|
Lateral Talocalcaneal Ligament
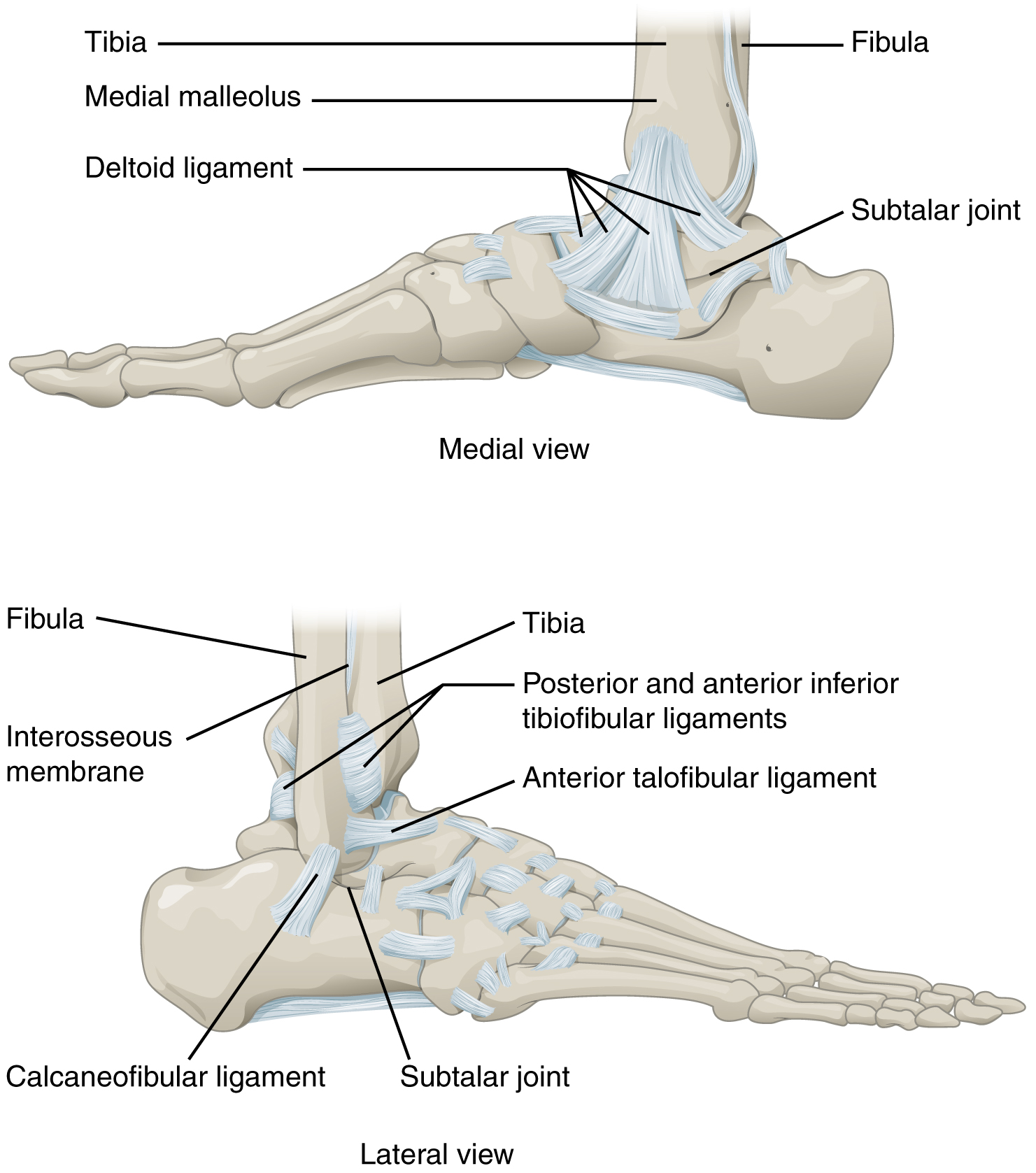
The lateral talocalcaneal ligament (external calcaneo-astragaloid ligament) is a ligament in the ankle. It is a short, strong fasciculus, passing from the lateral surface of the talus, immediately beneath its fibular facet to the lateral surface of the calcaneus. It is placed in front of, but on a deeper plane than, the calcaneofibular ligament The calcaneofibular ligament is a narrow, rounded cord, running from the tip of the lateral malleolus of the fibula downward and slightly backward to a tubercle on the lateral surface of the calcaneus. It is part of the lateral collateral ligam ..., with the fibers of which it is parallel. References Ligaments of the lower limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talocalcaneonavicular Articulation
The talocalcaneonavicular joint is a ball and socket joint in the foot; the rounded head of the talus is received into the concavity formed by the posterior surface of the navicular, the anterior articular surface of the calcaneus, and the upper surface of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament. Structure As its shape suggests, this joint is a synovial ball-and-socket joint. It is composed of three articular surfaces: * The articulation between the medial talar articular surface on the sustentaculum tali of the superior calcaneus and the corresponding medial facet found inferiorly on the talus neck * The articulation between the anterior talar articular surface of the superior calcaneus and the anterior facet of the corresponding talus found inferiorly on the talar head * The articulation between the articular surface of navicular and the head of talus (talonavicular joint) Ligaments The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament also called the spring ligament forms the whole floor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of Foot#Structure, foot bones known as the tarsus (skeleton), tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the Lateral malleolus, lateral and Medial malleolus, medial malleoli) that articulation (anatomy), articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the Ball-and-socket joint, ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock (anatomy), hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubercle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the Abductor hallucis muscle, abductor hallucis and Abductor di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have ligaments. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Comparative anatomy Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regeneration of periodontist ligament. The study of ligaments is known as . Humans Other ligame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankle
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" (without qualifiers) can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint. The main bones of the ankle region are the talus bone, talus (in the foot), the tibia, and fibula (both in the leg). The talocrural joint is a Synovial joint, synovial hinge joint that connects the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus. The articulation between the tibia and the talus bears more weight than that between the smaller fibula and the talus. Structure Region The ankle region is found at the junction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciculus
''Fasciculus vesanus'' is an extinct species of stem-group ctenophores known from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. It is dated to and belongs to middle Cambrian strata. The species is remarkable for its two sets of long and short comb rows, not seen in similar form elsewhere in the fossil record or among modern species. See also *'' Ctenorhabdotus capulus'' *'' Xanioascus canadensis'' Maotianshan shales The Maotianshan Shales () are a series of Early Cambrian sedimentary deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation or Heilinpu Formation, famous for their '' Konservat Lagerstätten'', deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized orga ... ctenophores **'' Maotianoascus octonarius'' **'' Sinoascus paillatus'' **'' Daihua sanqiong'' **'' Xianguangia sinica'' References External links * Monotypic prehistoric ctenophore genera Burgess Shale animals Fossil taxa described in 1978 Cambrian genus extinctions {{Ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of Foot#Structure, foot bones known as the tarsus (skeleton), tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the Lateral malleolus, lateral and Medial malleolus, medial malleoli) that articulation (anatomy), articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the Ball-and-socket joint, ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock (anatomy), hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubercle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the Abductor hallucis muscle, abductor hallucis and Abductor di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneofibular Ligament
The calcaneofibular ligament is a narrow, rounded cord, running from the tip of the lateral malleolus of the fibula downward and slightly backward to a tubercle on the lateral surface of the calcaneus. It is part of the lateral collateral ligament, which opposes the hyperinversion of the subtalar joint, as in a common type of ankle sprain. It is covered by the tendons of the fibularis longus and brevis muscles. Clinical significance The calcaneofibular ligament is commonly sprained ligament A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ... in ankle injuries. It may be injured individually, or in combination with other ligaments such as the anterior talofibular ligament and the posterior talofibular ligament. References Further reading * External links * * —Calcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |