|
LP-type Problem
In the study of algorithms, an LP-type problem (also called a generalized linear program) is an optimization problem that shares certain properties with low-dimensional linear programs and that may be solved by similar algorithms. LP-type problems include many important optimization problems that are not themselves linear programs, such as the problem of finding the smallest circle containing a given set of planar points. They may be solved by a combination of randomized algorithms in an amount of time that is linear in the number of elements defining the problem, and subexponential in the dimension of the problem. Definition LP-type problems were defined by as problems in which one is given as input a finite set of elements, and a function that maps subsets of to values from a totally ordered set. The function is required to satisfy two key properties: *Monotonicity: for every two sets , ''f''(''A'') ≤ ''f''(''B'') ≤ ''f''(''S''). *Locality: for every two sets and every el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Polytope
A convex polytope is a special case of a polytope, having the additional property that it is also a convex set contained in the n-dimensional Euclidean space \mathbb^n. Most texts. use the term "polytope" for a bounded convex polytope, and the word "polyhedron" for the more general, possibly unbounded object. Others''Mathematical Programming'', by Melvyn W. Jeter (1986) p. 68/ref> (including this article) allow polytopes to be unbounded. The terms "bounded/unbounded convex polytope" will be used below whenever the boundedness is critical to the discussed issue. Yet other texts identify a convex polytope with its boundary. Convex polytopes play an important role both in various branches of mathematics and in applied areas, most notably in linear programming. In the influential textbooks of Grünbaum and Ziegler on the subject, as well as in many other texts in discrete geometry, convex polytopes are often simply called "polytopes". Grünbaum points out that this is solely to avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
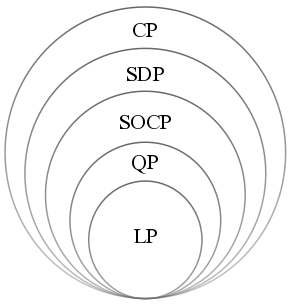
Convex Optimization
Convex optimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets (or, equivalently, maximizing concave functions over convex sets). Many classes of convex optimization problems admit polynomial-time algorithms, whereas mathematical optimization is in general NP-hard. Definition Abstract form A convex optimization problem is defined by two ingredients: * The ''objective function'', which is a real-valued convex function of ''n'' variables, f :\mathcal D \subseteq \mathbb^n \to \mathbb; * The ''feasible set'', which is a convex subset C\subseteq \mathbb^n. The goal of the problem is to find some \mathbf \in C attaining :\inf \. In general, there are three options regarding the existence of a solution: * If such a point ''x''* exists, it is referred to as an ''optimal point'' or ''solution''; the set of all optimal points is called the ''optimal set''; and the problem is called ''solvable''. * If f is unbou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centerpoint (geometry)
In statistics and computational geometry, the notion of centerpoint is a generalization of the median to data in higher-dimensional Euclidean space. Given a set of points in ''d''-dimensional space, a centerpoint of the set is a point such that any hyperplane that goes through that point divides the set of points in two roughly equal subsets: the smaller part should have at least a 1/(''d'' + 1) fraction of the points. Like the median, a centerpoint need not be one of the data points. Every non-empty set of points (with no duplicates) has at least one centerpoint. Related concepts Closely related concepts are the Tukey depth of a point (the minimum number of sample points on one side of a hyperplane through the point) and a Tukey median of a point set (a point maximizing the Tukey depth). A centerpoint is a point of depth at least ''n''/(''d'' + 1), and a Tukey median must be a centerpoint, but not every centerpoint is a Tukey median. Both terms are named a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotating Calipers
In computational geometry, the method of rotating calipers is an algorithm design technique that can be used to solve optimization problems including finding the width or diameter (computational geometry), diameter of a set of points. The method is so named because the idea is analogous to rotating a spring-loaded vernier caliper around the outside of a convex polygon. Every time one blade of the caliper lies flat against an edge of the polygon, it forms an antipodal point, antipodal pair with the point or edge touching the opposite blade. The complete "rotation" of the caliper around the polygon detects all antipodal pairs; the set of all pairs, viewed as a graph, forms a thrackle. The method of rotating calipers can be interpreted as the Duality (projective geometry), projective dual of a sweep line algorithm in which the sweep is across slopes of lines rather than across - or -coordinates of points. History The rotating calipers method was first used in the dissertation of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the centre of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest Chord (geometry), chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for the diameter of a sphere. In more modern usage, the length d of a diameter is also called the diameter. In this sense one speaks of diameter rather than diameter (which refers to the line segment itself), because all diameters of a circle or sphere have the same length, this being twice the radius r. :d = 2r \qquad\text\qquad r = \frac. The word "diameter" is derived from (), "diameter of a circle", from (), "across, through" and (), "measure". It is often abbreviated \text, \text, d, or \varnothing. Constructions With straightedge and compass, a diameter of a given circle can be constructed as the perpendicular bisector of an arbitrary chord. Drawing two diameters in this way can be used to locate the center of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicographic Order
In mathematics, the lexicographic or lexicographical order (also known as lexical order, or dictionary order) is a generalization of the alphabetical order of the dictionaries to sequences of ordered symbols or, more generally, of elements of a totally ordered set. There are several variants and generalizations of the lexicographical ordering. One variant applies to sequences of different lengths by comparing the lengths of the sequences before considering their elements. Another variant, widely used in combinatorics, orders subsets of a given finite set by assigning a total order to the finite set, and converting subsets into Sequence#Increasing_and_decreasing, increasing sequences, to which the lexicographical order is applied. A generalization defines an order on an ''n''-ary Cartesian product of partially ordered sets; this order is a total order if and only if all factors of the Cartesian product are totally ordered. Definition The words in a lexicon (the set of words u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordered Pair
In mathematics, an ordered pair, denoted (''a'', ''b''), is a pair of objects in which their order is significant. The ordered pair (''a'', ''b'') is different from the ordered pair (''b'', ''a''), unless ''a'' = ''b''. In contrast, the '' unordered pair'', denoted , always equals the unordered pair . Ordered pairs are also called 2-tuples, or sequences (sometimes, lists in a computer science context) of length 2. Ordered pairs of scalars are sometimes called 2-dimensional vectors. (Technically, this is an abuse of terminology since an ordered pair need not be an element of a vector space.) The entries of an ordered pair can be other ordered pairs, enabling the recursive definition of ordered ''n''-tuples (ordered lists of ''n'' objects). For example, the ordered triple (''a'',''b'',''c'') can be defined as (''a'', (''b'',''c'')), i.e., as one pair nested in another. In the ordered pair (''a'', ''b''), the object ''a'' is called the ''first entry'', and the object ''b'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplex Method
In mathematical optimization, Dantzig's simplex algorithm (or simplex method) is a popular algorithm for linear programming. The name of the algorithm is derived from the concept of a simplex and was suggested by T. S. Motzkin. Simplices are not actually used in the method, but one interpretation of it is that it operates on simplicial ''cones'', and these become proper simplices with an additional constraint. The simplicial cones in question are the corners (i.e., the neighborhoods of the vertices) of a geometric object called a polytope. The shape of this polytope is defined by the constraints applied to the objective function. History George Dantzig worked on planning methods for the US Army Air Force during World War II using a desk calculator. During 1946, his colleague challenged him to mechanize the planning process to distract him from taking another job. Dantzig formulated the problem as linear inequalities inspired by the work of Wassily Leontief, however, at that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimal Facility Location
The study of facility location problems (FLP), also known as location analysis, is a branch of operations research and computational geometry concerned with the optimal placement of facilities to minimize transportation costs while considering factors like avoiding placing hazardous materials near housing, and competitors' facilities. The techniques also apply to cluster analysis. Minimum facility location A simple facility location problem is the Weber problem, in which a single facility is to be placed, with the only optimization criterion being the minimization of the weighted sum of distances from a given set of point sites. More complex problems considered in this discipline include the placement of multiple facilities, constraints on the locations of facilities, and more complex optimization criteria. In a basic formulation, the facility location problem consists of a set of potential facility sites ''L'' where a facility can be opened, and a set of demand points ''D'' tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element Method
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. Computers are usually used to perform the calculations required. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two- or three-space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). There are also studies about using FEM to solve high-dimensional problems. To solve a problem, FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithmic Game Theory
Algorithmic game theory (AGT) is an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of game theory and computer science, focused on understanding and designing algorithms for environments where multiple strategic agents interact. This research area combines computational thinking with economic principles to address challenges that emerge when algorithmic inputs come from self-interested participants. In traditional algorithm design, inputs are assumed to be fixed and reliable. However, in many real-world applications—such as online auctions, internet routing, digital advertising, and resource allocation systems—inputs are provided by multiple independent agents who may strategically misreport information to manipulate outcomes in their favor. AGT provides frameworks to analyze and design systems that remain effective despite such strategic behavior. The field can be approached from two complementary perspectives: * ''Analysis'': Evaluating existing algorithms and systems throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |