|
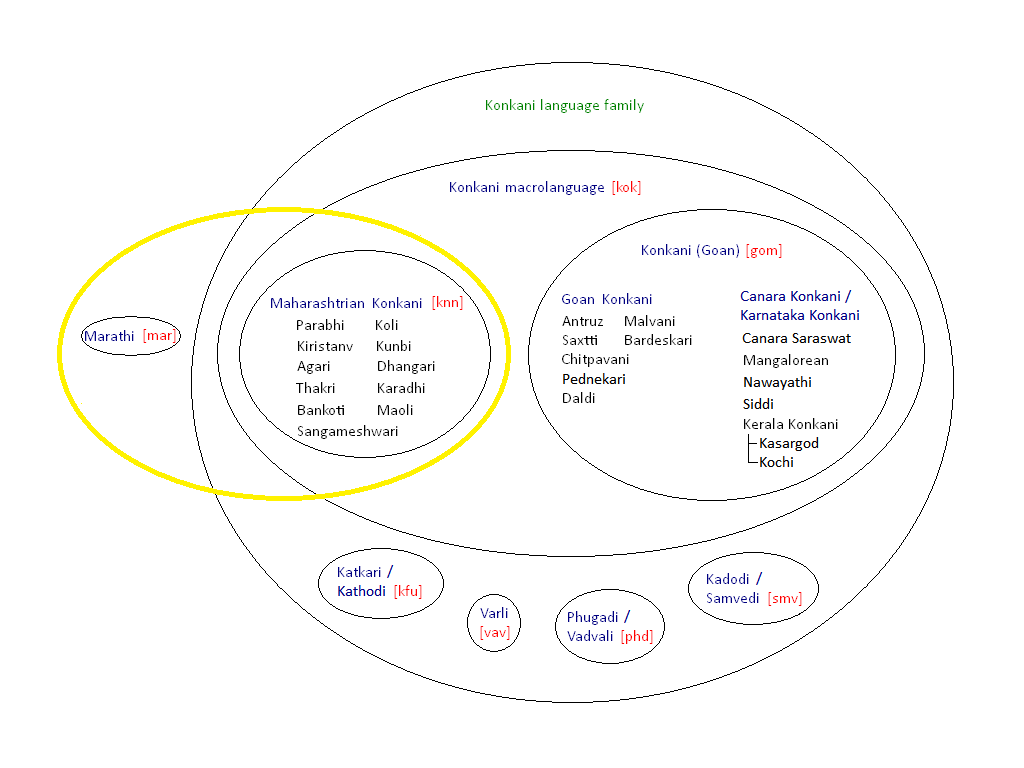
Konkani Language
Konkani () is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Konkani people, primarily in the Konkan region, along the western coast of India. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages mentioned in the Indian Constitution, and the official language of the Indian state of Goa. It is a minority language in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat & Damaon, Diu & Silvassa. Konkani is a member of the Southern Indo-Aryan language group. It retains elements of Vedic structures and shows similarities with both Western and Eastern Indo-Aryan languages. The first Konkani inscription is dated 1187 A.D. There are many Konkani dialects spoken along and beyond the Konkan region, from Damaon in the north to Carwar in the south, most of which are only partially and mutually intelligible with one another due to a lack of linguistic contact and exchanges with the standard and principal forms of Konkani. It is also spoken by migrants outside of the Konkan proper; in Surat, Cochin, Mangalore, Ahmed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglicised
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influence of English culture and business on other countries outside England or the United Kingdom, including their media, cuisine, popular culture, technology, business practices, laws, or political systems. Linguistic anglicisation is the practice of modifying foreign words, names, and phrases to make them easier to spell, pronounce or understand in English. The term commonly refers to the respelling of foreign words, often to a more drastic degree than that implied in, for example, romanisation. One instance is the word "dandelion", modified from the French ''dent-de-lion'' ("lion's tooth", a reference to the plant's sharply indented leaves). The term can also refer to phonological adaptation without spelling change: ''spaghetti'', for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharashtrian Konkani
Maharashtri Konkani or Konkan Marathi, is a group of Konkanic dialects spoken in the Konkan division of the Konkan region. George Abraham Grierson, a British Indian linguist of the colonial era referred to these dialects as the ''Konkan Standard of Marathi'' in order to differentiate it inside the Konkani language group. It is often mistakenly extended to cover Goan Konkani and Canara Konkani Canarese Konkani are a set of dialects spoken by minority Konkani people of the Canara sub-region of Karnataka, and also in Kassergode of Kerala that was part of South Canara.The Constitution Act 1992 (71st Amendment) Kanarese script is the p ..., which are distinct and different sets of Konkani dialects, because speakers of these dialect groups refer to their language as simply " Konkani". See also Malvani language References {{Indo-Aryan languages Languages of India Konkani Marathi language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada Script
The Kannada script (IAST: ''Kannaḍa lipi''; obsolete: Kanarese or Canarese script in English) is an abugida of the Brahmic family, used to write Kannada, one of the Dravidian languages of South India especially in the state of Karnataka. Kannada script is also widely used for writing Sanskrit texts in Karnataka. Several minor languages, such as Tulu, Konkani, Kodava, Sanketi and Beary, also use alphabets based on the Kannada script. The Kannada and Telugu scripts share very high mutual intellegibility with each other, and are often considered to be regional variants of single script. Other scripts similar to Kannada script are Sinhala script (which included some elements from the Kadamba script), and Old Peguan script (used in Burma). The Kannada script ( ''akṣaramāle'' or ''varṇamāle'') is a phonemic abugida of forty-nine letters. The character set is almost identical to that of other Brahmic scripts. Consonantal letters imply an inherent vowel. Letters rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy ( Magna Grecia). It was adopted by the Etruscans and subsequently by the Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet, and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing for most Western and Central, and some Eastern, European languages as well as many languages in other parts of the world. Name The script is either called Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modi Script
Modi ( mr, मोडी, , ; also Mudiya) is a script used to write the Marathi language, which is the primary language spoken in the state of Maharashtra, India. There are multiple theories concerning its origin. The Modi script was used alongside the Devanagari script to write Marathi until the 20th century when the Balbodh style of the Devanagari script was promoted as the standard writing system for Marathi. Etymology The name 'Modi' perhaps derives from the Marathi verb ''moḍaṇe'' ( Marathi: मोडणे), which means "to bend or break". Modi is believed to be derived from broken Devanagari characters, which lends support to that particular etymology. It is not to be confused with the name Modi. Origin theories Hemāḍpant origin theory Hemāḍpant was a minister during the reign of Mahadeva (ruled 1261–1271) and the initial years of the reign of Rāmachandra (ruled 1271 to 1309) of the Yadava Dynasty. Creation subtheory Hemāḍpant created t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goykanadi
or Kandavī is a Brahmic script that was once used in the territory of Goa to write Konkani and sometimes Marathi in the Konkan coast. Similarly, it was used by the trading Saraswat and Daivajna families along with the Modi script to maintain their accounts. Overview Goykanadi was used in Goa since the times of the Kadambas, although it lost its popularity after the 17th century. Goykanadi is very different from the Old Kannada script, with strikingly similar features. Unlike Old Kannada, Kandevi/Goykanadi letters were usually written with a distinctive horizontal bar, like the Nagari scripts. This script may have been evolved out of the Kadamba script, which was extensively used in Goa and Konkan. Usage and extinction The inquisition of Goa is seen as a blot in the history of the Konkani language. According to the orders of the Goa inquisition it was an offence to remain in possession of books in the local languages. All books, whatever their subject matter, written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nāgarī Script
The Nāgarī script or Northern Nagari of Kashi is the ancestor of Devanagari, Nandinagari and other variants, and was first used to write Prakrit and Sanskrit. The term is sometimes used as a synonym for Devanagari script.Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83George Cardona and Danesh Jain (2003), The Indo-Aryan Languages, Routledge, , pages 68-69 It came in vogue during the first millennium CE. The Nāgarī script has roots in the ancient Brahmi script family. Some of the earliest epigraph evidence attesting to the developing Sanskrit Nāgarī script in ancient India is from the 1st to 4th century CE inscriptions discovered in Gujarat., Rudradaman’s inscription from 1st through 4th century CE found in Gujarat, India, Stanford University Archives, pages 30-45 The Nāgarī script was in regular use by 7th century CE, and had fully evolved into Devanagari and Nandinagari scripts by about the end of first millennium of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmi Script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern Aśokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi 'sc. lipi'' which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T rriende Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the Aśokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a fully developed scri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agri Dialect
Agri or Aagri ( mr, आगरी) is a dialect of Maharashtrian Konkani which is spoken by members of the Agri (caste). Although it is commonly seen in comedy shows, it is not merely the language of humour but also the distinct dialect closely related to Koli Konkani, and the Aagri people speak it on a day-to-day basis. Until the late 20th century, it was an oral dialect and was passed down from one generation to the next. It is spoken in many cities such as Mumbai (Bombay), Thana (Trombay), Raigad (Colaba), Bhiwandi, Vasai (Bassein) and Palghar. References External links Akhil Agri Samaj Marathi language {{IndoAryan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koli Christians
Koli Christians are a religious subgroup of the Koli people, known as East Indians, the indigenous people of the Seven Islands of Bombay and the Bombay metro area, which is now also called Mumbai (Bombay). The Koli Christians were of the Son Koli caste, before their conversion from Hinduism to Christianity, in the former '' Bom Bahia'' of Portuguese India. Christian Kolis are also known as Thankar and Gaonkar Kolis in Maharashtra, where they played an important role in building churches and convents in the northern Konkan division of Maharashtra. Culture and custom In 1989, there were approximately 9,000 Koli Christians, most of whom were fishermen, like their Hindu counterparts. Koli Christians blend the customs and traditions of the Koli people with the beliefs of the Roman Catholic church. In accordance with Koli tradition, marriages among Koli Christians are typically arranged, and certain ceremonies are observed in common with Hindu Kolis, such as the ''Shakarpur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nawayathi Dialect
Nawayathi, also spelled as Nawayati, is a dialect of Konkani spoken by Nawayaths of the southwestern coast of India. It is an amalgam of Persian, Arabic and Marathi, with Konkani as its base. The Navayath language uses Persian script for writing. "Persian script" was being used to write by the Nawayathis long before the Urdu Urdu (;"Urdu" '' Languages of India Konkani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |