|
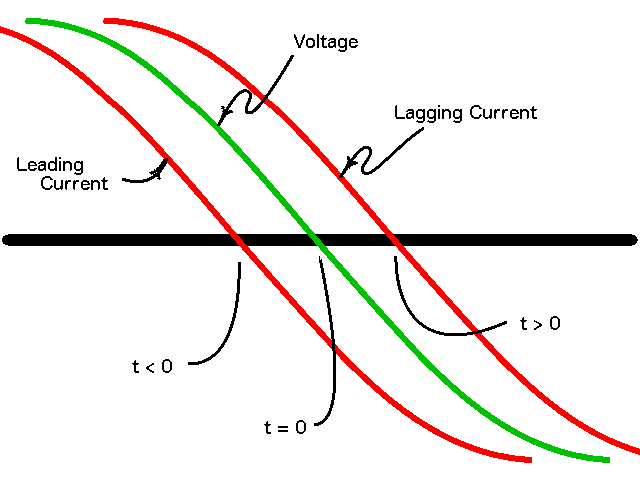
Leading And Lagging Current
Leading and lagging current are phenomena that occur as a result of alternating current. In a circuit with alternating current, the value of voltage and current vary sinusoidally. In this type of circuit, the terms ''lead, lag,'' and ''in phase'' are used to describe current with reference to voltage. Current is in phase with voltage when there is no phase shift between the sinusoids describing their time varying behavior. This generally occurs when the load drawing the current is resistive. In electric power flow, it is important to know how much current is leading or lagging because it creates the reactive power in the system, as opposed to the AC power#Active, reactive, and apparent power, active (real) power. It can also play an important role in the operation of three phase electric power systems. Angle notation Angle notation can easily describe leading and lagging current: A \angle \theta. In this equation, the value of theta is the important factor for leading and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage With Leading And Lagging Current
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), work needed per unit of Electric charge, charge to move a positive Test particle#Electrostatics, test charge from the first point to the second point. In the SI unit, International System of Units (SI), the SI derived unit, derived unit for voltage is the ''volt'' (''V''). The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in a Electric generator, generator). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. Since it is the difference in electric potential, it is a physical Scalar (physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |