|
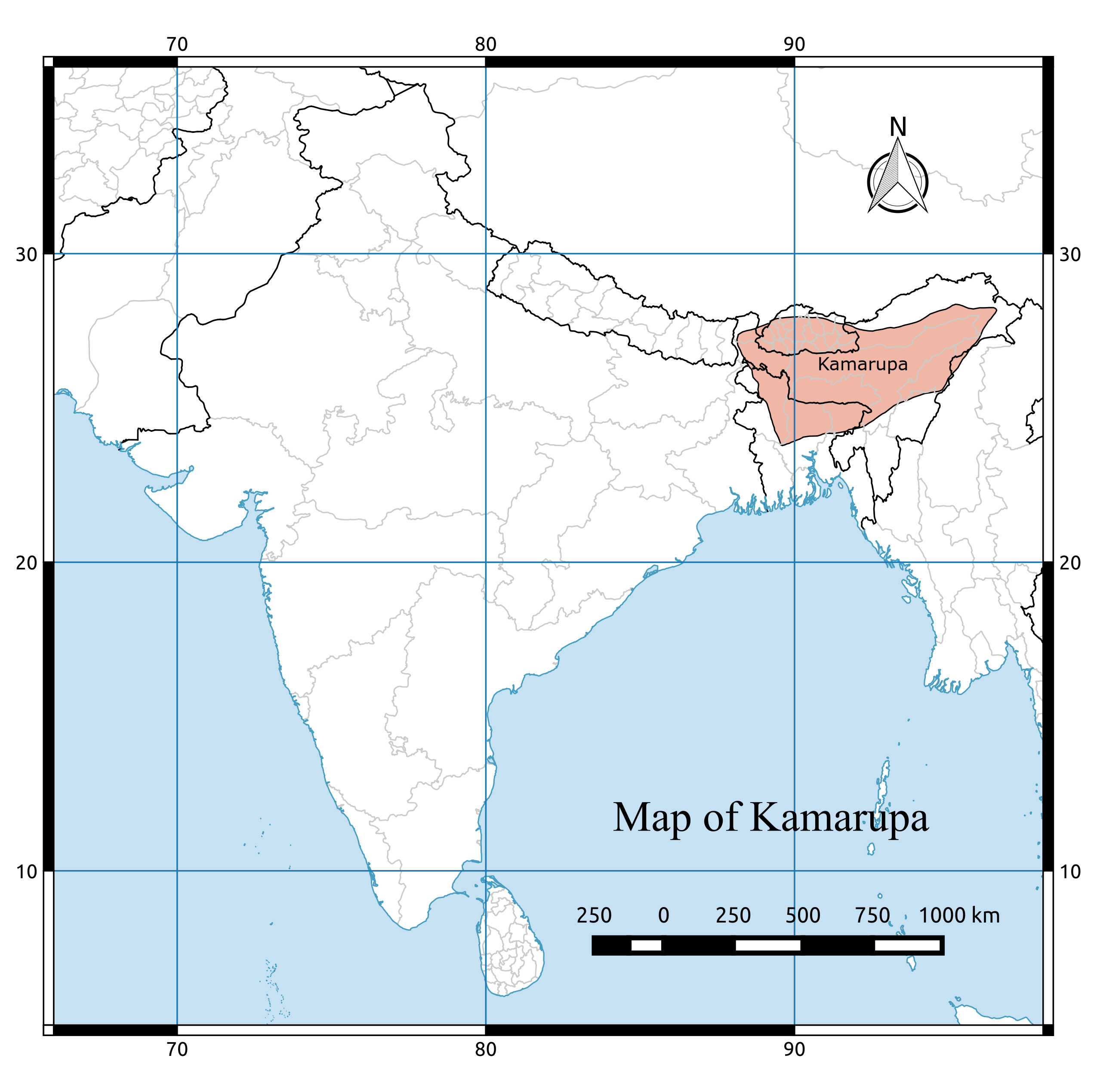
Khen Dynasty
The Khen dynasty (also Khyen dynasty) of Assam was a late medieval dynasty of erstwhile Kamata kingdom. After the fall of the Pala dynasty of Kamrupa, the western region was reorganized into Kamata kingdom, when Sandhya moved his capital from Kamarupanagara to Kamatapur in about 1257, due to the frequent clashes with the Kacharis from the east. Sandhya styled himself ''Kamateswara'' and the kingdom came to be known as "Kamata". The Khen dynasty at a later period took control of the kingdom. Origin According to the ''Gosani Mangala'' (1823), the Khen rulers had a humble origin, implying that they were probably local chieftains that rose to power after the fall of the Palas. Ethnically, the Khen rulers belonged to a Tibeto-Burman ethnolinguistic group. Ethnicity of Khen is not known precisely but may have been associated with Khyen of Indo-Burmese border or Kheng from the mountains. Though there is no contemporary historical evidence, some data from eighteenth-century's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval India
Medieval India refers to a long period of Post-classical history of the Indian subcontinent between the "ancient period" and "modern period". It is usually regarded as running approximately from the breakup of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century CE to the start of the Early modern period in 1526 with the start of the Mughal Empire, although some historians regard it as both starting and finishing later than these points. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Medieval and Late Medieval eras. In the Early Medieval period, there were more than 40 different states on the Indian subcontinent, which hosted a variety of cultures, languages, writing systems, and religions. At the beginning of the time period, Buddhism was predominant throughout the area, with the short-lived Pala Empire on the Indo Gangetic Plain sponsoring the Buddhist faith's institutions. One such institution was the Buddhist Nalanda University in modern-day Bihar, India, a centre of scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimasa Kingdom
The Dimasa Kingdom (also Kachari kingdom) was a late medieval/early modern kingdom in Assam, Northeast India ruled by Dimasa kings. The Dimasa kingdom and others (Kamata, Chutiya) that developed in the wake of the Kamarupa kingdom were examples of new states that emerged from indigenous communities in medieval Assam as a result of socio-political transformations in these communities. The British finally annexed the kingdom: the plains in 1832 and the hills in 1834. This kingdom gave its name to undivided Cachar district of colonial Assam. And after independence the undivided Cachar district was split into three districts in Assam: Dima Hasao district (formerly ''North Cachar Hills''), Cachar district, Hailakandi district. The Ahom Buranjis called this kingdom ''Timisa''. In the 18th century, a divine Hindu origin was constructed for the rulers of the Kachari kingdom and it was named Hidimba, and the kings as Hidimbesvar. The name Hiḍimbā continued to be used in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Assam
The History of Assam is the history of a confluence of people from the east, west, south and the north; the confluence of the Austroasiatic, Tibeto-Burman (Sino-Tibetan), Tai and Indo-Aryan cultures. Although invaded over the centuries, it was never a vassal or a colony to an external power until the third Burmese invasion in 1821 and subsequently the British ingress into Assam in 1824 during the First Anglo-Burmese War. Later documented rulers, and dynasties who are deemed to have ruled a portion of Assam are included in this list. File:Major kingdoms of Assam.png, 260px, Major kingdoms of Assam rect 50 50 650 120 Kamarupa Kingdom rect 45 240 160 310 Kamata Kingdom rect 165 240 300 310 Bhuyan chieftains rect 305 240 415 310 Ahom Kingdom rect 425 240 540 310 Chutiya Kingdom rect 550 240 660 310 Kachari Kingdom rect 4 425 80 495 Koch Bihar rect 120 425 190 495 Koch Hajo rect 125 660 640 760 History of Assam Ancient Kingdoms (c. 1200 BCE – 500 CE) Sonit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahom–Mughal Conflicts
Ahom–Mughal conflicts refer to the period between the first Mughal attack on the Ahom kingdom in Battle of Samdhara in 1616 till the final Battle of Itakhuli in 1682. The intervening period saw the fluctuating fortunes of both powers and the end of the rule of Koch Hajo. It ended with the Ahom influence extended to the Manas river which remained the western boundary of the kingdom till the advent of the British in 1826. Overview A group of Tai people, that came to be known as the Ahom in due course, migrated from present-day Myanmar to the Brahmaputra valley in the 13th century. They settled in with the locals initially and created a new state that came to be known as the Ahom kingdom; and in the 16th-century they vastly expanded their power and territory by absorbing the Chutia kingdom in Upper Assam, removing the Baro-Bhuyan confederacy in Nagaon and Darrang, and pushing the Dimasa kingdom further south. As the kingdom pushed west it came under attack from Turkic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Assam
File:Major kingdoms of Assam.png, upright=1.3, Major kingdoms of Assam rect 50 50 650 120 Kamarupa Kingdom rect 45 240 160 310 Kamata Kingdom rect 165 240 300 310 Bhuyan chieftains rect 305 240 415 310 Ahom Kingdom rect 425 240 540 310 Chutiya Kingdom rect 550 240 660 310 Kachari Kingdom rect 4 425 80 495 Koch Bihar rect 120 425 190 495 Koch Hajo rect 125 660 640 760 History of Assam The history of Assam is the history of a confluence of people from the east, west, south and the north; the confluence of the Austroasiatic, Tibeto-Burman (Sino-Tibetan), Tai and Indo-Aryan cultures. Although invaded over the centuries, it was never a vassal or a colony to an external power until the third Burmese invasion in 1821, and, subsequently, the British ingress into Assam in 1824 during the First Anglo-Burmese War. The Assamese history has been derived from multiple sources. The Ahom kingdom of medieval Assam maintained chronicles, called Buranjis, written in the Ahom and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamata Kingdom
The Kamata Kingdom (pron: ˈkʌmətɑ) emerged in western Kamarupa probably when Sandhya, a ruler of Kamarupanagara, moved his capital west to Kamatapur sometime after 1257 CE. Since it originated in the old seat of the Kamarupa kingdom, and since it covered most of the western parts of it, the kingdom is also sometimes called as Kamarupa-Kamata. It covered a region corresponding to present-day undivided districts of Kamrup, Goalpara, Jalpaiguri, and Cooch Behar district in India and Rangpur and northern parts of Mymensingh in Bangladesh. The rise of the Kamata kingdom marked the end of the ancient period in the history of Assam and the beginning of the medieval period. The last rulers were the Khens, who were later displaced in 1498 by Alauddin Hussain Shah, the ruler of the Bengal Sultanate. Though Hussain Shah developed extensive administrative structures, he lost political control to a confederation of Baro-Bhuyan within a few years. Biswa Singha removed the Baro-Bhu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koch Dynasty
Koch may refer to: People * Koch (surname), people with this surname * Koch dynasty, a dynasty in Assam and Bengal, north east India * Koch family * Koch people (or Koche), an ethnic group originally from the ancient Koch kingdom in north east India ** Koch language, a language spoken in India and Bangladesh * Koch, an alternate name of the Rabha tribe in northeast India and surrounding countries * Koch Kingdom, in and around Assam Places * Koch (crater), a crater on the Moon * Koch, Iran (other), places in Iran * Koch, Łódź Voivodeship, a village in central Poland * Koch, Mississippi, United States * Koch, South Sudan, a village in Unity State, South Sudan * Koch Bihar, a princely state in north east India * Koch County, an administrative area in Unity State, South Sudan * Koch Kingdom, Assam, 13th-16th centuries Businesses * Koch Entertainment LP, now known as E1 Entertainment ** Koch Records, former name of Entertainment One Music * Koch Industries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhuyan Chieftains
The Baro-Bhuyans (or ''Baro-Bhuyan Raj''; also ''Baro-Bhuians'' and Baro-Bhuiyans) refers to the confederacies of soldier-landowners in Assam and Bengal in the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. The confederacies consisted of loosely independent entities, each led by a warrior chief or a landlord ( zamindars). The tradition of Baro-Bhuyan is peculiar to both Assam and Bengal and differ from the tradition of ''Bhuihar'' of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar—in Assam this phenomenon came into prominence in the 13th century when they resisted the invasion of Ghiyasuddin Iwaj Shah"The Bara Bhuyans of Kamarupa played a similar role in the country's history round about the thirteenth century...Jadunath Sarkar holds that Husamuddin Iwaz (c 1213-27) reduced some of the Barabhuyans to submission when he attacked Kamarupa." and in Bengal when they resisted Mughal rule in the 16th century. ''Baro'' denotes the number twelve, but in general there were more than twelve chiefs or landlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alauddin Husain Shah
Ala-ud-din Husain Shah ( bn, আলাউদ্দিন হোসেন শাহ (1494–1519)Majumdar, R.C. (ed.) (2006). ''The Delhi Sultanate'', Mumbai: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, pp.215-20 was an independent late medieval Sultan of Bengal, who founded the Hussain Shahi dynasty. He became the ruler of Bengal after assassinating the Sultan, Shams-ud-Din Muzaffar Shah, whom he had served under as wazir. After his death in 1519, his son Nusrat Shah succeeded him. The reigns of Husain Shah and Nusrat Shah are generally regarded as the "golden age" of the Bengal sultanate. Origin and early life There are several opinions regarding the origin of Alauddin Husain Shah. According to a 1788 chronicle, ''Riyaz-us-Salatin'', Sayyid Husain Sharif Makki was the son of Sayyid Ashraf al-Husaini, a Sharif of Mecca, with ''al-Husaini'' suggesting descent from Husayn ibn Ali. An earlier work by Firishta also mentions Husain as a Sayyid and former inhabitant of Mecca. His father's name is backe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism. Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within the Trimurti, the triple deity of supreme divinity that includes Brahma and Shiva.Gavin Flood, An Introduction to Hinduism' (1996), p. 17. In Vaishnavism, Vishnu is the supreme being who creates, protects, and transforms the universe. In the Shaktism tradition, the Goddess, or Adi Shakti, is described as the supreme Para Brahman, yet Vishnu is revered along with Shiva and Brahma. Tridevi is stated to be the energy and creative power ( Shakti) of each, with Lakshmi being the equal complementary partner of Vishnu. He is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. According to Vaishnavism, the highest form of Ishvara is with qualities (Saguna), and have certain form, but is limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narakasura
Naraka, also known as Narakasura (), is an asura king in Hindu mythology. In Assamese tradition, he is regarded as the legendary progenitor of all three dynasties of Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa, and the founding ruler of the legendary Bhauma dynasty of Pragjyotisha. Though the myths about Naraka are first mentioned in the Mahabharata, later texts embellish them. According to later post-Vedic texts such as the Brahma Purana and Vishnu Purana, he was the son of Bhudevi, fathered either by the Varaha incarnation of Vishnu or Hiranyaksha. He is claimed as one who established Pragjyotisha. He was killed by Krishna and Satyabhama. His son Bhagadatta—of Mahabharata fame—succeeded him. The 10th/11th-century Kalika Purana embellishes the myths further and he is claimed to have come from Mithila and said to have established the kingdom of Pragjyotisha after overthrowing the last of the Kirata kings, Ghatakasura, of the Danava dynasty. It was foretold that he would be destroyed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the east and by Bangladesh to the north, south and west. Tripura is divided into 8 districts and 23 sub-divisions, where Agartala is the capital and the largest city in the state. Tripura has 19 different tribal communities with a majority of the Bengali population. Bengali, English and Kokborok are the state's official languages. The area of modern Tripura — ruled for several centuries by the Manikya Dynasty — was part of the Tripuri Kingdom (also known as Hill Tippera). It became a princely state under the British Raj during its tenure, and acceded to independent India in 1947. It merged with India in 1949 and was designated as a 'Part C State' ( union territory). It became a full-fledged state of India in 1972. Tripura lies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)