|
Kamina Base Airport
Kamina Air Base is a military airport located near Kamina in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was built as part of the Belgian near-national-redoubt concept after World War II.David Isby and Charles Kamps Jr., Armies of NATO's Central Front, Jane's Publishing Company, 1985. It accommodated ONUC military aircraft during the Congo Crisis. Facilities The airport resides at an elevation of above mean sea level. It has two runways, each with an asphalt surface measuring . See also * Kamina Airport * Air Force of the Democratic Republic of the Congo The Congolese Air Force (french: Force Aérienne Congolaise, or FAC) is the air force branch of the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Congo-Kinshasa). From 1971 to 1997, it was known as the Zairian Air Force (, or FAZA). Hi ... References {{authority control Airports in Haut-Lomami Military of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Kamina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force Of The Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Congolese Air Force (french: Force Aérienne Congolaise, or FAC) is the air force branch of the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Congo-Kinshasa). From 1971 to 1997, it was known as the Zairian Air Force (, or FAZA). History Shortly after the Congo became independent in 1960, the province of Katanga seceded, and the newly formed State of Katanga began building its own army. The Katangese seized most of the aircraft operated by the Aviation de la Force Publique and created the Katangese Air Force. The Congolese Air Force was created in mid-1961 largely to oppose the new Katangese Air Force. In 1963, Katanga was defeated by United Nations forces in Operation Grandslam, and the remaining assets of the Katangese Armed Forces were integrated into the Congolese Air Force. A Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) front company, Anstalt WIGMO, provided maintenance support to large parts of the FAC in the 1964–1968 period. The CIA also provided aircraft during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamina
Kamina is the capital city of Haut-Lomami Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Transport Kamina is known as an important railway node; three lines of the DRC railways run from Kamina toward the north, west, and south-east. The main railway line, the operating sections of the Cape to Cairo Railway, links the city with Tenke and Lubumbashi to the south and Kabalo and Kindu to the northeast. It has two airports, one civil ( Kamina Airport) and one military ( Kamina Base Airport). It lies along National Road 1 (N1) and Regional Road 630 (R630). Military The Belgian Armed Forces established a large military base in Kamina after the Second World War. The large base complex consisted of Base 1, an air base used for flying training, and Base 2, a paratroop training facility. From September 1953 to 1960, the Advanced Pilots' School of the Belgian Air Force operated some 60 North American Harvards from the base. When the Congo gained independence in June 1960, Belgium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in Central Africa. It is bordered to the northwest by the Republic of the Congo, to the north by the Central African Republic, to the northeast by South Sudan, to the east by Uganda, Rwanda, and Burundi, and by Tanzania (across Lake Tanganyika), to the south and southeast by Zambia, to the southwest by Angola, and to the west by the South Atlantic Ocean and the Cabinda exclave of Angola. By area, it is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 108 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the nation's economic center. Centered on the Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DAFIF
DAFIF () or the ''Digital Aeronautical Flight Information File'' is a comprehensive database of up-to-date aeronautical data, including information on airports, airways, airspaces, navigation data, and other facts relevant to flying in the entire world, managed by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) of the United States. Withdrawal of public access DAFIF was publicly available until October 2006 through the Internet; however, it was closed to public access because "increased numbers of foreign source providers are claiming intellectual property rights or are forewarning NGA that they intend to copyright their source". Currently, only federal and state government agencies, authorized government contractors, and Department of Defense customers are able to access the DAFIF data. At the time of the announcement, the NGA did not say who the "foreign source providers" were. It was subsequently revealed that the Australian Government was behind the move. The Australian go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
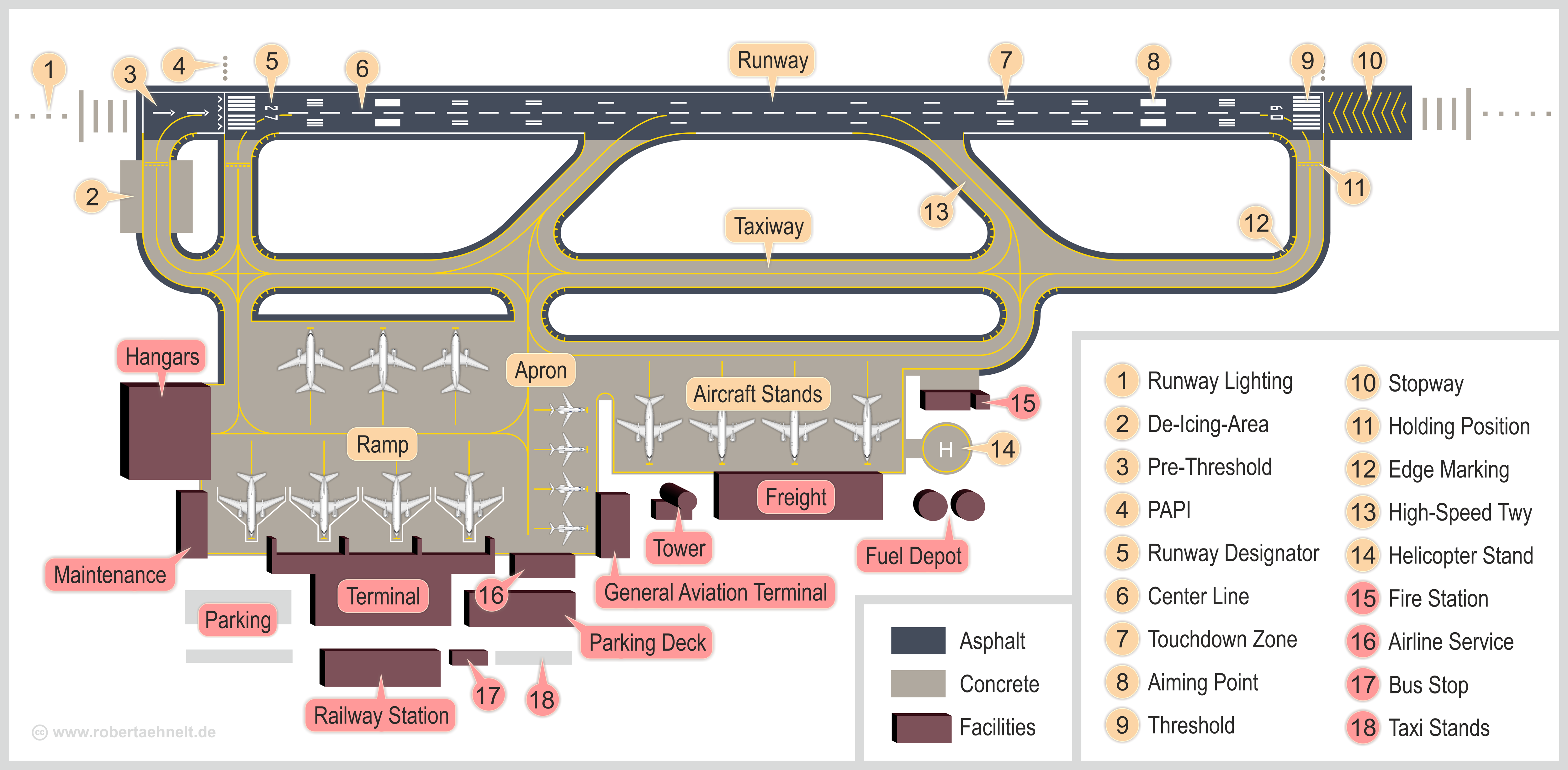
Airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ONUC
The United Nations Operation in the Congo (french: Opération des Nations Unies au Congo, abbreviated to ONUC) was a United Nations peacekeeping force deployed in the Republic of the Congo in 1960 in response to the Congo Crisis. ONUC was the UN's first peacekeeping mission with significant military capabilities, and remains one of the largest UN operations in both scale and operational scope. Following its independence from Belgium on 30 June 1960, the Congo descended into chaos and disorder, prompting its former colonial power to invade under the pretext of restoring law and order and protecting Belgian nationals. On 12 July 1960, the Congolese Government appealed to the UN for assistance, and on 14 July 1960 the United Nations Security Council passed Resolution 143 (S/4387) calling upon Belgium to withdraw its troops, and authorizing the Secretary-General to provide the Congolese Government with military assistance, as the Force Publique was not in a condition to meet it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congo Crisis
The Congo Crisis (french: Crise congolaise, link=no) was a period of political upheaval and conflict between 1960 and 1965 in the Republic of the Congo (today the Democratic Republic of the Congo). The crisis began almost immediately after the Congo became independent from Belgium and ended, unofficially, with the entire country under the rule of Joseph-Désiré Mobutu. Constituting a series of civil wars, the Congo Crisis was also a proxy conflict in the Cold War, in which the Soviet Union and the United States supported opposing factions. Around 100,000 people are believed to have been killed during the crisis. A nationalist movement in the Belgian Congo demanded the end of colonial rule: this led to the country's independence on 30 June 1960. Minimal preparations had been made and many issues, such as federalism, tribalism, and ethnic nationalism, remained unresolved. In the first week of July, a mutiny broke out in the army and violence erupted between black and whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while '' altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Sea Level
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value ( magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the '' arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the '' sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the '' population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface ( grass, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to manufacture Bréguet Aviation military aircraft. In January 1919, aviation pioneer Orville Wright underlined the need for "distinctly m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt concrete (commonly called asphalt, blacktop, or pavement in North America, and tarmac, bitumen macadam, or rolled asphalt in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland) is a composite material commonly used to surface roads, parking lots, airports, and the core of embankment dams. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the beginning of the twentieth century. It consists of mineral aggregate bound together with asphalt, laid in layers, and compacted. The process was refined and enhanced by Belgian-American inventor Edward De Smedt. The terms ''asphalt'' (or ''asphaltic'') ''concrete'', ''bituminous asphalt concrete'', and ''bituminous mixture'' are typically used only in engineering and construction documents, which define concrete as any composite material composed of mineral aggregate adhered with a binder. The abbreviation, ''AC'', is sometimes used for ''asphalt concrete'' but can also denote ''asphalt content'' or ''asphalt cement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamina Airport
Kamina Airport is an airport serving Kamina, a city in Haut-Lomami Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kamina Airport is separate from the larger military Kamina Air Base VOR (Ident: KMB) which is located east-northeast of the airport. Airlines and destinations Accidents and incidents *On June 21, 2007, a Let-410 twin turboprop operated by Karibu Airways crashed into a swamp shortly after taking off from Kamina Airport. One passenger, Mbuyu Mibanga, a member of the National Assembly of the Democratic Republic of the Congo was killed. At least 12 more were injured, including two Congolese doctors working for the World Health Organization. See also *Transport in the Democratic Republic of the Congo *List of airports in the Democratic Republic of the Congo References External linksKamina Airportat OpenStreetMap OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a free, open geographic database updated and maintained by a community of volunteers via open collaboration. Contributors collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |