|
Limine (bootloader)
Limine is a portable boot loader and the reference implementation for the Limine boot protocol. Multiboot2, chainloading, and the Linux boot protocols are also supported. Limine supports the ISO-9660 and FAT filesystems. Limine aims to provide a more robust alternative to bootloaders like GNU GRUB, as well as its own boot protocol as an alternative to the Multiboot specification, with the goal of reducing the amount of work needed for a kernel developer to get a workable 64-bit environment once booted. Limine is packaged by several Linux distributions, being offered by Arch Linux, where it is an option in archinstall, as well as included in EasyOS (a derivative of Puppy Linux), CachyOS, and Chimera Linux. Limine is also used by Cosmos and supported by SerenityOS. See also * GNU GRUB * BOOTMGR - current Windows bootloader * rEFInd - alternative boot loader for UEFI-based computers * Comparison of boot loaders The following tables compare general and technical informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Allocation Table
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers and was the default file system for the MS-DOS and Windows 9x operating systems. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on Hard disk drive, hard disks and other devices. The increase in disk drive capacity over time drove modifications to the design that resulted in versions: #FAT12, FAT12, #FAT16, FAT16, #FAT32, FAT32, and exFAT. FAT was replaced with NTFS as the default file system on Microsoft operating systems starting with Windows XP. Nevertheless, FAT continues to be commonly used on relatively small capacity solid-state storage technologies such as SD card, MultiMediaCard (MMC) and eMMC because of its compatibility and ease of implementation. Uses Historical FAT was used on hard disk drive, hard disks throughout the DOS and Windows 9x eras. Microsoft introduced NTFS with the Windows NT platform in 1993, but FAT remained the standard for the home use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Boot Loaders
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of available bootloaders. General information Technical information Note: The column MBR (Master Boot Record) refers to whether or not the boot loader can be stored in the first sector of a mass storage device. The column VBR (Volume Boot Record) refers to the ability of the boot loader to be stored in the first sector of any partition on a mass storage device. Storage medium support Operating system support File-system support Non-journaled Journaled Read-only Other features Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Comparison Of Boot Loaders BOOT Loaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REFInd
rEFInd is a boot manager for UEFI and EFI-based machines. It can be used to boot multiple operating systems that are installed on a single non-volatile device. It also provides a way to launch UEFI applications. It was forked from discontinued rEFIt in 2012, with 0.2.0 as its first release. rEFind supports the IA-32, x86-64, and AArch64 architectures. Features rEFInd has several features: * Automatic operating systems detection. * Customisable OS launch options. * Graphical or text mode. Theme is customisable. * Mac-specific features, including spoofing booting process to enable secondary video chipsets on some Mac. * Linux-specific features, including autodetecting EFI stub loader to boot Linux kernel directly and using fstab in lieu of rEFInd configuration file for boot order. * Support for Secure Boot. Adoption rEFInd is the default UEFI boot manager for TrueOS. rEFInd is included in official repositories of major Linux distributions. Development GNU-EFI and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BOOTMGR
The Windows Boot Manager (BOOTMGR) is the bootloader provided by Microsoft for Windows NT versions starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It is the first program launched by the BIOS or UEFI of the computer and is responsible for loading the rest of Windows. It replaced the NTLDR present in older versions of Windows. The boot sector or UEFI loads the Windows Boot Manager (a file named BOOTMGR on either the system or the boot partition), accesses the Boot Configuration Data store and uses the information to load the operating system through winload.exe or winresume.exe on BIOS systems, and winload.efi and winresume.efi on UEFI systems. Launching On system with BIOS firmware, the BIOS invokes MBR boot code from a hard disk drive at startup. The MBR boot code and the VBR boot code are OS-specific. In Microsoft Windows, the MBR boot code tries to find an active partition (the MBR is only 512 bytes), then executes the VBR boot code of an active partition. The VBR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SerenityOS
SerenityOS is a free and open source desktop operating system. It features a preemptive kernel, currently supports x86-64, ARM, and RISC-V based computers, and hosts multiple complex applications including its own web browser and integrated development environment (IDE). Development started in 2018—initially as a one-man project of Swedish programmer Andreas Kling—and is now developed by a community of hobbyists. The project is hosted at GitHub and is described as being not catered to "non-technical users". History Andreas Kling previously worked at Nokia and later at Apple on the WebKit team. He began developing the project in part to aid his recovery from addiction, and as such the name of the project derives from the Serenity Prayer. Starting in 2021, Kling began working full-time on SerenityOS, supported by community donations. On June 3rd, 2024, he stepped down as a project lead from the project (keeping his role as a maintainer) to work on the Ladybird browser. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos (operating System)
C# Open Source Managed Operating System (Cosmos) is a toolkit for building GUI and command-line based operating systems, written mostly in the programming language C# and small amounts of a high-level assembly language named X#. ''Cosmos'' is a backronym, in that the acronym was chosen before the meaning. It is open-source software released under a BSD license. , Cosmos encompasses an ahead-of-time (AOT) compiler named IL2CPU to translate Common Intermediate Language (CIL) into native instructions. Cosmos compiles user-made programs and associated libraries using IL2CPU to create a bootable native executable that can run independently. The resulting output can be booted from a USB flash drive, CD-ROM, over a network via Preboot Execution Environment (PXE), or inside a virtual machine. Recent releases also allow deploying to certain x86 embedded devices over Universal Serial Bus (USB). While C# is the primary language used by developers (both on the backend and by end users of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimera Linux
Chimera Linux is a Linux distribution striving for the minimum complexity of system configuration while retaining and expanding on the flexibility common to general purpose Linux based systems. It uses musl as its libc implementation, userland tools from FreeBSD, and dinit as its init system. For package management it uses apk-tools from Alpine Linux, but Chimera does not re-use Alpine packages, but instead uses its own novel package build system. The distribution has no upstream and defines itself as "independent" from this perspective. History Chimera Linux was started in 2021 by former Void Linux maintainer "q66". Features Chimera Linux makes use of userland components from FreeBSD, and the musl C library in-place of the GNU coreutils and glibc respectively. A strict default security model, employing the in-development dinit init system and the FreeBSD userland are some of the more radical approaches. Such changes would have been very hard for a distribution with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CachyOS
Arch Linux () is an open source, rolling release Linux distribution. Arch Linux is kept up-to-date by regularly updating the individual pieces of software that it comprises. Arch Linux is intentionally minimal, and is meant to be configured by the user during installation so they may add only what they require. Arch Linux provides monthly "snapshots" which are used as installation media. Pacman, a package manager written specifically for Arch Linux, is used to install, remove and update software packages. Additionally, the Arch User Repository (AUR), which is the community-driven repository for Arch Linux provides packages not included in the official repositories and alternative versions of packages; AUR packages can be downloaded and built manually, or installed through an AUR 'helper'. Arch Linux has comprehensive documentation in the form of a community-run wiki known as the ArchWiki. History Inspired by CRUX, another minimalist distribution, Judd Vinet started the Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
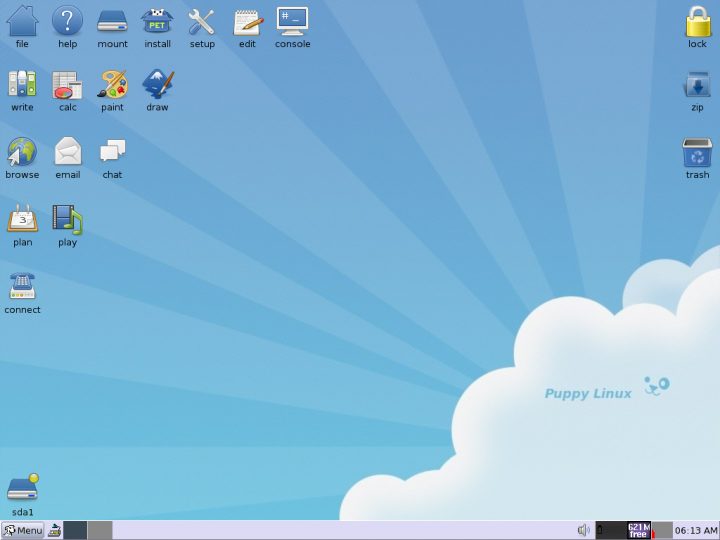
Puppy Linux
Puppy Linux is a family of light-weight Linux distributions that focus on ease of use and minimal memory footprint. The entire system can be run from random-access memory (RAM) with current versions generally taking up about 600 MB (64-bit), 300 MB (32-bit), allowing the boot medium to be removed after the operating system has started. Applications such as AbiWord, Gnumeric and MPlayer are included, along with a choice of lightweight web browsers and a utility for downloading other packages. The distribution was originally developed by Barry Kauler and other members of the community, until Kauler retired in 2013. The tool Woof can build a Puppy Linux distribution from the binary packages of other Linux distributions. History Barry Kauler started Puppy Linux in response to a trend of other distributions becoming stricter on system requirements over time. His own distribution, with an emphasis on speed and efficiency and being lightweight, started from "Boot disk HOWTO" and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Linux
Arch Linux () is an Open-source software, open source, rolling release Linux distribution. Arch Linux is kept up-to-date by regularly updating the individual pieces of software that it comprises. Arch Linux is intentionally minimal, and is meant to be configured by the user during installation so they may add only what they require. Arch Linux provides monthly "snapshots" which are used as Optical disc image, installation media. #Pacman, Pacman, a package manager written specifically for Arch Linux, is used to install, remove and update software packages. Additionally, the Arch User Repository (AUR), which is the community-driven repository for Arch Linux provides packages not included in the official repositories and alternative versions of packages; AUR packages can be downloaded and built manually, or installed through an AUR 'helper'. Arch Linux has comprehensive documentation in the form of a community-run wiki known as the ArchWiki. History Inspired by CRUX, another mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Distribution
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers (for example, Linux Mint) to servers (for example, Red Hat Enterprise Linux) and from embedded devices (for example, OpenWrt) to supercomputers (for example, Rocks Cluster Distribution). A distro typically includes many components in addition to the Linux kernel. Commonly, it includes a package manager, an init system (such as systemd, OpenRC, or runit), GNU tools and libraries, documentation, IP network configuration utilities, the getty TTY setup program, and many more. To provide a desktop experience (most commonly the Mesa userspace graphics drivers) a display server (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |