|
Lewisite
Lewisite (L) (A-243) is an organoarsenic compound. It was once manufactured in the United States, Japan, Germany and the Soviet Union for use as a Chemical warfare, chemical weapon, acting as a vesicant (blister agent) and lung irritant. Although the substance is colorless and odorless in its pure form, impure samples of lewisite are a yellow, brown, violet-black, green, or amber oily liquid with a distinctive odor that has been described as similar to Pelargonium, geraniums. Lewisite is named after the US chemist and soldier Winford Lee Lewis (1878–1943). Lewisite finds no other applications; a chemist from the United States Army's chemical warfare laboratories said that "no one has ever found any use for the compound". Chemical reactions The compound is prepared by the addition of arsenic trichloride to acetylene in the presence of a suitable catalyst: This chemical process can occur a second or third time, giving lewisite 2 and lewisite 3 as byproducts.Chemistry of Sulfur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewisite 3
Lewisite 3 (L-3) is an organoarsenic chemical weapon like lewisite 1 and lewisite 2 first synthesized in 1904 by Julius Arthur Nieuwland.McNutt, Patrick M., and Tracey L. Hamilton. "Ocular toxicity of chemical warfare agents." Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents. Academic Press, 2015. 535-555. It is usually found as a mixture of 2-chlorovinylarsonous dichloride (lewisite 1) as well as bis(2-chloroethenyl) arsinous chloride (lewisite 2) and tris(2-chlorovinyl)arsine (lewisite 3). Pure lewisite 1 is an oily, colorless liquid, however, the impure mixture can appear amber to black with an odor distinct to geraniums. Synthesis Lewisite 3 is made as a byproduct along with lewisite 2 in the reaction that makes lewisite 1.Chemistry of Sulfur Mustard and Lewisite https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK236079/ Acetylene reacts with AsCl3 in hydrochloric acid solution, with mercuric chloride as a catalyst, to give lewisite in 80 to 85% yield. :AsCl3 + C2H2 → (ClCH=CH)AsCl2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewisite 2
Lewisite 2 (L-2) is an organoarsenic chemical weapon with the formula AsCl(CH=CHCl)2. It is similar to lewisite 1 and lewisite 3 and was first synthesized in 1904 by Julius Arthur Nieuwland.McNutt, Patrick M., and Tracey L. Hamilton. "Ocular toxicity of chemical warfare agents." Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents. Academic Press, 2015. 535-555. It is usually found as a mixture of 2-chlorovinylarsonous dichloride (lewisite 1) as well as bis(2-chloroethenyl) arsinous chloride (lewisite 2) and tris(2-chlorovinyl)arsine (lewisite 3). Synthesis Lewisite 2 is made as a byproduct along with lewisite 3 in the reaction that makes lewisite 1.Chemistry of Sulfur Mustard and Lewisite https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK236079/ Acetylene reacts with AsCl3 in hydrochloric acid solution, with mercuric chloride as a catalyst, to give lewisite in 80 to 85% yield. :AsCl3 + C2H2 → (ClCH=CH)AsCl2 Lewisite 2 is formed when there are two additions of acetylene to the arsenic center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustard Gas
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard are names commonly used for the organosulfur compound, organosulfur chemical compound bis(2-chloroethyl) sulfide, which has the chemical structure S(CH2CH2Cl)2, as well as other Chemical species, species. In the wider sense, compounds with the substituents are known as ''sulfur mustards'' or ''nitrogen mustards'', respectively, where X = Cl or Br. Such compounds are potent alkylating agents, making mustard gas acutely and severely toxic. Mustard gas is a carcinogen. There is no preventative agent against mustard gas, with protection depending entirely on skin and airways protection, and no antidote exists for mustard poisoning. Also known as mustard agents, this family of compounds comprises infamous cytotoxicity, cytotoxins and blister agents with a long history of use as chemical weapons. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect; the substances, when Dispersion (chemistry), dispersed, are often not gases but a fine mist of liquid droplet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winford Lee Lewis
Winford Lee Lewis (May 29, 1878 – January 20, 1943) was a US soldier and chemist best known for his rediscovery of the chemical warfare agent lewisite in 1917. He was born in Gridley, California and died in his home in Evanston, Illinois in 1943 following a fall. Biography Winford Lee Lewis was born at home to George M Lewis and Sarah A Lewis on May 29, 1878, in Gridley, California. He was the youngest of seven children: he had six brothers and one sister. In 1908 he and his wife Myrlilla C Lewis had a daughter Miriam Lewis. He attended Stanford University and graduated in 1902. In 1909, he graduated with a degree in chemistry from the University of Chicago. He became a chemistry professor at Northwestern University until the outbreak of World War I. During the war, he served in the United States Chemical Warfare Service. It was during his service with the Chemical Warfare Service that he rediscovered Lewisite and assisted in its weaponization and mass production. After the war, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is notoriously toxic. It occurs naturally in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. It has various Allotropes of arsenic, allotropes, but only the grey form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is also a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices, and a component of the III–V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the persistent tox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Burn
A chemical burn occurs when living tissue is exposed to a corrosive substance (such as a strong acid, base or oxidizer) or a cytotoxic agent (such as mustard gas, lewisite or arsine). Chemical burns follow standard burn classification and may cause extensive tissue damage. The main types of irritant and/or corrosive products are: acids, bases, oxidizers / reducing agents, solvents, and alkylants. Additionally, chemical burns can be caused by biological toxins (such as anthrax toxin) and by some types of cytotoxic chemical weapons, e.g., vesicants such as mustard gas and Lewisite, or urticants such as phosgene oxime. Chemical burns may: * need no source of heat * occur immediately on contact * not be immediately evident or noticeable * be extremely painful * diffuse into tissue and damage cellular structures under skin without immediately apparent damage to skin surface Exposure to a toxic substance that is insufficient to cause a chemical burn can still be very seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
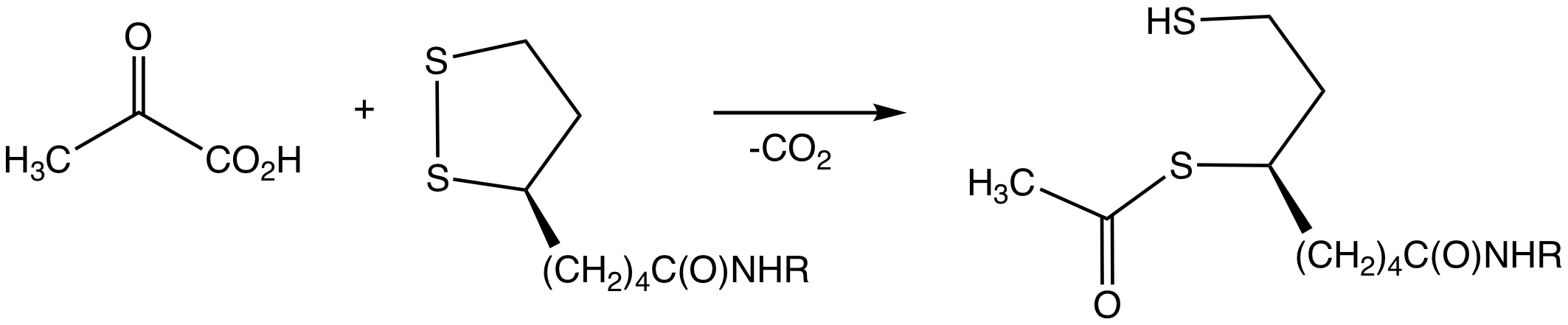
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is usually encountered as a component, referred to as E1, of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). PDC consists of other enzymes, referred to as E2 and E3. Collectively E1-E3 transform pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A into acetyl-CoA, CO2, and NADH. The conversion is crucial because acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration. To distinguish between this enzyme and the PDC, it is systematically called pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring). Mechanism The thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) converts to an ylide by deprotonation. The ylide attack the ketone group of pyruvate. The resulting adduct decarboxylates. The resulting 1,3-dipole reductively acetylates lipoamide-E2. In terms of details, biochem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A (CoASH or CoA) consists of a cysteamine, β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group (indicated in blue in the structural diagram on the right) of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. This thioester linkage is a "high energy" bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol). CoA is acetylated to acetyl-CoA by the breakdown of carbohydrates through glycolysis and by the breakdown of fatty acids through Beta oxidation, β-oxidation. Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle, where the acetyl group is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCA Cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-CoA Redox, oxidation. The energy released is available in the form of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. The Hans Krebs (biochemist), Krebs cycle is used by organisms that generate energy via Cellular respiration, respiration, either anaerobic respiration, anaerobically or aerobic respiration, aerobically (organisms that Fermentation, ferment use different pathways). In addition, the cycle provides precursor (chemistry), precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADH, which are used in other reactions. Its central importance to many Metabolic pathway, biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest metabolism components. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the Limb (anatomy), limbs and Organ (anatomy), organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into a somatic nervous system, somatic division and an autonomic nervous system, autonomic division. Each of these can further be differentiated into a sensory and a motor sector. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exceptions of the olfactory nerve and epithelia and the optic nerve (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living Organism, organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as amylose and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form is -glucose, while its Stereoisomerism, stereoisomer L-glucose, -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |