, watercraft, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft. The gun has been used extensively as a vehicle weapon and for aircraft armament by the United States since the 1930s. It was heavily used during World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Falklands War, the Soviet–Afghan War, the Gulf War, the Iraq War, and the War in Afghanistan. It is the primary heavy machine gun of NATO countries and has been used by man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosin–Nagant
The Mosin–Nagant is a five-shot, Bolt action, bolt-action, Magazine (firearms), internal magazine–fed military rifle. Known officially as the 3-line rifle M1891, in Russia and the former Soviet Union as Mosin's rifle (, ISO 9: ) and informally just mosinka (), it is primarily chambered for the 7.62×54mmR Cartridge (firearms), cartridge. Developed from 1882 to 1891, it was used by the armed forces of the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union and various other states. It is one of the most mass-produced military bolt-action rifles in history, with over 37 million units produced since 1891. In spite of its age, it has been used in various conflicts around the world up to the present day. History Initial design and tests During the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), Imperial Russian troops armed mostly with single-shot Berdan rifles suffered heavy casualties against Ottoman Empire, Ottoman troops equipped with Winchester rifle#Model 1866, Winchester 1866 repeating rifles, particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |