|
Lentic Ecosystems
A lake ecosystem or lacustrine ecosystem includes biotic (living) plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (non-living) physical and chemical interactions. Lake ecosystems are a prime example of lentic ecosystems (''lentic'' refers to stationary or relatively still freshwater, from the Latin ''lentus'', which means "sluggish"), which include ponds, lakes and wetlands, and much of this article applies to lentic ecosystems in general. Lentic ecosystems can be compared with lotic ecosystems, which involve flowing terrestrial waters such as rivers and streams. Together, these two ecosystems are examples of freshwater ecosystems. Lentic systems are diverse, ranging from a small, temporary rainwater pool a few inches deep to Lake Baikal, which has a maximum depth of 1642 m. The general distinction between pools/ponds and lakes is vague, but Brown states that ponds and pools have their entire bottom surfaces exposed to light, while lakes do not. In addition, some lakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LSE Pond
LSE may refer to: Education * London School of Economics, a public research university within the University of London * Lahore School of Economics, a private university in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan * Lincoln Southeast High School, a public government education school located in Lincoln, Nebraska * Louvain School of Engineering, faculty of engineering science at the University of Louvain (UCLouvain), Belgium Computing * ("Symbolic teaching language"), a computer programming language * Language-Sensitive Editor, a text editor used on Digital Equipment Corporation's VMS operating system * Large system extensions, a set of atomic memory operations such as fetch-and-add for the 64-bit ARM (AArch64) architecture * Latent sector error, an unrecoverable read error on a hard disk drive which has not yet been discovered Finance * Lahore Stock Exchange, now Pakistan Stock Exchange * London Stock Exchange * London Stock Exchange Group London Stock Exchange Group plc, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic Zone
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. In a manner analogous to stratification in the Earth's atmosphere, the water column can be divided vertically into up to five different layers (illustrated in the diagram), with the number of layers depending on the depth of the water. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
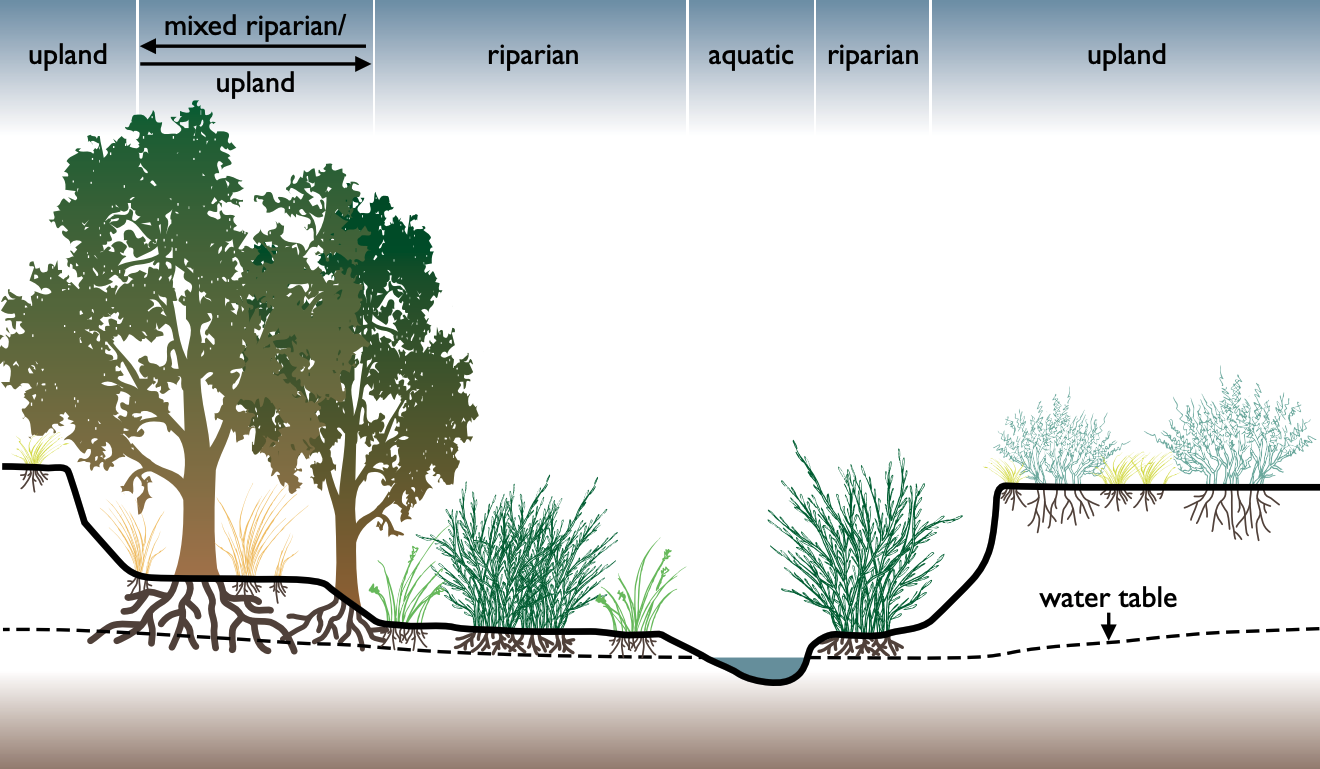
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riparian Zone
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin ''wiktionary:ripa, ripa'', meaning "bank (geography), river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by aquatic plant, hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profundal Zone
The profundal zone is the deep zone of a lake, located below the range of effective light penetration. This is typically below the thermocline, the vertical zone in the water through which temperature drops rapidly. The temperature difference may be large enough to hamper mixing with the littoral zone in some seasons which causes a decrease in oxygen concentrations. The profundal is often defined, as the deepest, vegetation-free, and muddy zone of the lacustrine benthal. The profundal zone is often part of the aphotic zone. Sediment in the profundal zone primarily comprises silt and mud. Organisms The lack of light and oxygen in the profundal zone determines the type of biological community that can live in this region, which is distinctly different from the community in the overlying waters. The profundal macrofauna is therefore characterized by physiological and behavioural adaptations to low oxygen concentration. While benthic fauna differs between lakes, Chironomidae and Olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
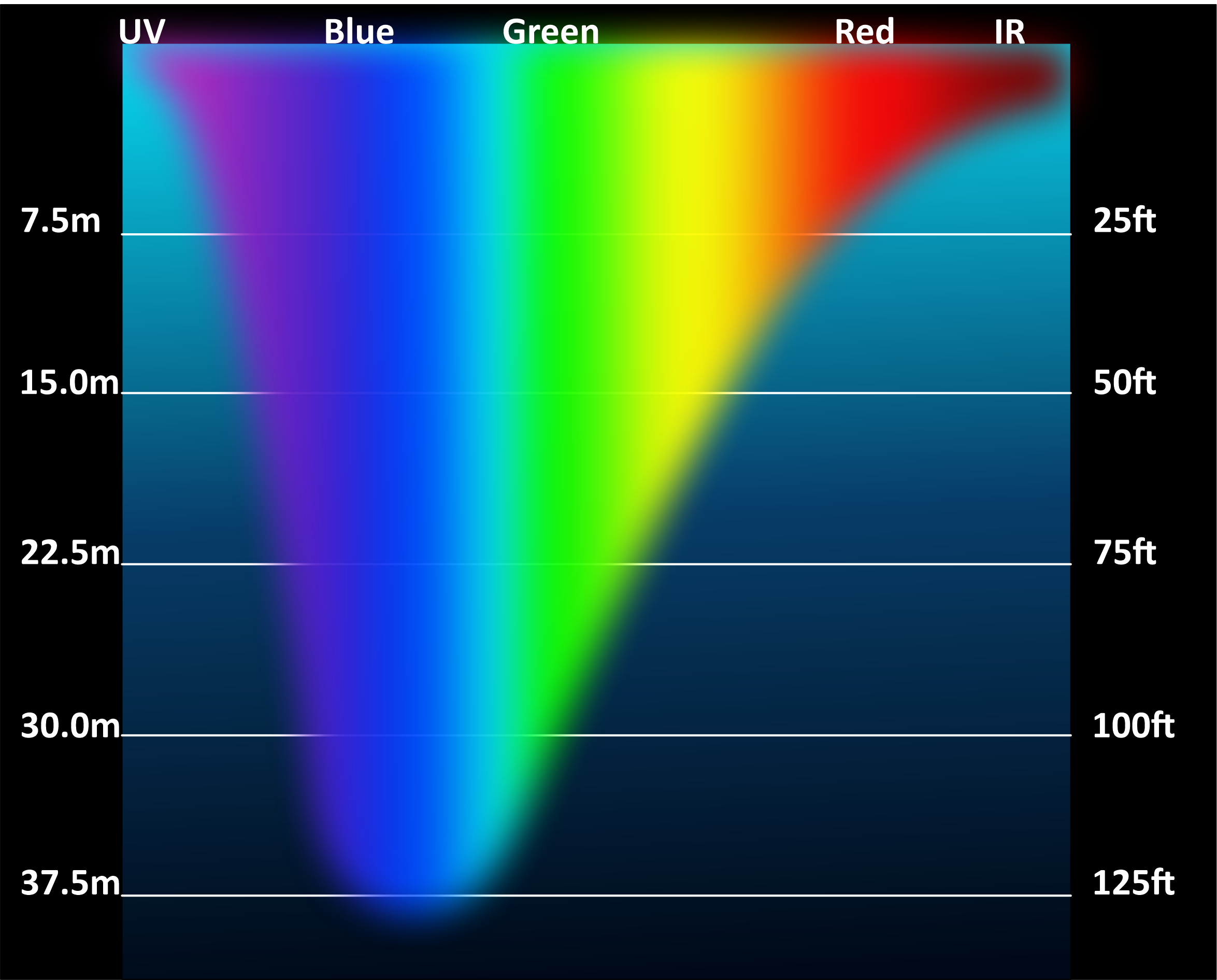
Aphotic Zone
The aphotic zone (aphotic from Greek prefix + "without light") is the portion of a lake or ocean where there is little or no sunlight. It is formally defined as the depths beyond which less than 1 percent of sunlight penetrates. Above the aphotic zone is the photic zone, which consists of the euphotic zone and the disphotic zone. The euphotic zone is the layer of water in which there is enough light for net photosynthesis to occur. The disphotic zone, also known as the twilight zone, is the layer of water with enough light for predators to see but not enough for the rate of photosynthesis to be greater than the rate of respiration. The depth at which less than one percent of sunlight reaches begins the aphotic zone. While most of the ocean's biomass lives in the photic zone, the majority of the ocean's water lies in the aphotic zone. Bioluminescence is more abundant than sunlight in this zone. Most food in this zone comes from dead organisms sinking to the bottom of the lake o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnetic Zone
The limnetic zone is the open and well-lit area of a freestanding body of fresh water, such as a lake or pond. Not included in this area is the littoral zone, which is the shallow, near-shore area of the water body. The key difference between the littoral zone and the limnetic zone is the presence of rooted plant growth. The floor under the limnetic zone cannot sustain plant growth due to a lack of sunlight for photosynthesis. In extremely shallow bodies of water, light may penetrate all the way to floor even in the deepest center parts of the lake. In this situation, there is an absence of a limnetic zone and the littoral zone spans the entire lake. Together, these two zones comprise the photic zone. There are two main sources of oxygen to the photic zone: atmospheric mixing and photosynthesis. Oxygen is dissolved when air interacts with water on the surface, and is increased with wave and wind action. Unlike the profundal zone, the limnetic zone is the layer that receives suf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photic Zone
The photic zone (or euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone) is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of Aquatic ecosystem, aquatic life due to the activity (Marine primary production, primary production) of the phytoplankton. The thicknesses of the photic and euphotic zones vary with the intensity of sunlight as a function of season and latitude and with the degree of water turbidity. The bottommost, or aphotic, zone is the region of perpetual darkness that lies beneath the photic zone and includes most of the ocean waters. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littoral Zone
The littoral zone, also called litoral or nearshore, is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely flood, inundated), to coastal areas that are permanently underwater, submerged — known as the ''foreshore'' — and the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the geographical meaning of ''littoral zone'' extends well beyond the intertidal zone to include all neritic waters within the bounds of continental shelves. Etymology The word ''littoral'' may be used both as a noun and as an adjective. It derives from the Latin language, Latin noun ''litus, litoris'', meaning "shore". (The doubled ''t'' is a late-medieval innovation, and the word is sometimes seen in the more classical-looking spelling ''litoral''.) Description The term has no single definition. What is regarded as the full extent of the littoral zone, and the way the littora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the surface of a river, lake, etc., often because chemicals that are used to help crops grow have been carried there by rain. Eutrophication may occur naturally or as a result of human actions. Manmade, or cultural, eutrophication occurs when sewage, Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater, fertilizer runoff, and other nutrient sources are released into the environment. Such nutrient pollution usually causes algal blooms and bacterial growth, resulting in the depletion of dissolved oxygen in water and causing substantial environmental degradation. Many policies have been introduced to combat eutrophication, including the United Nations Development Program (UNDP)'s sustainability development goals. Approaches for prevention and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, " watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of the drainage divide line. A drainage basin's boundaries are determined by watershed delineation, a common task in environmental engineering and science. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, rather than flowing to the ocean, water converges toward the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |