|
Kris Land (Designer)
The kris or is a Javanese culture, Javanese asymmetrical dagger with a distinctive blade-patterning achieved through alternating laminations of iron and nickelous iron (''pamor''). The kris is famous for its distinctive wavy blade, although many have straight blades as well, and is one of the Weapons of silat, weapons commonly used in the ''pencak silat'' martial art native to Indonesia. Kris have been produced in many regions of Indonesia for centuries, but nowhere—although the island of Bali comes close—is the kris so embedded in a mutually-connected whole of ritual prescriptions and acts, ceremonies, mythical backgrounds and epic poetry as in Central Java. Within Indonesia the kris is commonly associated with Javanese culture, although other ethnicities in it and surrounding regions are familiar with the weapon as part of their cultures, such as the Balinese people, Balinese, Sundanese people, Sundanese, Malays (ethnic group), Malay, Madurese people, Madurese, Banjar peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, projected to rise to 158 million at mid 2025, Java is the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, home to approximately 55.7% of the Demographics of Indonesia, Indonesian population (only approximately 44.3% of Indonesian population live outside Java). Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies. Java was also the center of the History of Indonesia, Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's eig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundanese People
The Sundanese (; ) are an Austronesian people, Austronesian ethnic group native to Java in Indonesia, primarily West Java. They number approximately 42 million and form Ethnic groups in Indonesia, Indonesia's second most populous ethnic group. They speak the Sundanese language, which is part of the Austronesian languages. The western area of the island of Java, namely the provinces of West Java, Banten, and Jakarta, as well as the westernmost part of Central Java, is called by the Sundanese people ''Tatar Sunda'' or ''Pasundan'' (meaning Sundanese land). Sundanese migrants can also be found in Lampung, South Sumatra, and, to a lesser extent, in Central Java and East Java. The Sundanese people can also be found on several other islands in Indonesia such as Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Bali and Papua (province), Papua. Origins Migration theories The Sundanese are of Austronesian peoples, Austronesian origins and are thought to have originated in Taiwan. They migrated through th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
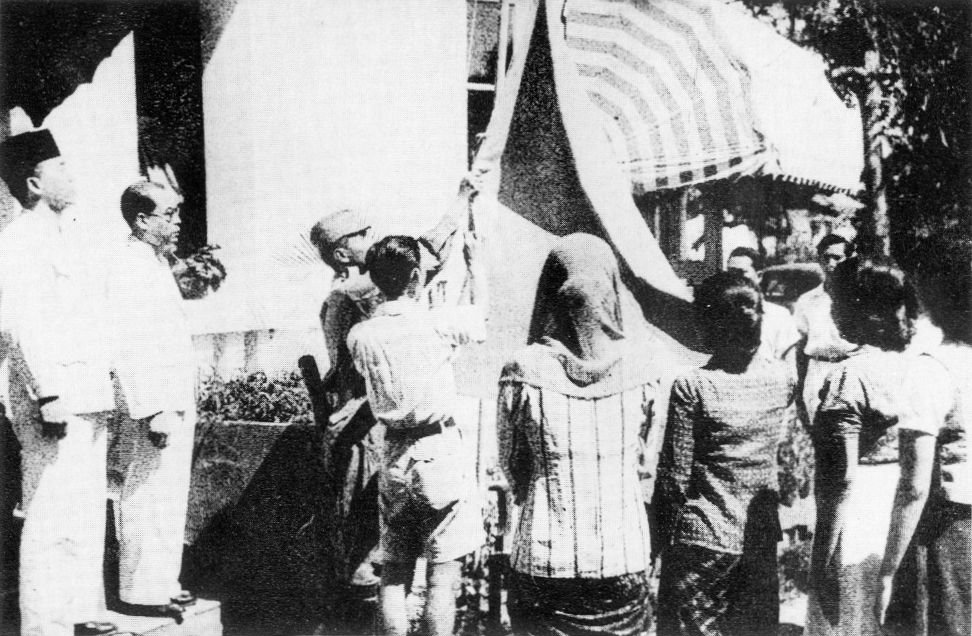
Indonesian National Revolution
The Indonesian National Revolution (), also known as the Indonesian War of Independence (, ), was an armed conflict and diplomatic struggle between the Republic of Indonesia and the Dutch Empire and an internal social revolution during Aftermath of WWII, postwar and Dutch East Indies#World War II and independence, postcolonial Indonesia. It took place between Indonesian Declaration of Independence, Indonesia's declaration of independence in 1945 and the Netherlands' Dutch–Indonesian Round Table Conference, transfer of sovereignty over the Dutch East Indies to the Republic of the United States of Indonesia at the end of 1949. The four-year struggle involved sporadic but bloody armed conflict, internal Indonesian political and communal upheavals, and two major international diplomatic interventions. Dutch military forces (and, for a while, the forces of the World War II Allies, World War II allies) were able to control the major towns, cities and industrial assets in Repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java War
The Java War (; ; ), also known in Indonesia as the Diponegoro War (; ), was an armed conflict in central and eastern Java from 1825 to 1830, between native Javanese rebels headed by Prince Diponegoro and the Dutch East Indies supported by Javanese princely states. It is considered a watershed in Javanese history, culture, and society. During the early nineteenth century, declining Dutch power along with increased centralization of colonial authorities through brief French and British controls had changed the political order established after the 1755 Treaty of Giyanti, at the expense of the native Javanese princely states. After the deaths of Sultans of Yogyakarta Hamengkubuwono III and IV, along with the return of Dutch presence, Hamengkubuwono III's eldest son Diponegoro became estranged from Yogyakarta's regency of Hamengkubuwono V and with the colonial government. With a millenarian movement emerging and claimed visions of a holy war, Diponegoro would launch his r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Batavia
The siege of Batavia was a military campaign led by Sultan Agung of Mataram to capture the Dutch port-settlement of Batavia in western Java. The first attempt was launched in 1628, and the second in 1629; both were unsuccessful. Prelude In the Indonesian Archipelago the Dutch East Indies Company (VOC) first established their base of operation in Amboina. To expand their trading network, the Dutch asked for the permission of the Sultanate of Mataram, then the rising power in Java, to build ''lojis'' (trading posts, most consisting of a fort and warehouses) along Java's northern coast. The second ruler of Mataram, Raden Mas Jolang, allowed one such settlement to be built in Jepara in 1613, perhaps in hope that the company will be a powerful ally against his most powerful enemy, the city state of Surabaya. After the VOC under their most renowned governor general Jan Pieterszoon Coen had wrested the port of Jacatra (Jayakarta) from Sultanate of Banten in 1619, they estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paregreg War
The Regreg War (often erroneously called the ''Paregreg'') was a civil war that took place in 1404–1406 within the Javanese empire of Majapahit. The conflict was fought as a war of independence between the '' Kedhaton Kulon'' (Western court) led by Wikramawardhana against the breakaway '' Kedhaton Wetan'' (Eastern court) of Blambangan led by Bhre Wirabhumi. This war of rivalry and secession had caused calamity, crisis, court's preoccupation, the drain of financial resources, and exhaustion, which is thought to be one of the causes of Majapahit's decline in the following years. Terminology This conflict is usually referred to as the Paregreg, but that term is based on a linguistic misunderstanding. In the Pararaton chronicle, in which the term for this war is found, events are labelled by adding the prefix ''pa-'' to one or more keywords. For example, the Javanese attack on Malayu in Sumatra in 1275 is called ''pamalayu'', the rebellion of Rangga Lawe in 1295 is referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bubat
The Battle of Bubat, also known as ''Pasunda Bubat'', is the battle between the Sunda Kingdom, Sundanese royal family and the Majapahit army that took place in Bubat Square on the northern part of Trowulan (Majapahit capital city) in 1279 Saka or 1357 CE. Historical account The historical account of ''Pasunda Bubat'' is mentioned in ''Carita Parahyangan'' (16th century) and ''Pararaton'' (15th century), but not found in the ''Nagarakretagama'' (14th century), while the story of the battle of Bubat is the main theme of the Balinese manuscript ''Kidung Sunda'' (c. mid 16th century). The Battle of Bubat was mentioned in a segment of the 15th-century Javanese chronicle of ''Pararaton''. The author of this manuscript is unknown, composed in the form of chronicles around 1474–1486, while the literary part was composed as history between 1500–1613. This manuscript was first published by J.L.A. Brandes, a Dutch philologist, in 1896, complete with translations, notes, and comments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasion Of Java
The Yuan dynasty under Kublai Khan attempted in 1293 to invade Java, an island in modern Indonesia, with 20,000 to 30,000 soldiers. This was intended as a punitive expedition against Kertanegara of Singhasari, who had refused to pay tribute to the Yuan and maimed one of their emissaries. However, in the intervening years between Kertanegara's refusal and the expedition's arrival on Java, Kertanegara had been killed and Singhasari had been usurped by Kediri Kingdom, Kediri. Thus, the Yuan expeditionary force was directed to obtain the submission of its successor state, Kediri Kingdom, Kediri, instead. After a fierce campaign, Kediri surrendered, but the Yuan forces were betrayed by their erstwhile ally, Majapahit, under Raden Wijaya. In the end, the invasion ended with Yuan failure and strategic victory for the new state, Majapahit. Background Kublai Khan, Kublai, the founder of the Yuan dynasty, had sent envoys to many states demanding that they pay tributes and submit themselve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamalayu Expedition
The Pamalayu campaign was a diplomatic and military expeditionary force sent by the Javanese King Kertanegara of Singhasari to conquer the Sumatran Melayu Kingdom. It was decreed in 1275, though perhaps not undertaken until later. Little is known about the results of the expedition. The Padang Roco Inscription dated from 1286 states that a religious statue of Amoghapasa was established at Dharmasraya on the orders of Kertanagara, and that all the inhabitants of Melayu and especially their king, Tribhuwanaraja rejoiced at the presentation of the gifts. History The expedition arguably established Javanese domination over Melayu and trade in the Strait of Malacca. To cement the relationship between the two kingdoms, a political marriage was arranged. According to the Pararaton, two Malay princesses, Dara Petak and Dara Jingga, went to Java, originally intended for Kertanegara. However following his demise by Jayakatwang, princess Dara Petak would later be married to Kertanegara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Genter
The Battle of Genter, also known as the Battle of Ganter, was a military engagement fought between two rival Javanese rulers in the early 13th century. The battle resulted in one ruler, Ken Arok, defeating his rival and routing their army. The battle cemented Arok's control over Eastern Java, and resulted in the ruler founding the Rajasa dynasty. History From the 8th to the 12th century, the island of Java was ruled by a number of kings and noble families. In the eastern part of the island, agriculture-centric feudal nations (namely the Sailendra, Kediri, Tumapel, and Majapahit kingdoms) intermittently fought over arable land on which to grow rice Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l .... In the early 13th century, these combatants were challenged by the emergence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makassar People
The native Makassar, Macassar, Makassarese, Makassan or Macassan are one of the indigenous Sulawesi people, native to the southern Celebic peninsular regions (concentrated around the Makassar area) in Indonesia. The Makassar people are rich in culture and they are acknowledged for their traditional culinary and maritime knowledges, together with the Bugis, its closest related ethnic group. The '' Phinisi'', a worldwide well-known boatbuilding of Southern Sulawesi-origin, a joint invention of Bugis-Makassar people, is internationally inscribed as the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). The Makassar people speak various Makassaric languages, including Standard Makassar, as well as Standard Indonesian and Makassar Malay. The Makassar people are amongst the first native people who are endowed with the harvesting and processing knowledge of '' holothuroidea'' (sea cucumber, natively found betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buginese People
The Bugis people, also known as Buginese, are an Austronesian peoples, Austronesian ethnic groupthe most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassar people, Makassarese and Toraja people, Torajan), in the south-western province of Sulawesi, third-largest island of Indonesia. The Bugis in 1605 converted to Islam from Animism. Although the majority of Bugis are Muslim, a small minority adhere to Christianity as well as a pre-Islamic indigenous belief called ''Tolotang''. The Bugis, whose population numbers around six million and constitutes less than 2.5% of the Demographics of Indonesia, Indonesian population, are influential in the politics in the country; and historically influential on the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Lesser Sunda Islands and other parts of the Maritime Southeast Asia, archipelago where they have migrated en masse, starting in the late seventeenth century. The third President of Indonesia, presid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |