|
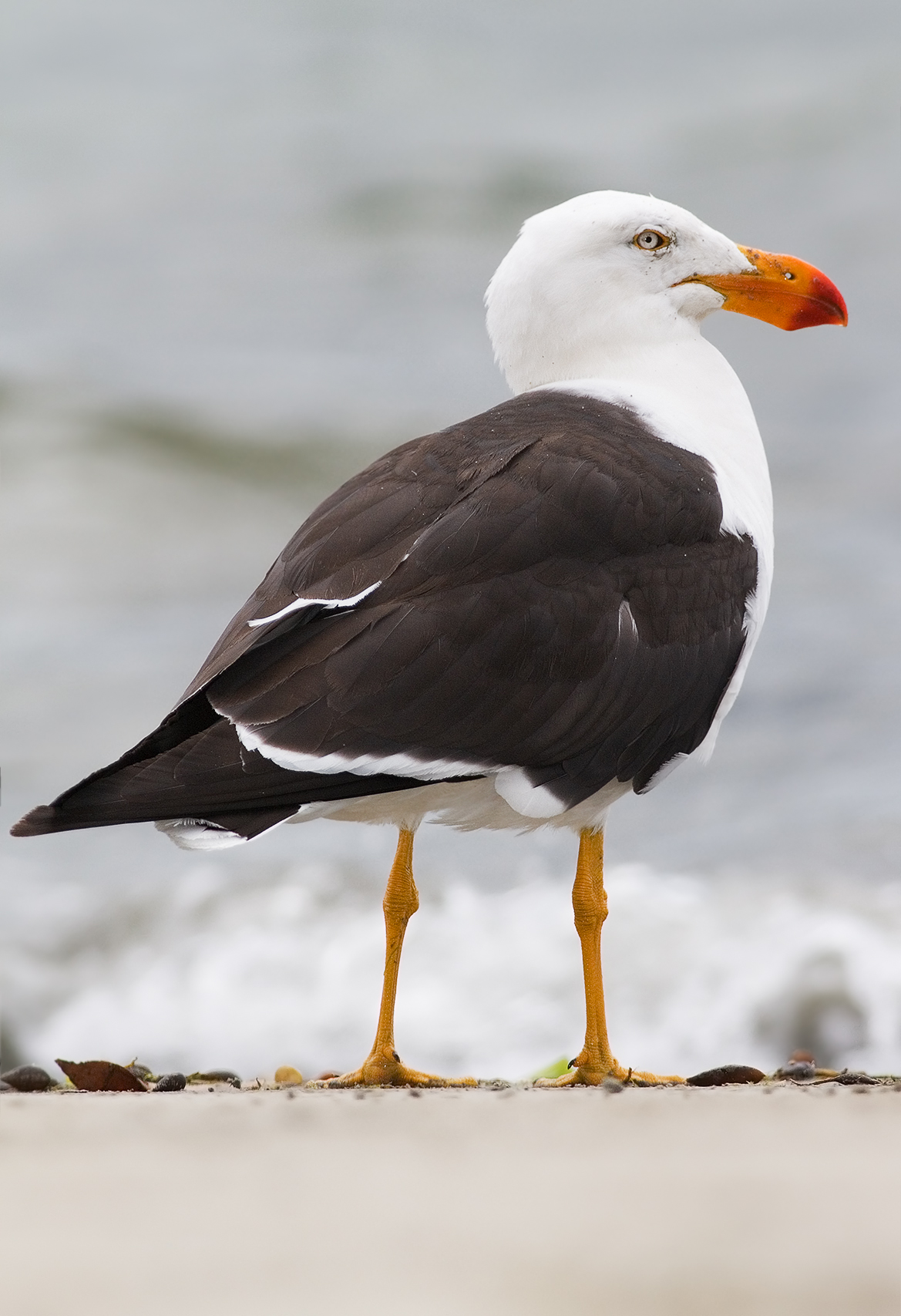
Larus Robustus
''Larus robustus'' is an extinct species of gull that lived during the Late Pleistocene. Etymology The genus name ''Larus'' derives from Ancient Greek, referring to a seabird. The species name ''robustus'' derives from Latin, meaning "hardness, strength." Description ''Larus robustus'' specimens stem from Fossil Lake, Oregon. Charles H. Sternberg collected the type specimen. ''Larus robustus'' is large gull, smaller than the glaucous gull (''Larus hyperboreus'') and significantly larger than the American herring gull (''Larus argentatus smithsonianus''). References External links ''Larus robustus''- Paleontology Database - Mindat.org ''Larus robustus (Shufeldt, 1891)''- GBIF The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international organisation that focuses on making scientific data on biodiversity available via the Internet using web services. The data are provided by many institutions from around the ... {{Taxonbar, from=Q123699292 Pleistocene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold Glacial period, glacial periods and warmer Interglacial, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Wilson Shufeldt
Robert Wilson Shufeldt Jr. (December 1, 1850January 21, 1934) was an American osteologist, myologist, museologist and ethnographer who contributed to comparative studies of bird anatomy and forensic science. He hated black people, strongly approved of the Ku Klux Klan, and was a proponent of white supremacy. A scandal and subsequent divorce from his second wife, the granddaughter of the famous ornithologist John James Audubon, led to a landmark judgment by the Supreme Court of the United States of America on the subject of alimony and bankruptcy. Life and career Son of Admiral Robert Wilson Shufeldt and Sarah Shufeldt, he was born in New York in 1850. After a school education in the United States and Havana, he joined as a Captain's clerk on the US Gunboat which was under the command of his father. In 1872 he joined Cornell University to study medicine and obtained a degree in 1876 from Columbian, Washington, D.C. He joined the Medical Department of the Army as a Lieuten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the subfamily Larinae. They are most closely related to terns and skimmers, distantly related to auks, and even more distantly related to waders. Until the 21st century, most gulls were placed in the genus ''Larus'', but that arrangement is now considered polyphyletic, leading to the resurrection of several genera. An older name for gulls is mews; this still exists in certain regional English dialects and is cognate with German , Danish ', Swedish ', Dutch ', Norwegian ', and French '. Gulls are usually grey or white, often with black markings on the head or wings. They normally have harsh wailing or squawking calls, stout bills, and webbed feet. Most gulls are ground-nesting piscivores or carnivores which take live food or scavenge opportunistically, particularly the ''Larus'' species. Live food often includes crustaceans, molluscs, fish and small birds. Gulls have unhinging jaws that provide the flexibility to consume large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larus
''Larus'' is a large genus of gulls with worldwide distribution (by far the greatest species diversity is in the Northern Hemisphere). Many of its species are abundant and well-known birds in their ranges. Until about 2005–2007, most gulls were placed in this genus, but this arrangement is now known to be polyphyletic, leading to the resurrection of the genera ''Chroicocephalus'', ''Ichthyaetus'', ''Hydrocoloeus'', and ''Leucophaeus'' for many other species formerly included in ''Larus''. They are in general medium-large birds, typically pale grey to black above and white below and on the head, often with black markings with white spots ("mirrors") on their wingtips and in a few species also some black on the tail. They have stout, longish beak, bills and webbed feet; in winter, the head is often streaked or smudged dark grey. The young birds are brown, and take three to five years to reach adult plumage, with subadult plumages intermediate between the young and adult. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Lake (Oregon)
Fossil Lake (designated by the Bureau of Land Management as Fossil Lake Area of Critical Environmental Concern) is a dry lakebed in the remote high desert country of northern Lake County in the U.S. state of Oregon. During the Pleistocene epoch, Fossil Lake and the surrounding basin were covered by an ancient lake. Numerous animals used the lake's resources. Over time, the remains of many of these animals became fossilized in the lake sediments. As a result, Fossil Lake has been an important site for fossil collection and scientific study for well over a century. Over the years, paleontologists have found the fossil remains of numerous mammals as well as bird and fish species there. Some of these fossils are 2 million years old. Location Fossil Lake is located in a remote area of northern Lake County, Oregon. It is from the unincorporated community of Christmas Valley by road. Fossil Lake is approximately southeast of Bend and north of Lakeview by straight-line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Hazelius Sternberg
Charles Hazelius Sternberg (June 15, 1850 – July 20, 1943) was an American fossil collector and paleontology, paleontologist. He was active in both fields from 1876 to 1928, and collected fossils for Edward Drinker Cope and Othniel C. Marsh, and for the British Museum, the San Diego Natural History Museum and other museums. The Sternberg family is legendary in the history of paleontology. Charles Hazelius was the patriarch, and his three sons, George F. Sternberg, Charles Mortram Sternberg and Levi Sternberg were also professional fossil collectors. In 1908, the Sternbergs found a remarkable duckbill dinosaur mummy in the Lance Formation of eastern Wyoming, the first such fossil found. After spirited bidding, the fossil was sold to the American Museum of Natural History. Biography Charles Hazelius Sternberg was born near Cooperstown, New York to Reverend Levi Sternberg and Margaret Levering Miller. At the age of 17, Sternberg moved to Ellsworth County, Kansas where his older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucous Gull
The glaucous gull (''Larus hyperboreus'') is a large gull, the second-largest gull in the world. The genus name is from Latin , which appears to have referred to a gull or other large seabird. The specific name is Latin for "northern" from the Ancient Greek ''Huperboreoi'' people from the far north "Glaucous" is from Latin and denotes the grey colour of the gull. An older English name for this species is burgomaster. Distribution This gull breeds in Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and winters south to shores of the Holarctic. It is migratory, wintering from in the North Atlantic and North Pacific Oceans as far south as the British Isles and northernmost states of the United States, also on the Great Lakes. A few birds sometimes reach the southern USA and northern Mexico. Description This is a large and powerful gull, second-largest of all gull species and very pale in all plumage, with no black on either the wings or the tail. Adults are pale grey above, with a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Herring Gull
The American herring gull or Smithsonian gull (''Larus smithsonianus'' or ''Larus argentatus smithsonianus'') is a large gull that breeds in North America, where it is treated by the American Ornithological Society as a subspecies of herring gull (''L. argentatus''). Adults are white with gray back and wings, black wingtips with white spots, and pink legs. Immature birds are gray-brown and are darker and more uniform than European herring gulls, with a darker tail. As is common with other gulls, they are colloquially referred to simply as seagulls. It occurs in a variety of habitats including coasts, lakes, rivers, parking lots and garbage dumps. Its broad diet includes invertebrates, fish, and many other items. It usually nests near water, laying around three eggs in a scrape on the ground. Taxonomy This gull was first described as a new species in 1862 by Elliott Coues based on a series of specimens from the Smithsonian Institution. It was later reclassified as a subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindat
Mindat may refer to: Places * Mindat District, a district in Chin State, Myanmar (Burma), consisting of two townships and many villages ** Mindat Township, Myanmar *** Mindat, Chin State, a town in Chin State, Myanmar, administrative seat of Mindat Township Other uses * Mindat, alternative name for the Kʼchò language in Myanmar * Mindat Min, a Burmese prince * Mindat.org, an online mineralogy database {{dab, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |