|
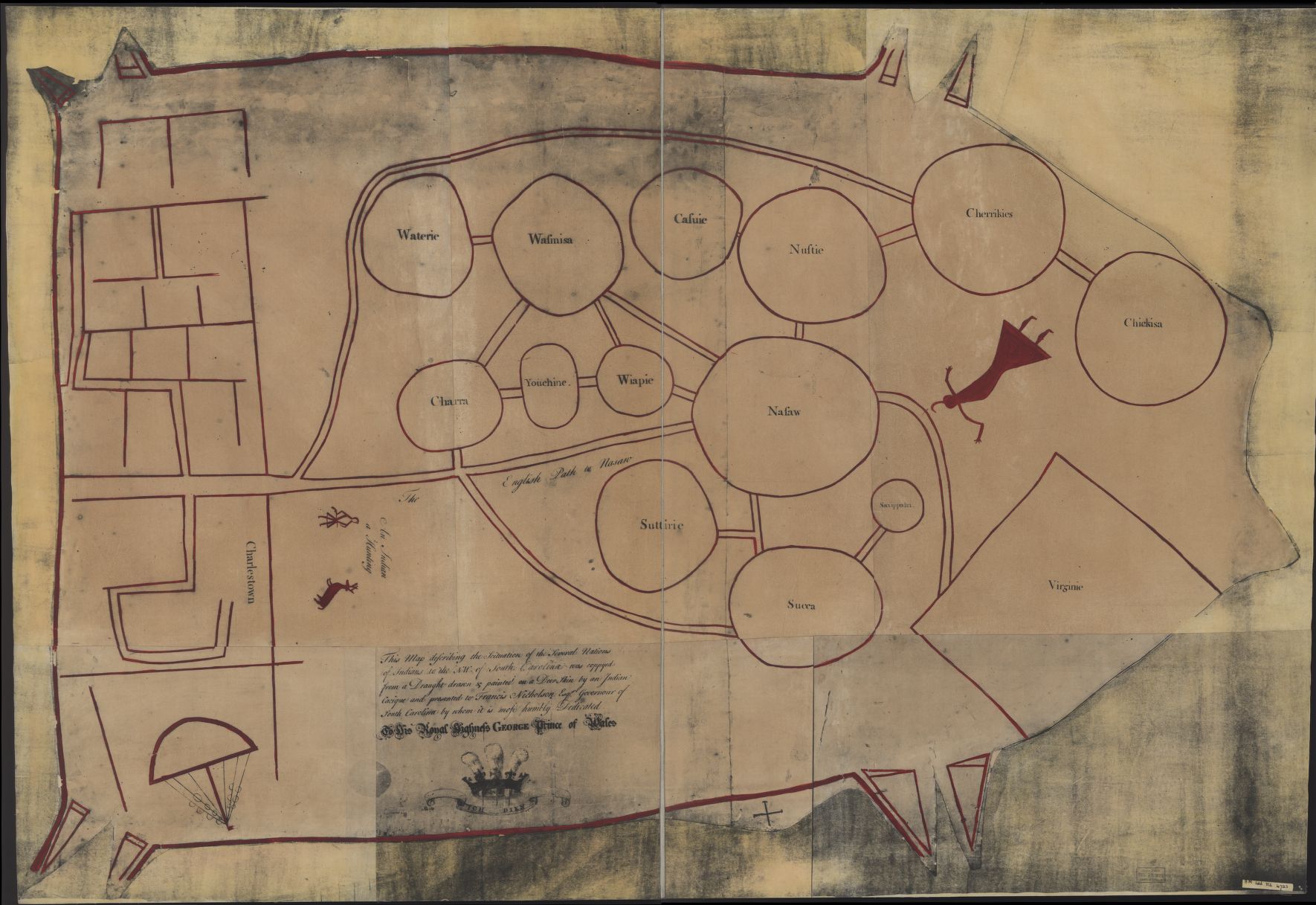
Koroa
The Koroa were one of the groups of Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands who lived in the Mississippi Valley before French colonization. The Koroa lived in the Yazoo River basin in present-day northwest Mississippi. Language The Koroa are believed to have spoken a dialect of Tunica language, Tunica. However, French missionaries described the Koroa (which they spelled Courouais) as speaking the same language as the Yazoo but a different tongue from the Tunica. They may have described a distinct dialect or a related Tunican languages, Tunican language. Name Jacques Marquette referred to this tribe by the name ''Akoroa''. History 15th century The Koroa may be the tribe identified by Hernando de Soto (explorer), Hernando de Soto's expedition as the ''Coligua'' or ''Cologoa''. They may have met the Spanish expedition in 1541 near present-day Little Rock, Arkansas. 17th century The Koroa lived on both sides of the Mississippi River when the French encountered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica People
The Tunica people are a group of linguistically and culturally related Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes in the Mississippi River Valley, which include the Tunica (also spelled Tonica, Tonnica, and Thonnica); the Yazoo tribe, Yazoo; the Koroa (Akoroa, Courouais); and possibly the Tioux. They first encountered Europeans in 1541 – members of the Hernando de Soto expedition. The Tunica language is an language isolate, isolate. Over the next centuries, under pressure from hostile neighbors, the Tunica migrated south from the Central Mississippi Valley to the Lower Mississippi Valley. Eventually they moved westward and settled around present-day Marksville, Louisiana. Since the early 19th century, they have intermarried with the Biloxi tribe, an unrelated Siouan-speaking people from the vicinity of Biloxi, Mississippi and shared land. Remnant peoples from other small tribes also merged with them. In 1981 they were federally recognized and now call thems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazoo People
The Yazoo were a tribe of the Native American Tunica people historically located along the lower course of the Yazoo River in an area known as the Mississippi Delta. They were closely related to other Tunica language–speaking peoples, especially the Tunica, Koroa, and possibly the Tioux. Language Nothing is definitely known about their language, believed to be related to Tunica, a language isolate. History 17th century French explorers and missionaries documented the tribe. In 1699, Father Antoine Davion of the Quebec Seminary of Foreign Missions in New France (Canada) established a mission among the Tunica. 18th century At this time, the Yazoo, like the Chickasaw, were under the influence of the English traders from Carolina on the Atlantic coast. In 1702, the Yazoo aided the Koroa in killing the French priest Nicholas Foucault and his three companions. The seminary temporarily withdrew Fr Antoine from the area. In 1718, the French established a fort nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natchez People
[https://archive.org/details/dcouverteett01marg The Internet Archive website] The Natchez ( , ) are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people who originally lived in the Natchez Bluffs area in the Lower Mississippi Valley, near the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi, in the United States. The Hernando de Soto, DeSoto chronicle failed to record their presence when they came down the river in 1543. They speak a language Language isolate, with no known close relatives, although it may be very distantly related to the Muskogean languages of the Muscogee, Creek Confederacy.Geoffrey Kimball, "Natchez" in ''Native Languages of the Southeastern United States'', ed. Janine Scancarelli and Heather Kay Hardy, University of Nebras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinipissa
The Quinipissa (sometimes spelled Kinipissa in French sources) were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands who were living on the lower Mississippi River, in present-day Louisiana, as reported by René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle in 1682. In 1682, La Salle encountered a group of Quinipissa living with the Koroa in a village on the western bank of the Mississippi River. The Quinipissa joined the Mougoulacha. The combined group shared a village with the Bayagoula. In 1700, the Bayagoula massacred both the Quinipissa and Mougoulacha, and they were not mentioned again by chroniclers of the time. Language The Quinipissa may have spoken the same language as the Mougoulacha and Bayagoula. The Bayagoula language is only attested with a single word. Albert Gatschet considered Quinipissa a Muskogean language ''Coast Choctaw'' ("Coast Chaʼhta") based on evidence that many peoples of this area spoke the lingua franca Mobilian Jargon and have names that appear to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Mississippian Culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center, located in what is present-day southern Illinois. The Mississippian way of life began to develop in the Mississippi River Valley (for which it is named). Cultures in the tributary Tennessee River Valley may have also begun to develop Mississippian characteristics at this point. Almost all dated Mississippian sites predate 1539–1540 (when Hernando de Soto explored the area), with notable exceptions being Natchez communities. These maintained Mississippian cultural practices into the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous People Of The Southeastern Woodlands
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Franz Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions.Jackson and Fogelson 3 Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopelea are usually seen as marginally southeastern and their traditional lands represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sites And Peoples Visited By The Hernando De Soto Expedition
This is a list of sites and peoples visited by the Hernando de Soto Expedition in the years 1539–1543. In May 1539, de Soto left Havana, Cuba, with nine ships, over 620 men and 220 surviving horses and landed at Charlotte Harbor, Florida. This began his three-year odyssey through the Southeastern North American continent, from which de Soto and a large portion of his men would not return. They met many varied Native American groups, most of them bands and chiefdoms related to the widespread Mississippian culture. Only a few of these ancestral cultures survived into the seventeenth century, or their descendants combined as historic tribes known to later Europeans. Others have been recorded only in the written historical accounts of de Soto's expedition. Florida * Uzita * Mocoso * Urriparacoxi * Timucua * Ocale * Acuera * Potano * Alachua culture * Northern Utina * Yustaga * Uzachile * Anhaica * Apalachee * Narváez expedition's "Bay of Horses" Georgia The peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Tribes In Mississippi
Native may refer to: People * '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood * '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes * List of Australian plants termed "native", whose common name is of the form "native . . . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, United States. Their traditional territory was in northern Mississippi, northwestern and northern Alabama, western Tennessee and southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as a member of the Muskogean language family. In the present day, they are organized as the Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Chickasaw Nation. Chickasaw people have a migration story in which they moved from a land west of the Mississippi River to reach present-day northeast Mississippi, northwest Alabama, and into Lawrence County, Tennessee. They had interaction with French, English, and Spanish colonists during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial period. The United States considered the Chickasaw one of the Five Civilized Tribes of the Southeast, as they adopted numerous practices of European Americans. Resisting European-American settlers encroaching on their territory, they were forced by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Davion
Antoine Davion was originally from Saint-Omer in Artois, France. He served in various churches on the Île d'Orléans in Québec before departing for the Mississippi River in 1698 to help establish missions among the indigenous peoples. He would serve among the Tunica Indians from 1699 until about 1722 when he would retire to New Orleans New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 .... He would return to France and die among his family in 1726. References''Handbook of the American Frontier: The southeastern woodlands.''Joseph Norman Heard. 1726 deaths French Roman Catholic missionaries Year of birth missing Roman Catholic missionaries in New France People from Saint-Omer {{France-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |